|
Agha Shaukat Ali
Agha Shaukat Ali (1919–2013) was a civil servant turned politician in the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir, British Indian Empire. He served as the General Secretary of the Muslim Conference party in the years preceding the Partition of India. Having migrated to Pakistan after the partition, he served as a Pakistani civil servant, writer and diplomat. Family background Agha Shaukat Ali was born in the aristocratic Agha family in Srinagar in 1919. The family belonged to the military Qizilbash aristocracy which had migrated from Kandahar in the early 19th century and since then held offices of Royal Physicians, Ministers and Courtiers to the Dogra dynasty. His mother Begum Zaffar Ali, an educationist and legislator, was the first woman matriculate of Kashmir. His maternal grandfather, Khan Bahadur Aga Syed Hussain, then Governor and later Home and Judicial Minister in the princely state, was the first matriculate of Kashmir. Shaukat Ali's eldest brother was A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Srinagar
Srinagar (English: , ) is the largest city and the summer capital of Jammu and Kashmir, India. It lies in the Kashmir Valley on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus, and Dal and Anchar lakes. The city is known for its natural environment, gardens, waterfronts and houseboats. It is known for traditional Kashmiri handicrafts like the Kashmir shawl (made of pashmina and cashmere wool), and also dried fruits. It is the 31st-most populous city in India, the northernmost city in India to have over one million people, and the second-largest metropolitan area in the Himalayas (after Kathmandu, Nepal). Origin of name The earliest records, such as Kalhana's ''Rajatarangini'', mentions the Sanskrit name ''shri-nagara'' which have been interpreted distinctively by scholars in two ways: one being ''sūrya-nagar'', meaning "''City of the Surya''" (trans) ''"City of Sun''" and other being ''"The city of "Shri''" (श्री), the Hindu goddess of wealth, meaning "' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shalimar Gardens, Lahore
The Shalimar Gardens ( ur, , translit=Shālāmār Bāgh) are a Mughal garden complex located in Lahore, Pakistan. The gardens date from the period when the Mughal Empire was at its artistic and aesthetic zenith, and are now one of Pakistan's most popular tourist destinations. The Shalimar Gardens were laid out as a Persian paradise garden intended to create a representation of an earthly utopia in which humans co-exist in perfect harmony with all elements of nature. Construction of the gardens began in 1641 during the reign of Emperor Shah Jahan, and was completed in 1642. In 1981 the Shalimar Gardens were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site as they embody Mughal garden design at the apogee of its development. Names The courtiers told the Maharaja Ranjit Singh "that Shala was a Turkic word which means pleasure and the mar means the place to live in". "The arguments of the courtiers in favour of the Turkic signification of the word failing to make any impression on Ranjit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
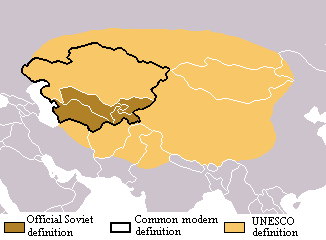
Soviet Central Asia
Soviet Central Asia (russian: link=no, Советская Средняя Азия, Sovetskaya Srednyaya Aziya) was the part of Central Asia administered by the Soviet Union between 1918 and 1991, when the Central Asian republics declared independence. It is nearly synonymous with Russian Turkestan in the Russian Empire. Soviet Central Asia went through many territorial divisions before the current borders were created in the 1920s and 1930s. Administrative divisions Former divisions Turkestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic By the end of the 19th century, Russian tsars effectively ruled over most of the territory that later would constitute Soviet Central Asia. Russia annexed Lake Issyk Kul in north east Kyrgyzstan from China in the early 1860s, lands of Turkmens, Khanate of Khiva, Emirate of Bukhara in the second half of 1800s. Emerging from the Russian Empire following the Russian Revolution of 1917 and the Russian Civil War of 1918–1921, the USSR was a union o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna, Virginia
Vienna () is a town in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. As of the 2020 U.S. census, Vienna has a population of 16,473. Significantly more people live in ZIP codes with the Vienna postal addresses (22180, 22181, and 22182), bordered approximately by Interstate 66 on the south, Interstate 495 on the east, Route 7 to the north, and Hunter Mill Road to the west, than in the town itself. History Non-native settlement in the region dates to ca. 1740. In 1754, prominent soldier and land owner Colonel Charles Broadwater settled within the town boundaries. Broadwater's son-in-law, John Hunter built the first recorded house there in 1767, naming it Ayr Hill to recall his birthplace, Ayr, Scotland. That name was then applied to the tiny developing community. The name of the town was changed in the 1850s, when a doctor, William Hendrick, settled there if the town renamed itself after his hometown, Phelps, New York, which was then known as Vienna. On June 17, 1861, a relatively-mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pervez Musharraf
General Pervez Musharraf ( ur, , Parvez Muśharraf; born 11 August 1943) is a former Pakistani politician and four-star general of the Pakistan Army who became the tenth president of Pakistan after the successful military takeover of the federal government in 1999. He also served as the 10th Chairman Joint Chiefs of Staff Committee from 1998 to 2001 and the 7th Chief of Army Staff from 1998 to 2007. Born in Delhi during the British Raj, Musharraf was raised in Karachi and Istanbul. He studied mathematics at Forman Christian College in Lahore and was also educated at the Royal College of Defence Studies in the United Kingdom. Musharraf entered the Pakistan Military Academy in 1961 and was commissioned to the Pakistan Army in 1964. Musharraf saw action during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 as a second lieutenant. By the 1980s, he was commanding an artillery brigade. In the 1990s, Musharraf was promoted to major general and assigned an infantry division, and later commanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
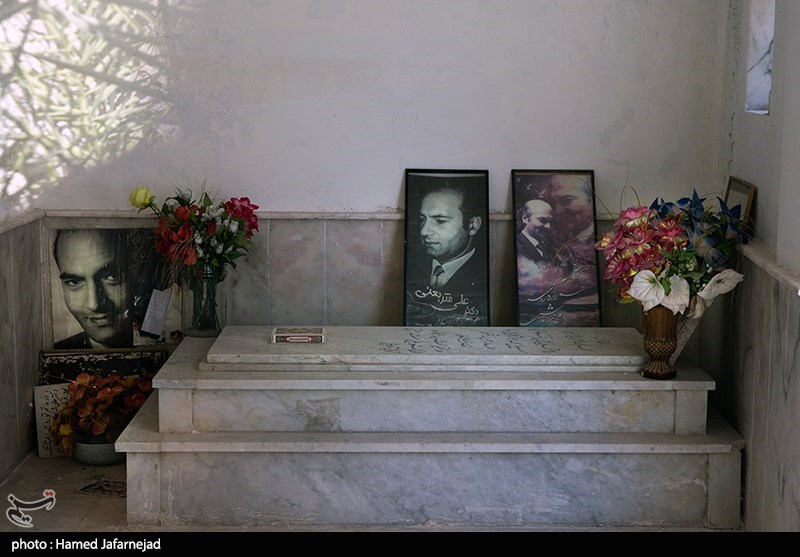
Ali Shariati
Ali Shariati Mazinani ( fa, علی شریعتی مزینانی, 23 November 1933 – 18 June 1977) was an Iranian revolutionary and sociologist who focused on the sociology of religion. He is held as one of the most influential Iranian intellectuals of the 20th century and has been called the "ideologue of the Iranian Revolution", although his ideas did not end up forming the basis of the Islamic Republic. Biography Ali Shariati (Ali Masharati) was born in 1933 in Mazinan, a suburb of Sabzevar, in northeastern Iran. His father's family were clerics. His father, Mohammad-Taqi, was a teacher and Islamic scholar. In 1947, he opened the Centre for the Propagation of Islamic Truths in Mashhad, in Khorasan Province. It was a social Islamic forum which became embroiled in the oil nationalisation movement of the 1950s. Shariati's mother was from a small land-owning family. His mother was from Sabzevar, a little town near Mashhad. In his years at the Teacher's Training College in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Iqbal
Sir Muhammad Iqbal ( ur, ; 9 November 187721 April 1938), was a South Asian Muslim writer, philosopher, Quote: "In Persian, ... he published six volumes of mainly long poems between 1915 and 1936, ... more or less complete works on philosophical themes" (p. xiii)" Scholar and politician, whose poetry in the Urdu language is considered among the greatest of the twentieth century, Quote: "In Urdu, Iqbal is allowed to have been far the greatest poet of this century, and by most critics to be the only equal of Ghalib (1797–1869). ... the Urdu poems, addressed to a real and familiar audience close at hand, have the merit of being direct, spontaneous utterances on tangible subjects. (p. xiii)" and whose vision of a cultural and political ideal for the Muslims of British Raj, British-ruled India was to animate the impulse for Pakistan. He is commonly referred to by the honorific Allama (from ). Born and raised in Sialkot, Punjab region, Punjab in an ethnic Kashmiri Muslims, Kash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulbright Scholar
The Fulbright Program, including the Fulbright–Hays Program, is one of several United States Cultural Exchange Programs with the goal of improving intercultural relations, cultural diplomacy, and intercultural competence between the people of the United States and other countries, through the exchange of persons, knowledge, and skills. Via the program, competitively-selected American citizens including students, scholars, teachers, professionals, scientists, and artists may receive scholarships or grants to study, conduct research, teach, or exercise their talents abroad; and citizens of other countries may qualify to do the same in the United States. The program was founded by United States Senator J. William Fulbright in 1946 and is considered to be one of the most widely recognized and prestigious scholarships in the world. The program provides approximately 8,000 grants annually – roughly 1,600 to U.S. students, 1,200 to U.S. scholars, 4,000 to foreign students, 900 to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodrow Wilson School Of Public And International Affairs
The Princeton School of Public and International Affairs (formerly the Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs) is a professional public policy school at Princeton University. The school provides an array of comprehensive coursework in the fields of international development, foreign policy, science and technology, and economics and finance through its undergraduate (AB) degrees, graduate Master of Public Affairs (MPA), Master of Public Policy (MPP), and PhD degrees. The school is consistently ranked as one of the best institutions for the study of international relations and public affairs in the country and in the world. ''Foreign Policy'' ranks the Princeton School as No. 2 in the world for International Relations at the undergraduate and No. 4 at the graduate level, behind the Edmund A. Walsh School of Foreign Service at Georgetown University. History In 1930, Princeton University established the School of Public and International Affairs, which was original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayub Khan (President Of Pakistan)
Muhammad Ayub Khan (Urdu: ; 14 May 1907 – 19 April 1974), was the second President of Pakistan. He was an army general who seized the presidency from Iskander Mirza in a coup in 1958, the first successful coup d'état in the country's history. Popular demonstrations and labour strikes supported by the protests in East Pakistan ultimately led to his forced resignation in 1969. During his presidency, differences between East and West Pakistan arose to an enormous degree, that ultimately led to the Independence of East Pakistan. Trained at the British Royal Military College, Ayub Khan fought in World War II as a colonel in the British Indian Army before deciding to transfer to the Pakistan Army in the aftermath of the partition of India in 1947. His assignments included command of the 14th Division in East-Bengal. He was elevated to become the first native Commander-in-Chief of the Pakistan Army in 1951 by Prime Minister Liaquat Ali Khan, succeeding General Douglas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ram Chandra Kak
Ram Chandra Kak (5 June 1893 – 10 February 1983) was the prime minister of Jammu and Kashmir during 1945–1947. One of the very few Kashmiri Pandits to ever hold that post, Kak had the intractable job of navigating the troubled waters of the transfer of power from British Raj to the independent dominions of India and Pakistan. He handled the activism of the state's political parties, the National Conference and Muslim Conference, and warded off pressure from the new dominions for the accession of the state. He advised the Maharaja to stay independent for at least a year before making the final decision. His actions were highly unpopular with the state's activist Muslims, and he was dismissed from the post of prime minister shortly before the independence of India and Pakistan in August 1947. Kak was also a pioneering archaeologist who excavated the major sites of antiquities in Kashmir Valley and wrote a definitive treatise on them. Early life Ram Chandra Kak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaudhry Ghulam Abbas
Chaudhry Ghulam Abbas (4 February 1904 – 18 December 1967) was a leading politician of Jammu and Kashmir and the President of the Muslim Conference party. After his migration to Pakistan administered Kashmir in 1947, he became the head of the Azad Kashmir (AJK) government. Early life and career Chaudhry Ghulam Abbas was born in a middle-class Rajput family of Chaudhry Nawab Khan on 4 February 1904 at Jammu. He graduated from the Prince of Wales College, Jammu. He received his law degree from the Lahore Law College and started his career as a lawyer in Jammu. He was offered a position of Sub-Judge but he refused to serve the Dogra Raj in Kashmir. He reorganized the socio-political organization Young Men’s Muslim Association, which was established earlier in 1909 and was the only platform that Muslims were using to raise their political voice in Jammu and Kashmir. This organization held some massive demonstrations against the Dogra rule. As a result, the Association became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.png)