|
Agelena Labyrinthica
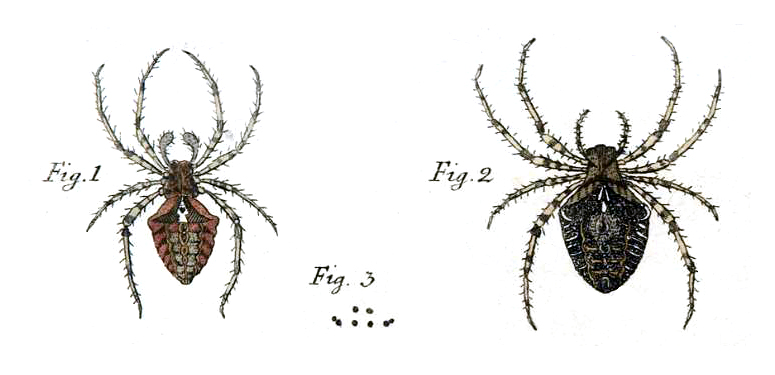
''Agelena labyrinthica'' is a species of spider in the family Agelenidae. It is a widespread species in Europe. Range and habitat ''Agelena labyrinthica'' build flat plate surface webs connected to funnel-shaped retreats similar to labyrinths, which are typically constructed between low lying grass and vegetation. These webs can be at ground level, or up to from the ground, however, the majority are found approximately off of the ground. These spiders are fairly common in Europe and Central Europe, and are typically concentrated in areas near forests and low lying vegetation, as well as in dry grasslands. Description Funnel-web spiders typically range in size from for males and for females. ''Agelena labyrinthica'', however, has a body length of up to . The abdomen is dark with a pale central band flanked by white chevron marks. The cephalothorax is yellow-brown and bears two, broad longitudinal stripes positioned towards the front of the spider. Common to all spiders in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Alexander Clerck
Carl Alexander Clerck (1709 – 22 July 1765) was a Sweden, Swedish entomologist and arachnology, arachnologist. Clerck came from a family in the petty Swedish nobility, nobility and entered the University of Uppsala in 1726. Little is known of his studies; although a contemporary of Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus, it is unknown whether he had any contact with him during his time in Uppsala. His limited means forced him to leave university early and enter into government service, later ending up working in the administration of the City of Stockholm. His interest in natural history appears to have come at a more mature age, influenced by a lecture of Linnaeus he attended in Stockholm in 1739. In the following years he collected and categorized many spiders, published together with more general observations on the morphology and behaviour of spiders, in his ''Svenska Spindlar'' ("Swedish spiders", 1757, also known by its Latin subtitle, ''Aranei Suecici''). He also started the publication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichobothria
Trichobothria (singular trichobothrium) are elongate setae ("hairs") present in arachnids, various orders of insects, and myriapods that function in the detection of airborne vibrations and currents, and electrical charge. In 1883, Friedrich Dahl observed that they were deflected by the sound waves from a violin and labelled them 'hearing hairs'. Morphology Unlike the ordinary setae, which are tapered, the trichobothria have the same gauge throughout their length. They fit into the bottom of a broad and deep cup to which connects a membrane with extreme flexibility which adds an extraordinary mobility to them. The least air vibration is able to get them moving and to excite the small group of sensory cells which ensures their innervation. Distribution Trichobothria are present in most orders of the Arachnida, except in Solifugae, Ricinulei and Opiliones (Grassé, 1949). Although the distribution of trichobothria on the bodies of arachnids is often used by systematists (especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiders Described In 1757
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel, however, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had a separate t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiders Of Europe
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel, however, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had a separate t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agelena
Agelena is a genus of agelenid spiders first described by Charles Athanase Walckenaer in 1805. Sometimes referred to as Eurasian grass spiders, they trap their prey by weaving entangling non-sticky funnel webs. They are limited to the Old world, occurring from Africa to Japan. Many species have been moved to other genera, particularly to ''Allagelena'', '' Benoitia'' and ''Mistaria''. ''Agelena limbata'' is one of the most common web-weaving spider species in Japan. Species , the World Spider Catalog accepted 46 species: *'' Agelena annulipedella'' Strand, 1913 — Central Africa *''Agelena atlantea'' Fage, 1938 — Morocco *'' Agelena australis'' Simon, 1896 — South Africa *'' Agelena babai'' Tanikawa, 2005 — Japan *'' Agelena barunae'' Tikader, 1970 — India *'' Agelena borbonica'' Vinson, 1863 — Réunion *'' Agelena canariensis'' Lucas, 1838 — Canary Is., Morocco, Algeria *'' Agelena chayu'' Zhang, Zhu & Song, 2005 — China *'' Agelena choi'' Paik, 1965 — Korea * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matriphagy
Matriphagy is the consumption of the mother by her offspring. The behavior generally takes place within the first few weeks of life and has been documented in some species of insects, nematode worms, pseudoscorpions, and other arachnids as well as in caecilian amphibians. The specifics of how matriphagy occurs varies among different species, but the process is best described in the Desert spider, '' Stegodyphus lineatus'', where the mother harbors nutritional resources for her young through food consumption. The mother is able to regurgitate small portions of food for her growing offspring, but between 1–2 weeks after hatching the progeny capitalize on this food source by eating her alive. Typically, offspring only feed on their biological mother as opposed to other females in the population. In other arachnid species, matriphagy occurs after the ingestion of nutritional eggs known as trophic eggs (e.g. Black lace-weaver ''Amaurobius ferox'', Crab spider ''Australomisidia ergandr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
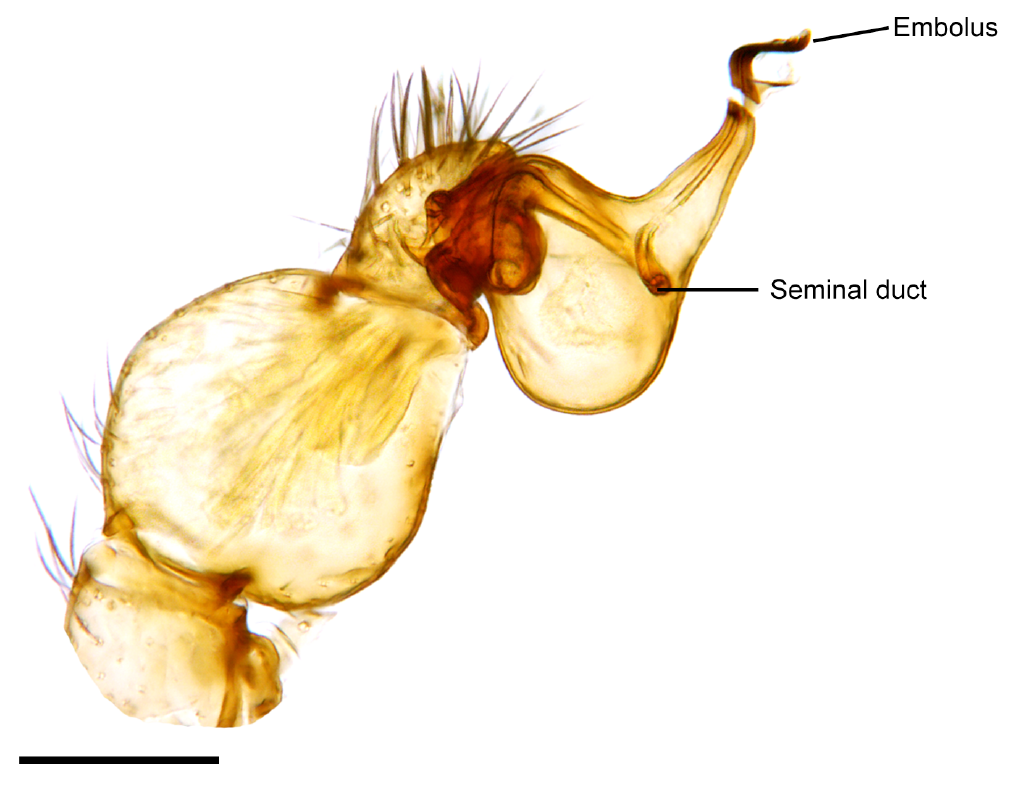
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles: the coxa, the trochanter, the femur, the short patella, the tibia, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spiders, or chelate weapons ( pincers) of great size, as in scorpions. The pedipalps of Solifugae are covered in setae, but have not been studied in detail. Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiothetic
Idiothetic literally means "self-proposition" (Greek derivation), and is used in navigation models (e.g., of a rat in a maze) to describe the use of self-motion cues, rather than allothetic, or external, cues such as landmarks, to determine position and movement. The word is sometimes also spelled "ideothetic" (e.g., Chen et al, 1994 ). Idiothetic cues include vestibular, optic flow and proprioception. Idiothetic cues are important for the type of navigation known as path integrationMittelstaedt, H. and Mittelstaedt, M.-L. (1973). "Mechanismen der orientierung ohne richtende aussenreize." Fortschr. Zool. 21:46–58. in which subjects navigate purely using such self-motion cues. This is achieved by an animal through the signals generated by angular and linear accelerations in the course of its exploration. These information generate and update a vector towards the starting point and an accurate path for return. The term ''idiothetic'' is also used in robotics and in personality p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portable Document Format
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems.Adobe Systems IncorporatedPDF Reference, Sixth edition, version 1.23 (53 MB) Nov 2006, p. 33. Archiv/ref> Based on the PostScript language, each PDF file encapsulates a complete description of a fixed-layout flat document, including the text, fonts, vector graphics, raster images and other information needed to display it. PDF has its roots in "The Camelot Project" initiated by Adobe co-founder John Warnock in 1991. PDF was standardized as ISO 32000 in 2008. The last edition as ISO 32000-2:2020 was published in December 2020. PDF files may contain a variety of content besides flat text and graphics including logical structuring elements, interactive elements such as annotations and form-fields, layers, rich media (including video con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Arachnology
The American Arachnological Society (AAS) is a scientific organization founded in 1972 in order to promote the study of arachnids by seeking to achieve closer cooperation and understanding between amateur and professional arachnologists along with publication of the ''Journal of Arachnology.'' The society holds annual meetings around the United States and membership is open to all individuals who share the common objectives held by the society. Journal The AAS publishes the ''Journal of Arachnology''. Selected publications * See also * International Society of Arachnology The International Society of Arachnology (ISA) promotes the study of arachnids and the exchange of information among researchers in this field. It acts as an umbrella organisation for regional societies and individuals interested in spiders, and ... References External links AAS Constitution {{authority control Arachnological societies Environmental organizations based in Rhode Island Zoology organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Science+Business Media
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)