|
Agile Tooling
Agile tooling is the design and fabrication of manufacturing related-tools such as dies, molds, patterns, jigs and fixtures in a configuration that aims to maximise the tools' performance, minimise manufacturing time and cost, and avoid delay in prototyping. A fully functional agile tooling laboratory consists of CNC milling, turning and routing equipment. It can also include additive manufacturing platforms (such as fused filament fabrication, selective laser sintering, Stereolithography, and direct metal laser sintering), hydroforming, vacuum forming, die casting, stamping, injection molding and welding equipment. Agile tooling is similar to rapid tooling, which uses additive manufacturing to make tools or tooling quickly, either directly by making parts that serve as the actual tools or tooling components, such as mold inserts; or indirectly by producing patterns that are in turn used in a secondary process to produce the actual tools. Another similar technique is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high-tech, but it is most commonly applied to industrial design, in which raw materials from the primary sector of the economy, primary sector are transformed into finished goods on a large scale. Such goods may be sold to other manufacturers for the production of other more complex products (such as aircraft, Major appliance, household appliances, furniture, sports equipment or automobiles), or distributed via the tertiary industry to end users and consumers (usually through wholesalers, who in turn sell to retailers, who then sell them to individual customers). Manufacturing engineering is the field of engineering that designs and optimizes the manufacturing process, or the steps through whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
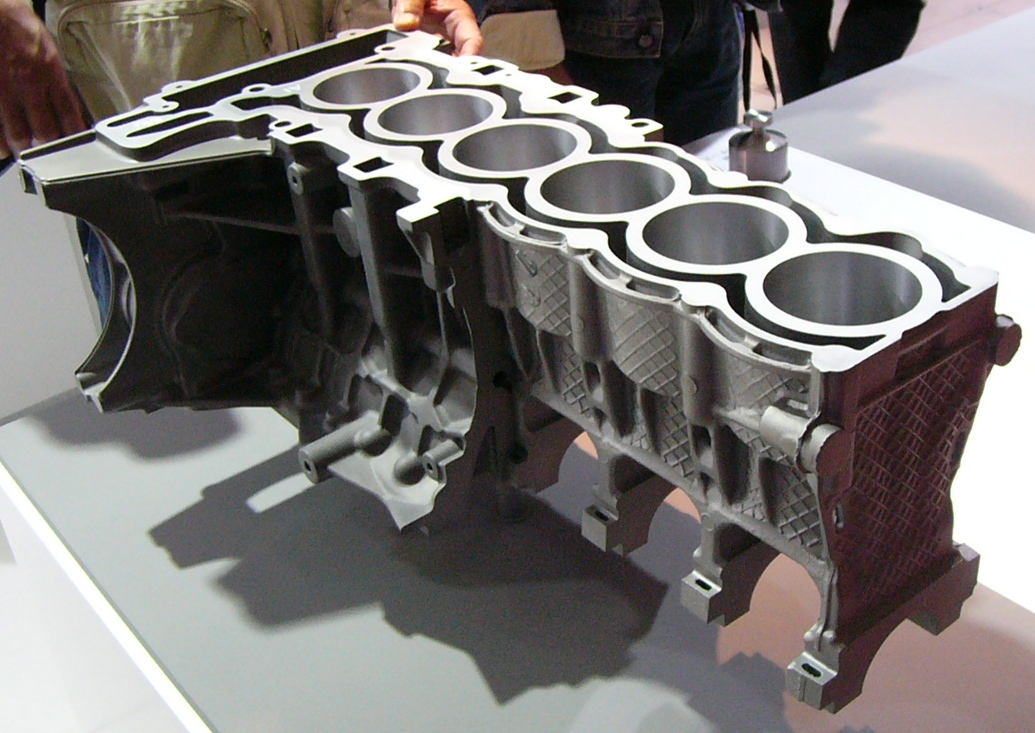
Die Casting
Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process. Most die castings are made from non-ferrous metals, specifically zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot- or cold-chamber machine is used. The casting equipment and the metal dies represent large capital costs and this tends to limit the process to high-volume production. Manufacture of parts using die casting is relatively simple, involving only four main steps, which keeps the incremental cost per item low. It is especially suited for a large quantity of small- to medium-sized castings, which is why die casting produces more castings than any other casting process. Die castings are characterized by a very good s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporation
A corporation is an organization—usually a group of people or a company—authorized by the state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law "born out of statute"; a legal person in legal context) and recognized as such in law for certain purposes. Early incorporated entities were established by charter (i.e. by an '' ad hoc'' act granted by a monarch or passed by a parliament or legislature). Most jurisdictions now allow the creation of new corporations through List of company registers, registration. Corporations come in many different types but are usually divided by the law of the jurisdiction where they are chartered based on two aspects: by whether they can issue share capital, stock, or by whether they are formed to make a profit (accounting), profit. Depending on the number of owners, a corporation can be classified as ''aggregate'' (the subject of this article) or ''corporation sole, sole'' (a legal entity consisting of a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globalization
Globalization, or globalisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences), is the process of foreign relations, interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. The term ''globalization'' first appeared in the early 20th century (supplanting an earlier French term ''mondialization''), developed its current meaning some time in the second half of the 20th century, and came into popular use in the 1990s to describe the unprecedented international connectivity of the Post-Cold War era, post-Cold War world. Its origins can be traced back to 18th and 19th centuries due to advances in transportation and Information and communications technology, communications technology. This increase in global interactions has caused a growth in international trade and the exchange of ideas, beliefs, and culture. Globalization is primari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Improvement Process
A continual improvement process, also often called a continuous improvement process (abbreviated as CIP or CI), is an ongoing effort to improve products, services, or processes. These efforts can seek " incremental" improvement over time or "breakthrough" improvement all at once. Delivery (customer valued) processes are constantly evaluated and improved in the light of their efficiency, effectiveness and flexibility. Some see CIPs as a meta-process for most management systems (such as business process management, quality management, project management, and program management). W. Edwards Deming, a pioneer of the field, saw it as part of the 'system' whereby feedback from the process and customer were evaluated against organisational goals. The fact that it can be called a management process does not mean that it needs to be executed by 'management'; but rather merely that it makes decisions about the implementation of the delivery process and the design of the delivery process it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buhler 2
Buhler, Buehler, or Bühler may refer to: * Bühler, Appenzell Ausserrhoden, Switzerland * Bühler (river), in Baden-Württemberg, Germany * Buhler (surname) * Buhler, Kansas, United States * Bühler Group, a Swiss plant equipment manufacturer * Buhler Industries, a Canadian farm equipment manufacturer * Buehler Foods, a grocery store chain in Illinois, Indiana, and Kentucky * Buehler's, a grocery store chain in northeastern Ohio, USA See also * * Bueler (other) Bueler or Bueller may refer to: * Tim Bueler, founder of the High School Conservative Clubs of America * Ferris Bueller, a fictional character in the 1986 movie ''Ferris Bueller's Day Off'' ** ''Ferris Bueller (TV series)'' * Bueller, the developm ... * Buhle {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ram Press At Ohio State U
Ram, ram, or RAM may refer to: Animals * A male sheep * Ram cichlid, a freshwater tropical fish People * Ram (given name) * Ram (surname) * Ram (director) (Ramsubramaniam), an Indian Tamil film director * RAM (musician) (born 1974), Dutch * Raja Ram (musician) (Ronald Rothfield), Australian * Ram Dass (Richard Alpert), US spiritual teacher and author * Kavitark Ram Shriram (born 1950s), Google founding board member * Ram Herrera, a Tejano musician Religion * Rama, incarnation of the god Vishnu in Hinduism * Ram and Rud, progenitors of the second generation of humans in Mandaeism Places * Ram, Serbia, Veliko Gradište * Lake Ram, Golan Heights, Syria * Ram Island (other), several islands with the name * Ram Fortress, Serbia * Ram Range, a mountain range in the Canadian Rockies * Ram River in Alberta, Canada * Ramingining Airport, IATA airport code "RAM" Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Ram'' (album), a 1971 album by Paul and Linda McCartney * RAM (band), Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equipment
Equipment most commonly refers to a set of tool A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates ba ...s or other objects commonly used to achieve a particular objective. Different jobs require different kinds of equipment.Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon Olsen, ''Production and Operations Analysis: Seventh Edition'' (2015), p. 490. Types of equipment Types of equipment include: See also * * * * :Equipment References {{Tool-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Center
Center or centre may refer to: Mathematics *Center (geometry), the middle of an object * Center (algebra), used in various contexts ** Center (group theory) ** Center (ring theory) * Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity Places United States * Centre, Alabama * Center, Colorado * Center, Georgia * Center, Indiana * Center, Jay County, Indiana * Center, Warrick County, Indiana * Center, Kentucky * Center, Missouri * Center, Nebraska * Center, North Dakota * Centre County, Pennsylvania * Center, Portland, Oregon * Center, Texas * Center, Washington * Center, Outagamie County, Wisconsin * Center, Rock County, Wisconsin **Center (community), Wisconsin *Center Township (other) *Centre Township (other) *Centre Avenue (other) *Center Hill (other) Other countries * Centre region, Hainaut, Belgium * Centre Region, Burkina Faso * Centre Region (Cameroon) * Centre-Val de Loire, formerly Centre, France * Centre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time To Market
In commerce, time to market (TTM) is the length of time it takes from a product being conceived until its being available for sale. The reason that time to market is so important is since being late erodes the addressable market into which producers have to sell their product. A common assumption is that TTM matters most for first-of-a-kind products, but actually a late product launch in any industry can negatively impact revenues—from reducing the window of opportunity to generate revenues to causing the product to become obsolete faster. Measuring TTM There are no standards for measuring TTM, and measured values can vary greatly. First, there is great variation in how different organizations define the start of the period. For example, in the automotive industry the development period starts when the product concept is approved. Other organizations realize that little will happen until the project is staffed, which can take a long time after approval if developers are tied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is a group of techniques used to quickly fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly using three-dimensional computer aided design ( CAD) data. Construction of the part or assembly is usually done using 3D printing or " additive layer manufacturing" technology. The first methods for rapid prototyping became available in the mid 1987 and were used to produce models and prototype parts. Today, they are used for a wide range of applications and are used to manufacture production-quality parts in relatively small numbers if desired without the typical unfavorable short-run economics. This economy has encouraged online service bureaus. Historical surveys of RP technology start with discussions of simulacra production techniques used by 19th-century sculptors. Some modern sculptors use the progeny technology to produce exhibitions and various objects. The ability to reproduce designs from a dataset has given rise to issues of rights, as it is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Tooling
Rapid tooling (RT) denotes manufacturing on a slim timeline. Some of the main advantages to rapid tooling trades is that it decreases the time and cost of the product. With rapid tools being fast and easily reproducible, it requires less stock for finished tools. These tools will be produced on demand and are available almost immediately. Special tools or tools where no supplier is existing on the market any more can be reproduced without bigger design and production efforts. However, the disadvantages are that it is not as accurate and also shortens the lifespan of the product. Rapid tooling is mainly used for specific needs including prototyping and troubleshooting existing problems. Rapid prototyping is not often used for large scale and long term operations for a part. Nevertheless, rapid tooling is starting to be used to create molds for commercial operations because the time lag is so short between start to finish and since a CAD file is the only thing needed for the design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |