|
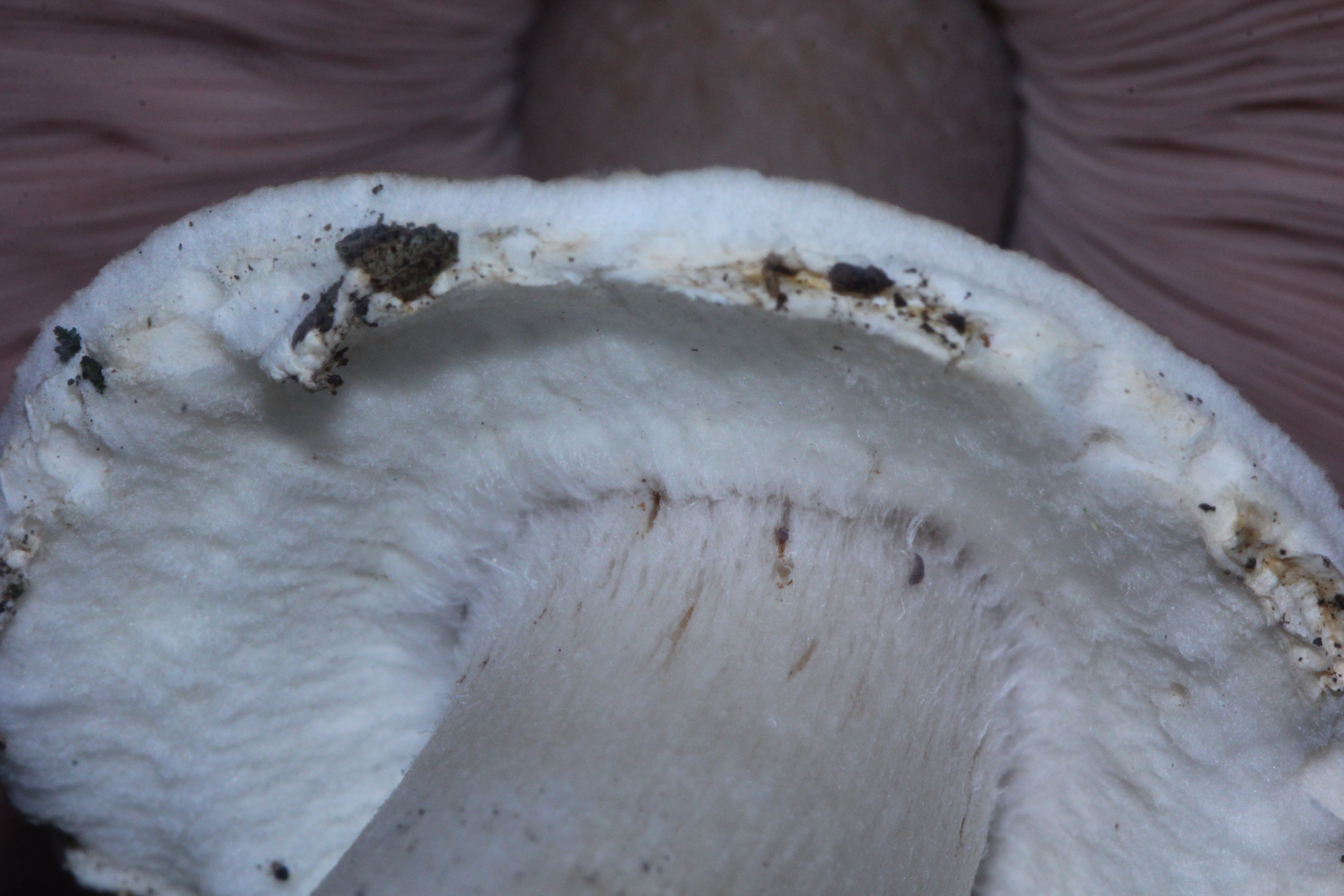
Agaricus Silvicola
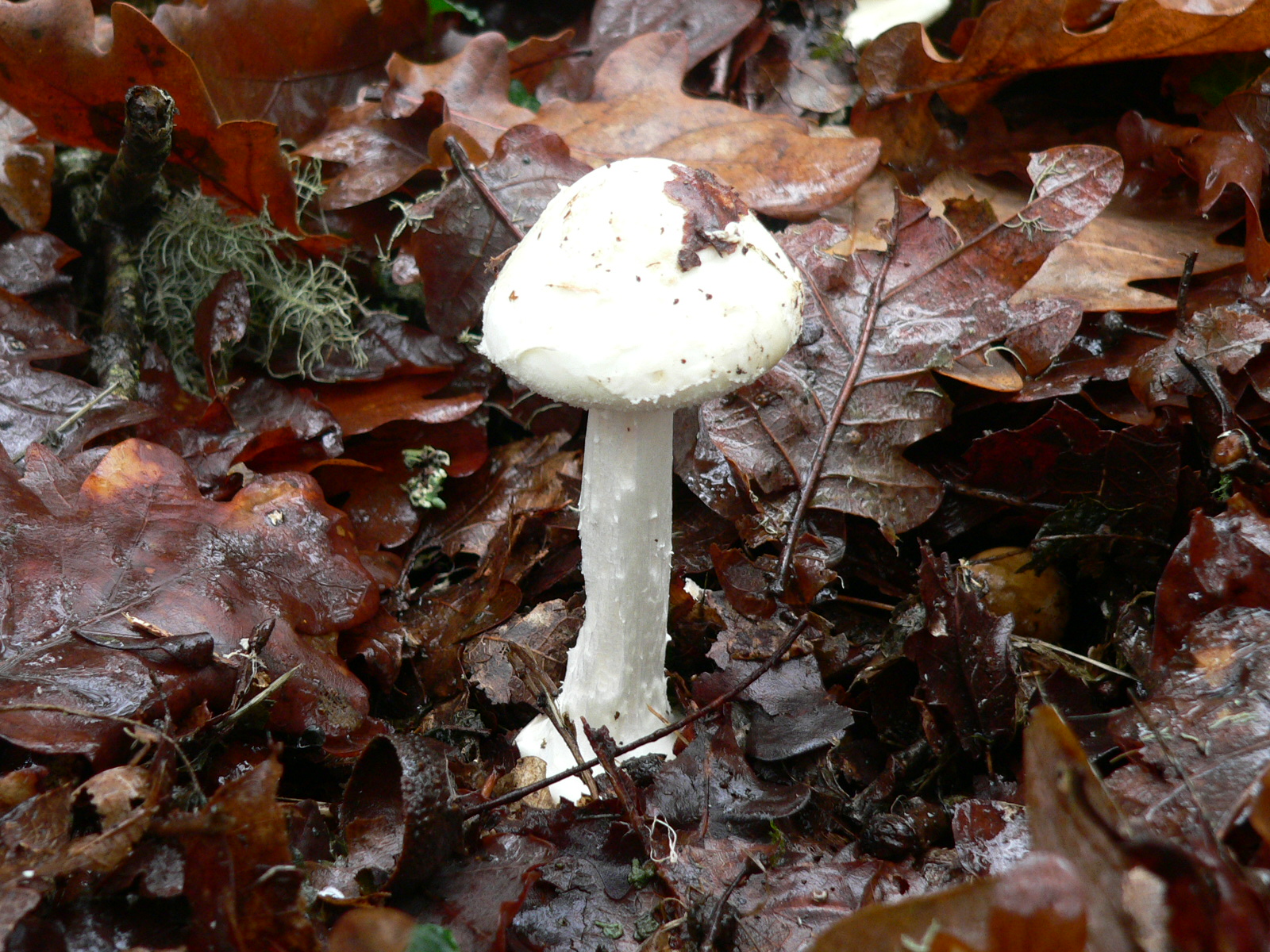
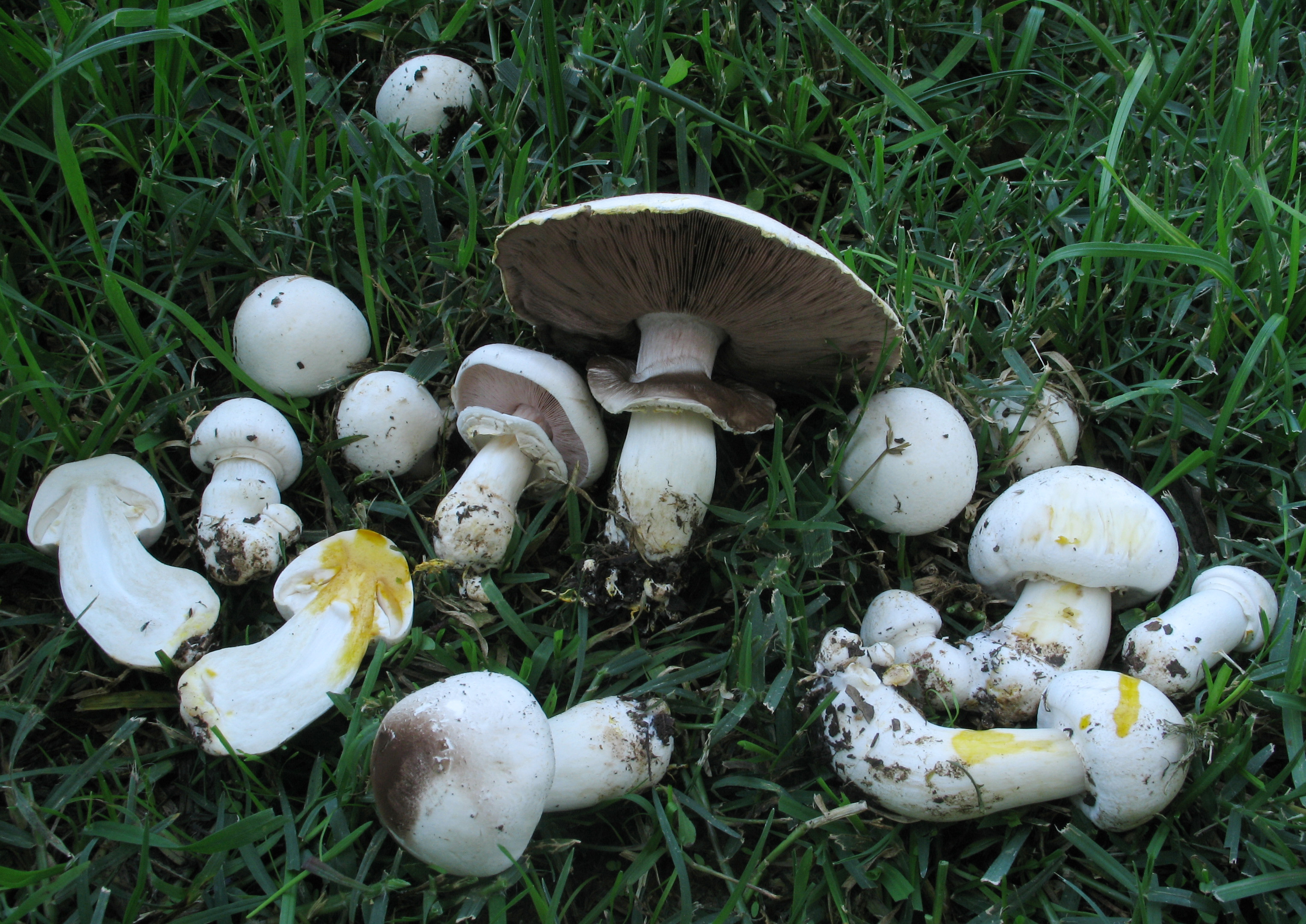
''Agaricus silvicola'', also known as the wood mushroom, is a species of Agaricus mushroom related to the button mushroom. Taxonomy Originally described as the variety ''Agaricus campestris'' var. ''silvicola'' by Carlo Vittadini in 1832, it was promoted to distinct species status by Charles Horton Peck in 1873. Varieties with larger bases have been described as '' A. abruptibulbus''. Description The cap is light cream, and bruises yellow ochre when damaged. It is in diameter, which makes it slightly smaller than its close relative ''Agaricus arvensis'', the "horse mushroom". The stem is , and usually has a bulbous base. It is much the same colour as the cap, and has a fragile drooping ring. The flesh is thin and white, and smells of aniseed. It looks fairly similar to a young death cap. The spores are brown, elliptical, and smooth. Distribution and habitat ''Agaricus silvicola'' grows in both deciduous and coniferous woodland in Britain, Europe, and North America. Appe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlo Vittadini
Carlo Vittadini (11 June 1800, in Bertonico – 20 November 1865, in Milan) was an Italian physician, doctor and mycology, mycologist. Life He studied in Milan and at the University of Pavia, where he attended the classes given by Giuseppe L. Moretti (1782–1853). He became a doctor of medicine in 1826 with a thesis entitled ''Tentamen mycologicum seu Amanitarum '' where he described 14 species of the genus ''Amanita''. Outside of several publications on diseases of silkworms, he specialised in obstetrics, working in Milan. He is the author of several important works on Italian mushroom species. Works * * ''Monographia tuberacearum'' (Rusconi, Milan, 1831) - Describes 65 species, of which 51 were new. * ''Descrizione dei funghi mangerecci più comuni dell'Italia e de'velenosi che possono co'medesimi confondersi'' (1835) - Describes 56 species, of which 15 were new. * ''Monographia Lycoperdineorum'' (1842) - Completes his 1831 study and describes 50 species, of which 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiospore
A basidiospore is a reproductive spore produced by Basidiomycete fungi, a grouping that includes mushrooms, shelf fungi, rusts, and smuts. Basidiospores typically each contain one haploid nucleus that is the product of meiosis, and they are produced by specialized fungal cells called basidia. Typically, four basidiospores develop on appendages from each basidium, of which two are of one strain and the other two of its opposite strain. In gills under a cap of one common species, there exist millions of basidia. Some gilled mushrooms in the order Agaricales have the ability to release billions of spores. The puffball fungus ''Calvatia gigantea'' has been calculated to produce about five trillion basidiospores. Most basidiospores are forcibly discharged, and are thus considered ballistospores. These spores serve as the main air dispersal units for the fungi. The spores are released during periods of high humidity and generally have a night-time or pre-dawn peak concentration in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Described In 1832
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edible Fungi
Edible mushrooms are the fleshy and edible fruit bodies of several species of macrofungi (fungi which bear fruiting structures that are large enough to be seen with the naked eye). They can appear either below ground (hypogeous) or above ground (epigeous) where they may be picked by hand. Edibility may be defined by criteria that include absence of poisonous effects on humans and desirable taste and aroma. Edible mushrooms are consumed for their nutritional and culinary value. Mushrooms, especially dried shiitake, are sources of umami flavor. Edible mushrooms include many fungal species that are either harvested wild or cultivated. Easily cultivated and common wild mushrooms are often available in markets, and those that are more difficult to obtain (such as the prized truffle, matsutake, and morel) may be collected on a smaller scale by private gatherers. Some preparations may render certain poisonous mushrooms fit for consumption. Before assuming that any wild mushroom is e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Agaricus Species
''Agaricus'' is a genus of mushrooms containing both edible and poisonous species, with over 400 members worldwide and possibly again as many disputed or newly-discovered species. The genus includes the common ("button") mushroom (''Agaricus bisporus'') and the field mushroom ('' A. campestris''), the dominant cultivated mushrooms of the West. Members of ''Agaricus'' are characterized by having a fleshy cap or pileus, from the underside of which grow a number of radiating plates or gills, on which are produced the naked spores. They are distinguished from other members of their family, Agaricaceae, by their chocolate-brown spores. Members of ''Agaricus'' also have a stem or stipe, which elevates it above the object on which the mushroom grows, or substrate, and a partial veil, which protects the developing gills and later forms a ring or annulus on the stalk. The genus contains the most widely consumed and best-known mushroom today, '' A. bisporus'', with '' A. arvensis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus Xanthodermus
''Agaricus xanthodermus'', commonly known as the yellow-staining mushroom or simply the yellow-stainer, is a mushroom of the genus ''Agaricus'', which displays a strong yellow colouration at the base of the stem when cut. It is poisonous for most people, causing gastrointestinal upset, but can be eaten by some without apparent negative effect. Taxonomy This species was first officially defined under the name ''Agaricus xanthodermus'' in 1876 by Léon Gaston Genevier, in a letter published in the bulletin of the French Botanical Society. Genevier described the ''Agaricus'' mushrooms commonly eaten (perhaps sometimes inadvisedly) in the region of Nantes, and attempted to clarify the distinctions between them. He proposed a detailed reclassification into 5 species, including this new one. Apparently up until that time, these yellow-staining mushrooms were considered to be just varieties of other species which are edible: '' A. arvensis'', A. edulis', and '' A. silvi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus Subrutilescens
''Agaricus subrutilescens'', also known as the wine-colored agaricus, is a mushroom of the genus ''Agaricus''. It was first described scientifically in 1925 as ''Psalliota subrutilescens'', and later transferred to ''Agaricus'' in 1938. Description ''Agaricus subrutilescens'' has a cap that is across, dry, and has many wine to brown colored fibrils, especially near the center. The gills are close and white at first, turning pinkish and then dark brown in age. The stalk has a skirt-like ring and is long, thick, white, and covered with soft woolly scales below the ring. The flesh is white and does not stain, and the odor and taste are mild. The purplish fibrous cap and shaggy white stem differentiate this mushroom from others which resemble it. Similar species include ''Agaricus hondensis'' and ''Agaricus moelleri''. This mushroom is regarded variously described as edible, inedible, or responsible for causing gastric upset. Habitat and distribution The mushroom fruits in un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus Semotus
''Agaricus semotus'' is a woodland mushroom of the fungus order '' Agaricales''. It, like many of its relatives, can be found spread throughout wooded, moist areas in the southern United States, and has been found in areas ranging from California to Florida; it is also indigenous to Great Britain and Europe. ''A. semotus'' has also been collected in New Zealand. Although various authors disagree about its edibility, its modest size prevents it from being a significant source of nutrition. Description The cap is 2–7 cm in diameter, initially convex while flattening with age; it typically has a low umbo–a raised, conical mound in the center of the cap. The surface color can range from a lighter cream to a darker tan, with brownish scales thinning out towards the margin of the cap. The gills are free from the stalk and packed closely together, showing a pink to salmon color in youth and aging to a darker brown. The stalk is 3–7 cm tall and 0.4–0. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus Osecanus
''Agaricus'' is a genus of mushrooms containing both edible and poisonous species, with over 400 members worldwide and possibly again as many disputed or newly-discovered species. The genus includes the common ("button") mushroom (''Agaricus bisporus'') and the field mushroom ('' A. campestris''), the dominant cultivated mushrooms of the West. Members of ''Agaricus'' are characterized by having a fleshy cap or pileus, from the underside of which grow a number of radiating plates or gills, on which are produced the naked spores. They are distinguished from other members of their family, Agaricaceae, by their chocolate-brown spores. Members of ''Agaricus'' also have a stem or stipe, which elevates it above the object on which the mushroom grows, or substrate, and a partial veil, which protects the developing gills and later forms a ring or annulus on the stalk. The genus contains the most widely consumed and best-known mushroom today, '' A. bisporus'', with '' A. arvensis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus Hondensis
''Agaricus hondensis'', commonly known as the felt-ringed agaricus, is a species of fungus in the family Agaricaceae. The species was officially described in 1912 by mycologist William Alphonso Murrill, along with three other ''Agaricus'' species that have since been placed in synonymy with ''A. hondensis''. Found in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, ''A. hondensis'' fruits in the fall under conifers or in mixed forests. The fungus produces fruit bodies (mushrooms) with white to gray-brown caps up to in diameter covered with pale pinkish-brown scales that darken in age. The tightly-packed gills on the cap underside are initially white before becoming pinkish, lilac-gray, and finally brownish as the spores mature. The stout stipe is bulbous and has a thick, white, felt-like ring. The mushroom is poisonous, and causes severe gastrointestinal upset if consumed. It has an unpleasant odor similar to phenol or creosote, and develops a soapy-metallic taste w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus Campestris
''Agaricus campestris'' is a widely eaten gilled mushroom closely related to the cultivated button mushroom ''Agaricus bisporus''. It is commonly known as the field mushroom or, in North America, meadow mushroom. Taxonomy This species was originally noted and named in 1753 by Carl Linnaeus as ''Agaricus campestris''. It was placed in the genus ''Psalliota'' by Lucien Quelet in 1872. Some variants have been isolated over the years, a few of which now have species status, for example, ''Agaricus bernardii'' Quel. (1878), ''Agaricus bisporus'' (J.E. Lange) Imbach (1946), '' Agaricus bitorquis'' (Quel.) Sacc. (1887), ''Agaricus cappellianus'' Hlavacek (1987), and ''Agaricus silvicola'' (Vittad.) Peck (1872). Some were so similar they did not warrant even varietal status, while others have retained it. ''Agaricus campestris'' var. ''equestris'' (F.H.Moller) Pilat (1951) is still valid. ''A. campestris'' var. ''isabellinus'' (F.H.Moller) Pilat (1951), and ''A. campestris'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus Albolutescens
''Agaricus albolutescens'' is a moderate-sized, stocky-statured mushroom with a pleasant odor; it bruises slowly but persistently yellow. This character distinguishes it from other ''Agaricus'' species, such as ''Agaricus xanthodermus'', a mildly toxic species which has a phenolic or medicinal odor, and bruises fleetingly yellow. Fieldmarks of ''Agaricus albolutescens'' include a tendency to discolor tawny-brown, rather than merely yellow, and chocolate-brown free gills. ''Agaricus silvicola'' is very similar but has a less dramatic bruising reaction, more yellowish than tawny, a normal rather than stocky stature, and slightly smaller spores. ''A. albolutescens'' and ''A. silvicola'' represent a single polymorphic species or a species complex. Description Pileus The cap is 6–12 cm broad, and convex; it becomes planoconvex to planodepressed. The margin is incurved, then decurved, overlapping the gills. Occasionally, it is wavy and appendiculate from veil fragments. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |