|
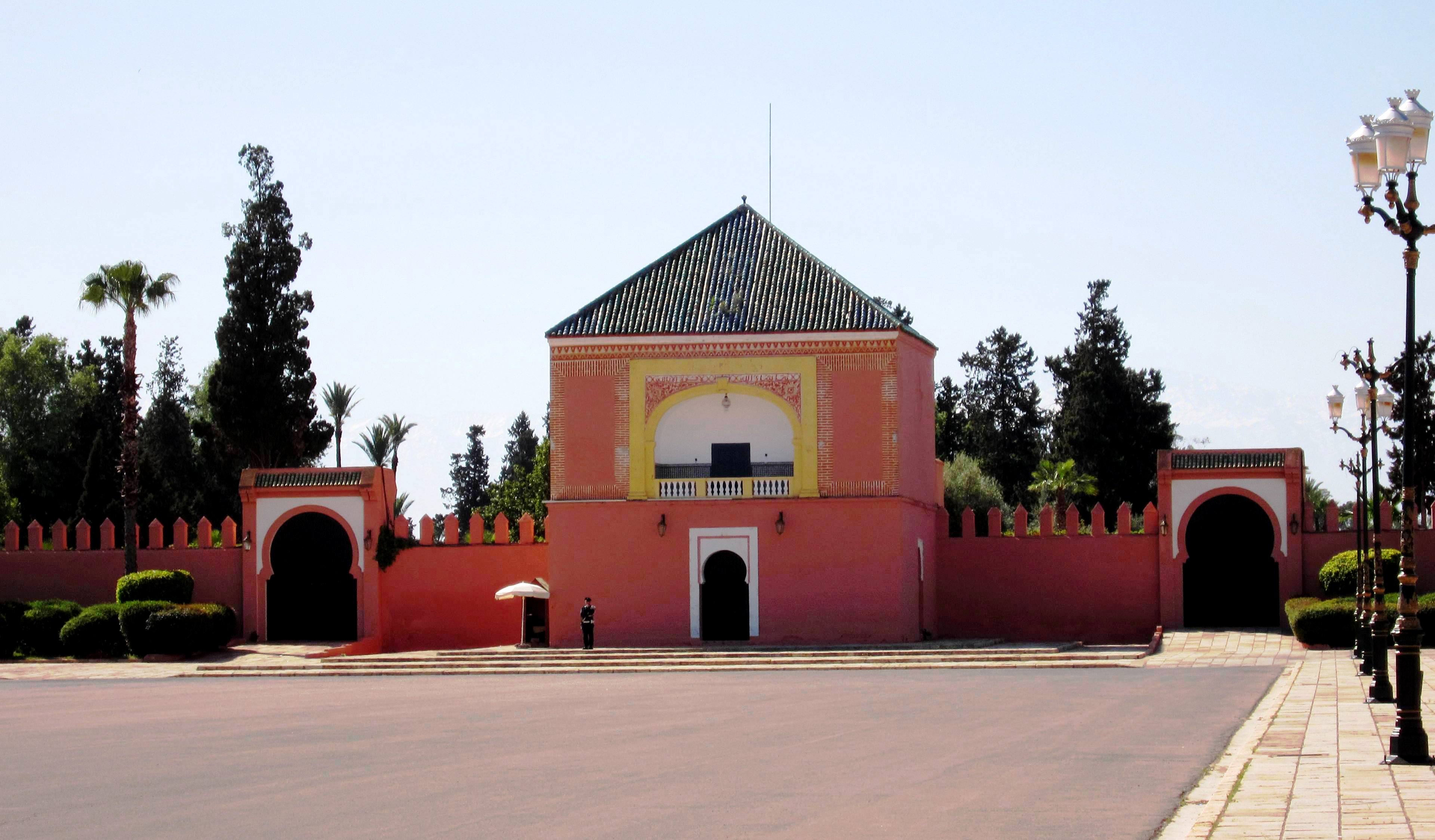
Agdal Garden
The Agdal Gardens (or Aguedal Gardens) are a large area of historic gardens and Orchard, orchards in Marrakesh, Morocco. The gardens are located to the south of the city's historic Kasbah of Marrakesh, Kasbah and its royal palace. Together with the Medina quarter, medina of Marrakech and the Menara Gardens, the Agdal Gardens were listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site in 1985. The gardens contain several historic water reservoirs as well as several historic palaces and pavilions, including the ''Dar el-Hana'' and the ''Dar al-Bayda''. Etymology The name ''Agdal'' is a Polysemy, polysemic term derived from Berber languages, Tamazight (Berber) meaning a "walled meadow" or a summer pasture for transhumance. The same name is also used for similar walled parks and gardens in other historic Moroccan cities such as Fez, Morocco, Fez, Meknes, and Rabat. History Almohad creation The tradition of creating gardens on the outskirts of the city began early with the Almoravid dynasty, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
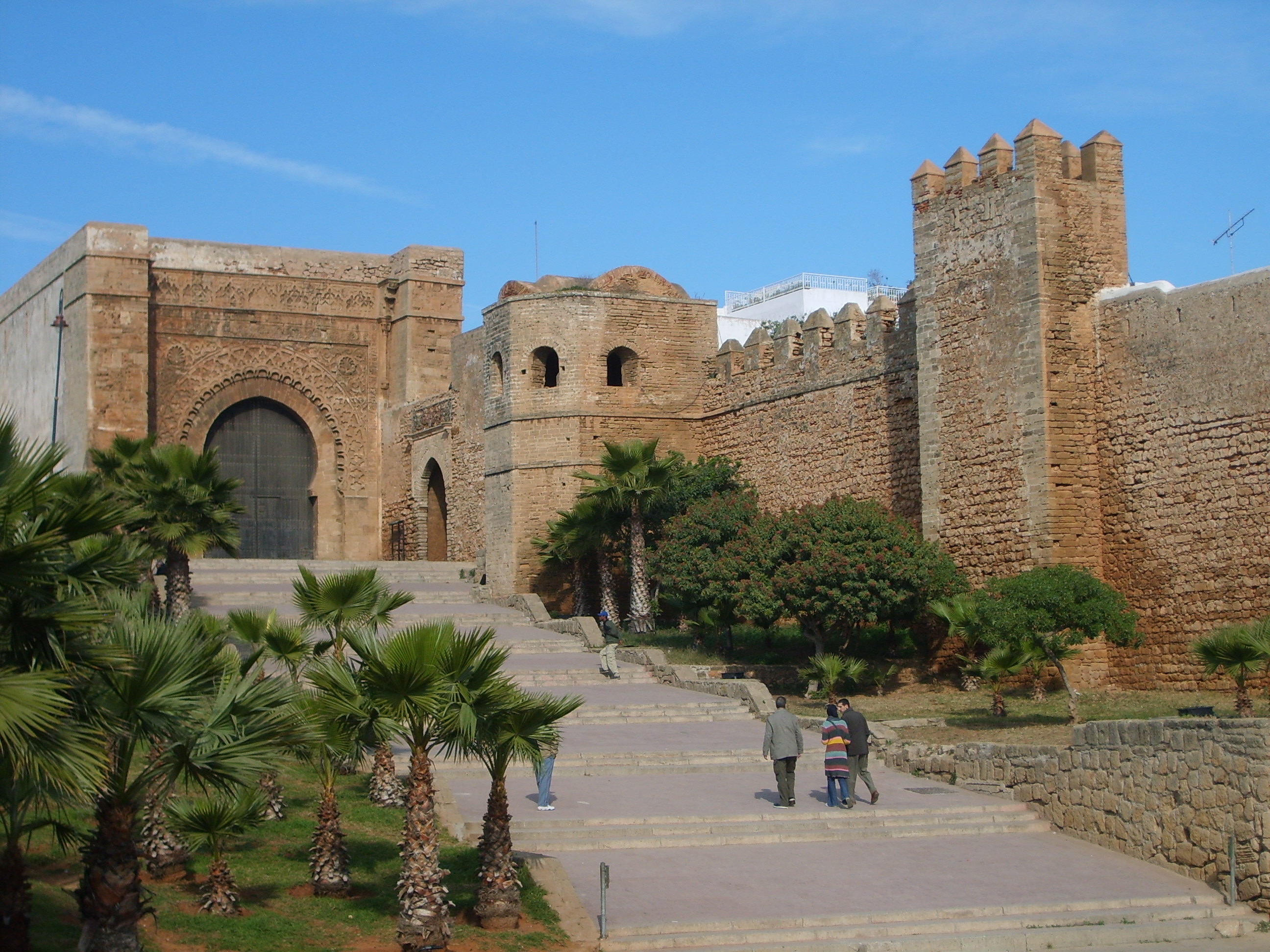
Almohad Caliphate
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, خِلَافَةُ ٱلْمُوَحِّدِينَ or or from ar, ٱلْمُوَحِّدُونَ, translit=al-Muwaḥḥidūn, lit=those who profess the unity of God) was a North African Berber Muslim empire founded in the 12th century. At its height, it controlled much of the Iberian Peninsula (Al Andalus) and North Africa (the Maghreb). The Almohad movement was founded by Ibn Tumart among the Berber Masmuda tribes, but the Almohad caliphate and its ruling dynasty were founded after his death by Abd al-Mu'min al-Gumi. Around 1120, Ibn Tumart first established a Berber state in Tinmel in the Atlas Mountains. Under Abd al-Mu'min (r. 1130–1163) they succeeded in overthrowing the ruling Almoravid dynasty governing Morocco in 1147, when he conquered Marrakesh and declared himself caliph. They then extended their power over all of the Maghreb by 1159. Al-Andalus soon followed, and all of Muslim Iberia was under Almohad rule by 1172. The tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Badi Palace
El Badi Palace ( ar, قصر البديع, lit=Palace of Wonder/Brilliance, also frequently translated as the "Incomparable Palace") or Badi' Palace is a ruined palace located in Marrakesh, Morocco. It was commissioned by the sultan Ahmad al-Mansur of the Saadian dynasty a few months after his accession in 1578, with construction and embellishment continuing throughout most of his reign. The palace, decorated with materials imported from numerous countries ranging from Italy to Mali, was used for receptions and designed to showcase the Sultan's wealth and power. It was one part of a larger Saadian palace complex occupying the Kasbah district of Marrakesh. The palace was neglected after al-Mansur's death in 1603 and eventually fell into ruin after the decline of the Saadian dynasty. Its valuable materials (especially marble) were stripped away and reused in other buildings across Morocco. Today it is a major tourist attraction in Marrakesh as well as an exhibition space; notably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riad (architecture)
A riad ( ar, رياض, riyāḑ; also spelled "riyad") is a type of traditional Moroccan and Andalusi interior garden or courtyard associated with house and palace architecture. Its origin is generally attributed to Persian gardens that spread during the Islamic period. The term is nowadays often used in Morocco to refer to a hotel or guesthouse-style accommodation with shared common areas and private rooms, often within a restored traditional mansion. History The term ''riad'' originates from the Arabic term for garden, رياض (''riyad''). Historically, the term referred to a type of interior garden common to historic Moorish architecture in Al-Andalus (Iberian Peninsula) and North Africa: in particular, a rectangular courtyard garden that is symmetrically divided into four parts along its central axes and typically has a fountain at its middle. Riad architecture ultimately has ancient roots in Mediterranean and Middle Eastern domestic architecture. Houses centered around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmad Al-Mansur
Ahmad al-Mansur ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد المنصور, Ahmad Abu al-Abbas al-Mansur, also al-Mansur al-Dahabbi (the Golden), ar, أحمد المنصور الذهبي; and Ahmed al-Mansour; 1549 in Fes – 25 August 1603, Fes) was the Saadi Sultan of Morocco from 1578 to his death in 1603, the sixth and most famous of all rulers of the Saadis. Ahmad al-Mansur was an important figure in both Europe and Africa in the sixteenth century. His powerful army and strategic location made him an important power player in the late Renaissance period. He has been described as "a man of profound Islamic learning, a lover of books, calligraphy and mathematics, as well as a connoisseur of mystical texts and a lover of scholarly discussions." Early life Ahmad was the fifth son of Mohammed ash-Sheikh who was the first Saadi sultan of Morocco. His mother was Lalla Masuda. After the murder of their father, Mohammed in 1557 and the following struggle for power, the two brothers Ahmad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdallah Al-Ghalib
Abdallah al-Ghalib Billah (; b. 1517 – d. 22 January 1574, 1557–1574) was the second Saadian sultan of Morocco. He succeeded his father Mohammed al-Shaykh as Sultan of Morocco. Biography Early life With his first wife Sayyida Rabia, Mohammed al-Shaykh had three sons, but the two oldest had died while he was still alive (in 1550 and in 1551). Abdallah, the third, was 40 years old when he became sultan and received the name al-Ghalib Billah. Before that he had been vice-king of Marrakesh and governor of Fes. Shortly after Abdallah came to power, three of his younger brothers fled the country and joined the Ottoman Turks. Abd al-Malik and Ahmad, both future Sultans of Morocco, spent 17 years in exile in the Ottoman Empire, moving between Algiers and Constantinople, where they were trained by the Ottomans. During a relatively peaceful reign Abdallah succeeded in warding off both the Spanish and the Turks and in consolidating the sovereignty of the Saadians over Moroc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused by a variety of factors, such as climate change and overexploitation of soil as a result of human activity. Throughout geological history, the development of deserts has occurred naturally. In recent times, the potential influences of human activity, improper land management, deforestation and climate change on desertification is the subject of many scientific investigations. Definitions of words As recently as 2005, considerable controversy existed over the proper definition of the term "desertification." Helmut Geist (2005) identified more than 100 formal definitions. The most widely acceptedGeist (2005)p. 2/ref> of these was that of the Princeton University Dictionary which defined it as "the process of fertile land ''transforming int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavilion
In architecture, ''pavilion'' has several meanings: * It may be a subsidiary building that is either positioned separately or as an attachment to a main building. Often it is associated with pleasure. In palaces and traditional mansions of Asia, there may be pavilions that are either freestanding or connected by covered walkways, as in the Forbidden City (Chinese pavilions), Topkapi Palace in Istanbul, and in Mughal buildings like the Red Fort. * As part of a large palace, pavilions may be symmetrically placed building ''blocks'' that flank (appear to join) a main building block or the outer ends of wings extending from both sides of a central building block, the '' corps de logis''. Such configurations provide an emphatic visual termination to the composition of a large building, akin to bookends. The word is from French (Old French ) and it meant a small palace, from Latin (accusative of ). In Late Latin and Old French, it meant both ‘butterfly’ and ‘tent’, becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saadi Sultanate
The Saadi Sultanate (also rendered in English as Sa'di, Sa'did, Sa'dian, or Saadian; ar, السعديون, translit=as-saʿdiyyūn) was a state which ruled present-day Morocco and parts of West Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was led by the Saadi dynasty, an Arab Moroccan Sharifian dynasty. The dynasty's rise to power started in 1510 when Muhammad al-Qa'im was declared leader of the tribes of the Sous valley in their resistance against the Portuguese who occupied Agadir and other coastal cities. Al-Qai'm's son, Ahmad al-Araj, secured control of Marrakesh by 1525 and, after a period of rivalry, his brother Muhammad al-Shaykh captured Agadir from the Portuguese and eventually captured Fez from the Wattasids, securing control over nearly all of Morocco. After Muhammad al-Shaykh's assassination by the Ottomans in 1557 his son Abdallah al-Ghalib enjoyed a relatively peaceful reign. His successors, however, fought with each other, culminating in the 1578 Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Yusuf Yaqub Al-Mansur
Abū Yūsuf Yaʿqūb ibn Yūsuf ibn Abd al-Muʾmin al-Manṣūr (; c. 1160 – 23 January 1199 Marrakesh), commonly known as Yaqub al-Mansur () or Moulay Yacoub (), was the third Almohad Caliph. Succeeding his father, al-Mansur reigned from 1184 to 1199. His reign was distinguished by the flourishing of trade, architecture, philosophy and the sciences, as well as by victorious military campaigns in which he was successful in repelling the tide of the ''Reconquista'' in the Iberian Peninsula. Military actions Al-Mansur's father was killed in Portugal on 29 July 1184; upon reaching Seville with his father's body on 10 August, he was immediately proclaimed the new caliph. Al-Mansur vowed revenge for his father's death, but fighting with the Banu Ghaniya, delayed him in Africa. After inflicting a new defeat on the Banu Ghaniya, he set off for the Iberian Peninsula to avenge his father's death. His 13 July 1190 siege of Tomar, center of the Portuguese Templars failed to capture th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian (), also known by its endonym Farsi (, ', ), is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964) and Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate history in the cultural sphere of Greater Iran. It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in the Persian alphabet, a derivation of the Arabic script, and within Tajikistan in the Tajik alphabet, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg , caption = The Berber ethnic flag , population = 36 million , region1 = Morocco , pop1 = 14 million to 18 million , region2 = Algeria , pop2 = 9 million to ~13 million , region3 = Mauritania , pop3 = 2.9 million , region4 = Niger , pop4 = 2.6 million, Niger: 11% of 23.6 million , region5 = France , pop5 = 2 million , region6 = Mali , pop6 = 850,000 , region7 = Libya , pop7 = 600,000 , region8 = Belgium , pop8 = 500,000 (including descendants) , region9 = Netherlands , pop9 = 467,455 (including descendants) , region10 = Burkina Faso , pop10 = 406,271, Burkina Faso: 1.9% of 21.4 million , region11 = Egypt , pop11 = 23,000 or 1,826,580 , region12 = Tunisia , pop12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |