|
Agricultural Spiritualism
Agricultural spiritualism or the Spirit of Agriculture refers to the idea that the concepts of food production (economics), production and consumption (economics), consumption and the essential spiritualism, spiritual nature of human race, humanity are linked. It teaches that spirituality is inherent to human consciousness, is perhaps a product of it, and is accessible to all who cultivate it. The association with agriculture includes such agricultural metaphors as "cultivate" in language used by most mysticism, mystics across history. Followers of this idea state the following reasons to justify this link: Agriculture was the preoccupation of the majority of the population of the world at the time that the major scriptures of the continuing religions were compiled; the approach that agriculture takes to creating the optimal conditions for production of its harvest is the same as that recommended by the traditional religions for producing insight or wisdom; historically, the adoptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells to provide energy, maintain life, or stimulate growth. Different species of animals have different feeding behaviours that satisfy the needs of their unique metabolisms, often evolved to fill a specific ecological niche within specific geographical contexts. Omnivorous humans are highly adaptable and have adapted to obtain food in many different ecosystems. The majority of the food energy required is supplied by the industrial food industry, which produces food with intensive agriculture and distributes it through complex food processing and food distribution systems. This system of conventional agriculture relies heavily on fossil fuels, which means that the food and agricu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altruism
Altruism is the principle and moral practice of concern for the welfare and/or happiness of other human beings or animals, resulting in a quality of life both material and spiritual. It is a traditional virtue in many cultures and a core aspect of various religious and secular worldviews. However, the object(s) of concern vary among cultures and religions. In an extreme case, altruism may become a synonym of selflessness, which is the opposite of selfishness. The word "altruism" was popularized (and possibly coined) by the French philosopher Auguste Comte in French, as ''altruisme'', for an antonym of egoism. He derived it from the Italian ''altrui'', which in turn was derived from Latin ''alteri'', meaning " other people" or "somebody else". Altruism in biological observations in field populations of the day organisms is an individual performing an action which is at a cost to themselves (e.g., pleasure and quality of life, time, probability of survival or reproduction), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
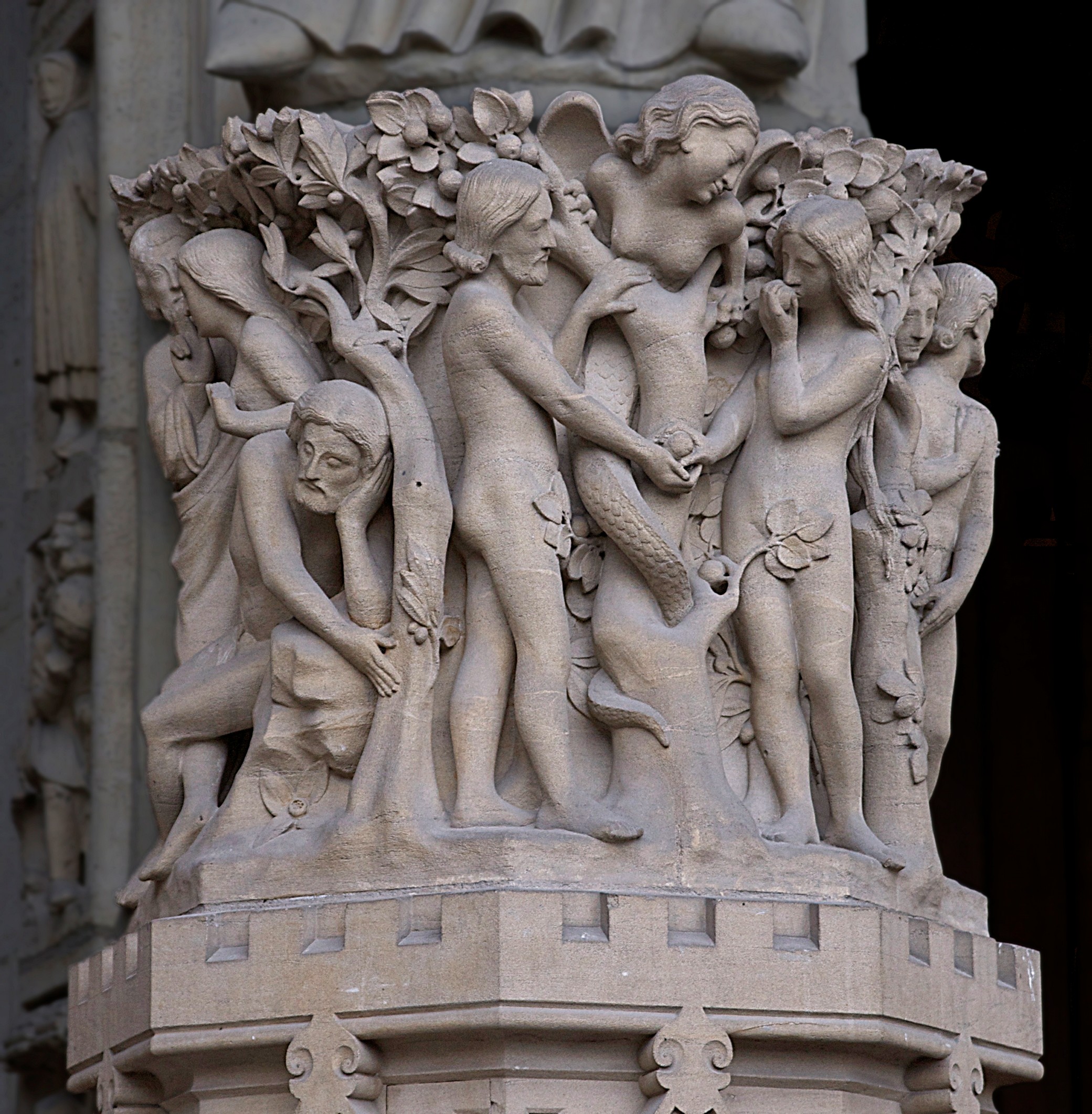
Fall Of Man
The fall of man, the fall of Adam, or simply the Fall, is a term used in Christianity to describe the transition of the first man and woman from a state of innocent obedience to God in Christianity, God to a state of guilty disobedience. * * * * The doctrine of the Fall comes from a biblical interpretation of Book of Genesis, Genesis, chapters 1–3. At first, Adam and Eve lived with God in the Garden of Eden, but the Serpents in the Bible, serpent tempted them into Taboo#In religion and mythology, eating the Forbidden fruit, fruit from the tree of knowledge of good and evil, which God had forbidden. After doing so, they became ashamed of their nakedness and God expelled them from the Garden to prevent them from eating from the Tree of life (biblical), tree of life and becoming Immortality, immortal. In Nicene Christianity, mainstream (Nicene) Christianity, the doctrine of the Fall is closely related to that of original sin or ancestral sin. They believe that the Fall brought sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Goddess
An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the "chthonic" deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an " Earth Mother" complementary to the " Sky Father" in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god. Other Earth goddesses include: * Chinese folk religion - Houtu (Di Mu) * Meitei mythology and religion - Leimarel Sidabi, Panthoibi, Phouoibi * Ancient Greek religion - Gaia, Cybele, Demeter, Persephone, Rhea * Ancient Roman religion - Terra, Ceres, Ops, Proserpina * Slavic - Mat Zemlya * Andean (Inca, Aymara) - Pachamama * Hinduism - Bhumi * Native American - Spider Grandmother * Romanian - Muma Padurii, Mama Gaia * Mongolian and Turkic - Umay (Eje) * Old Norse religion - Sif and Jörð * Lithuanian mythology - Žemyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fertility Deities
A fertility deity is a god or goddess associated with fertility, sex, pregnancy, childbirth, and crops. In some cases these deities are directly associated with these experiences; in others they are more abstract symbols. Fertility rites may accompany their worship. The following is a list of fertility deities. African *Ala, Igbo goddess of fertility *Asase Ya, Ashanti earth goddess of fertility *Deng, Dinka sky god of rain and fertility *Mbaba Mwana Waresa, Zulu goddess of fertility, rainbows, agriculture, rain, and bees *Oshun (known as ''Ochún'' or ''Oxúm'' in Latin America) also spelled Ọṣun, is an orisha, a spirit, a deity, or a goddess that reflects one of the manifestations of God in the Ifá and Yoruba religions. She is one of the most popular and venerated orishas. Oshun is the deity of the river and fresh water, luxury and pleasure, sexuality and fertility, and beauty and love. She is connected to destiny and divination. Ancient Egyptian *Amun, creator-god, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fertility Rite
Fertility rites or fertility cult are religious rituals that are intended to stimulate reproduction in humans or in the natural world. Such rites may involve the sacrifice of "a primal animal, which must be sacrificed in the cause of fertility or even creation". Characteristics "Fertility rites may occur in calendric cycles, as rites of passage within the life cycle, or as ad hoc rituals....Commonly fertility rituals are embedded within larger-order religions or other social institutions." As with cave pictures "hatshow animals at the point of mating... ndserved magic fertility rites", such rites are "...a form of sympathetic magic" in which the forces of nature are to be influenced by the example acted out in the ritual. At times, "ceremonies intended to assure the fecundity of the earth or of a group of women...involve some form of phallic worship". Geographical varieties Ancient Greece Central to fertility rites in classical Greece was " Demeter, goddess of fertility.. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion And Agriculture
Religion and agriculture have been closely associated since neolithic times and the development of early Orphic religions based upon fertility and the seasons. See also * Agricultural spiritualism * Christianity and agriculture * Earth goddess * Fall of man * Fertility rite * Human sacrifice * List of fertility deities References External links * Bernard Stiegler Bernard Stiegler (; 1 April 1952 – 5 August 2020) was a French philosopher. He was head of the Institut de recherche et d'innovation (IRI), which he founded in 2006 at the Centre Georges-Pompidou. He was also the founder in 2005 of the polit ...Take Care* Paul Hanley (2006The Spirit of Agriculture George Ronald, Oxford. 226 pp Agriculture in society Religion and society {{Agri-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blog
A blog (a truncation of "weblog") is a discussion or informational website published on the World Wide Web consisting of discrete, often informal diary-style text entries (posts). Posts are typically displayed in reverse chronological order so that the most recent post appears first, at the top of the web page. Until 2009, blogs were usually the work of a single individual, occasionally of a small group, and often covered a single subject or topic. In the 2010s, "multi-author blogs" (MABs) emerged, featuring the writing of multiple authors and sometimes professionally edited. MABs from newspapers, other media outlets, universities, think tanks, advocacy groups, and similar institutions account for an increasing quantity of blog traffic. The rise of Twitter and other "microblogging" systems helps integrate MABs and single-author blogs into the news media. ''Blog'' can also be used as a verb, meaning ''to maintain or add content to a blog''. The emergence and growth of blogs i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggañña Sutta
Aggañña Sutta is the 27th Sutta of the Digha Nikaya collection (Pāli version). The sutta describes a discourse imparted by the Lord Buddha to two brahmins, Bharadvaja and Vasettha, who left their family and vanna to become monks. The two brahmans are insulted and maligned by their own caste for their intention to become members of the Sangha. The Buddha explains that vanna(class) and lineage cannot be compared to the achievement of morality practice and the Dhamma, as anyone from the four vannas can become a monk and reach the state of Arahant. Then, he explains about the beginning of the Earth and the birth of social order and its structure, including the vannas. The Buddha emphasizes the message of universality in the Dhamma and how the Dhamma is the best of all things. The Beginning The Sutta begins when the Buddha is staying in Savitri, in the temple donated by Visakha, the mother of Migara. At that time, two brahmins, Bharadvaja and Vasettha, are training with the monks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashram
An ashram ( sa, आश्रम, ) is a spiritual hermitage or a monastery A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which ... in Indian religions. Etymology The Sanskrit noun is a thematic nominal derivative from the root 'toil' (< Proto-Indo-European, PIE *''ḱremh2'') with the prefix 'towards.' An ashram is a place where one strives towards a goal in a disciplined manner. Such a goal could be ascetic, spirituality, spiritual, yogic or any other. Overview  An ashram wo ...
An ashram wo ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahatma Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (; ; 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948), popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist Quote: "... marks Gandhi as a hybrid cosmopolitan figure who transformed ... anti-colonial nationalist politics in the twentieth-century in ways that neither indigenous nor westernized Indian nationalists could." and political ethicist Quote: "Gandhi staked his reputation as an original political thinker on this specific issue. Hitherto, violence had been used in the name of political rights, such as in street riots, regicide, or armed revolutions. Gandhi believes there is a better way of securing political rights, that of nonviolence, and that this new way marks an advance in political ethics." who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule, and to later inspire movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific ''Mahātmā'' (Sanskrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food System
The term food system describes the interconnected systems and processes that influence nutrition Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food to support its life. It provides organisms with nutrients, which can be metabolized to create energy and chemical structures. Failure to obtain sufficient n ..., food, health, community development, and agriculture. A food system includes all processes and infrastructure involved in feeding a population: growing, harvesting, processing, Food packaging, packaging, transporting, Agricultural marketing, marketing, consumption, Food distribution, distribution, and disposal of food and food-related items. It also includes the inputs needed and outputs generated at each of these steps. Food systems fall within agri-food systems, which encompass the entire range of actors and their interlinked value-adding activities in the primary production of food and non-food agricultural products, as well as in foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |