|
Aesop's Fable
Aesop's Fables, or the Aesopica, is a collection of fables credited to Aesop, a slave and storyteller believed to have lived in ancient Greece between 620 and 564 BCE. Of diverse origins, the stories associated with his name have descended to modern times through a number of sources and continue to be reinterpreted in different verbal registers and in popular as well as artistic media. The fables originally belonged to oral tradition and were not collected for some three centuries after Aesop's death. By that time, a variety of other stories, jokes and proverbs were being ascribed to him, although some of that material was from sources earlier than him or came from beyond the Greek cultural sphere. The process of inclusion has continued until the present, with some of the fables unrecorded before the Late Middle Ages and others arriving from outside Europe. The process is continuous and new stories are still being added to the Aesop corpus, even when they are demonstrably more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perugia - Fontana Maggiore - 7 - Esopo (gru E Lupo & Lupo E Agnello) - Foto G
Perugia (, , ; lat, Perusia) is the capital city of Umbria in central Italy, crossed by the River Tiber, and of the province of Perugia. The city is located about north of Rome and southeast of Florence. It covers a high hilltop and part of the valleys around the area. The region of Umbria is bordered by Tuscany, Lazio, and Marche. The history of Perugia goes back to the Etruscan period; Perugia was one of the main Etruscan cities. The city is also known as the universities town, with the University of Perugia founded in 1308 (about 34,000 students), the University for Foreigners (5,000 students), and some smaller colleges such as the Academy of Fine Arts "Pietro Vannucci" ( it, Accademia di Belle Arti "Pietro Vannucci") public athenaeum founded in 1573, the Perugia University Institute of Linguistic Mediation for translators and interpreters, the Music Conservatory of Perugia, founded in 1788, and other institutes. Perugia is also a well-known cultural and artistic cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Wasps
''The Wasps'' ( grc-x-classical, Σφῆκες, translit=Sphēkes) is the fourth in chronological order of the eleven surviving plays by Aristophanes. It was produced at the Lenaia festival in 422 BC, during Athens' short-lived respite from the Peloponnesian War. As in his other early plays, Aristophanes satirizes the Athenian general and demagogue Cleon. He also ridicules the law courts, one of the institutions that provided Cleon his power. The play has been thought to exemplify Old Comedy. Plot The play begins with a strange scene—a large net has been spread over a house, the entry is barricaded and two slaves, Xanthias and Sosias, are sleeping in the street outside. A third man is positioned at the top of an exterior wall with a view into the inner courtyard but he too is asleep. The two slaves wake and we learn from their banter that they are keeping guard over a "monster." The man asleep above them is their master and the monster is his father—he has an unusual disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Old Woman And The Doctor
The Old Woman and the Doctor (or Physician) is a story of Greek origin that was included among Aesop's Fables and later in the 4th century CE joke book, the ''Philogelos''. It is numbered 57 in the Perry Index. A rare fable This fable falls into the category of jokes that were added to the Aesop corpus through the attraction of his name. Because it was largely preserved in Greek sources, it was not noted in the rest of Europe until the Renaissance. One of its first appearances then was in an early Tudor period jest book, '' Merry Tales and Quick Answers'' (c.1530), under the title "Of the olde woman that had sore eyes". The joke involves a woman who asks a surgeon (in this case) to cure her from approaching blindness on the understanding that he would not be paid until she was cured. The surgeon applied salves but stole from the house anything moveable during the course of his visits. Once the cure was completed, the woman refused him payment on the grounds that now her sight was wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeus And The Tortoise
Zeus and the Tortoise appears among Aesop’s Fables and explains how the tortoise got her shell. It is numbered 106 in the Perry Index. From it derives the proverbial sentiment that ‘There’s no place like home’. Home is best The fable tells how the king of the gods invited all the animals to his wedding but the tortoise never arrived. When asked why, her excuse was that she preferred her own home, so Zeus made her carry her house about forever after. That excuse in Greek was Οἶκος φίλος, οἶκος ἄριστος, literally ‘the home you love is the best’. The fabulist then goes on to comment that ‘most people prefer to live simply at home than to live lavishly at someone else's’. The saying became proverbial and was noticed as connected with the fable by Erasmus in his ''Adagia''. The earliest English version of such a proverb, emerging in the 16th century, echoes the comment on the fable: “Home is home, though it’s never so homely”. The sentim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Ant And The Grasshopper
The Ant and the Grasshopper, alternatively titled The Grasshopper and the Ant (or Ants), is one of Aesop's Fables, numbered 373 in the Perry Index. The fable describes how a hungry grasshopper begs for food from an ant when winter comes and is refused. The situation sums up moral lessons about the virtues of hard work and planning for the future. Even in Classical times, however, the advice was mistrusted by some and an alternative story represented the ant's industry as mean and self-serving. Jean de la Fontaine's delicately ironic retelling in French later widened the debate to cover the themes of compassion and charity. Since the 18th century the grasshopper has been seen as the type of the artist and the question of the place of culture in society has also been included. Argument over the fable's ambivalent meaning has generally been conducted through adaptation or reinterpretation of the fable in literature, arts, and music. Fable and counter-fable The fable concerns a gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etiology
Etiology (pronounced ; alternatively: aetiology or ætiology) is the study of causation or origination. The word is derived from the Greek (''aitiología'') "giving a reason for" (, ''aitía'', "cause"); and ('' -logía''). More completely, etiology is the study of the causes, origins, or reasons behind the way that things are, or the way they function, or it can refer to the causes themselves. The word is commonly used in medicine (pertaining to causes of disease) and in philosophy, but also in physics, psychology, government, geography, spatial analysis, theology, and biology, in reference to the causes or origins of various phenomena. In the past, when many physical phenomena were not well understood or when histories were not recorded, myths often arose to provide etiologies. Thus, an etiological myth, or origin myth, is a myth that has arisen, been told over time or written to explain the origins of various social or natural phenomena. For example, Virgil's ''Aeneid'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco Rodríguez Adrados
Francisco Rodríguez Adrados (29 March 192221 July 2020) was a Spanish Hellenist, linguist and translator. He worked most of his career at the Complutense University of Madrid. He was a member of the Real Academia Española and Real Academia de la Historia. Life Rodríguez Adrados was born on 29 March 1922 in Salamanca. He studied classical philology at the University of Salamanca, where he obtained a degree in 1944. He later obtained a doctorate in classical philology from the Complutense University of Madrid. Rodríguez Adrados became a teacher of Greek at the Instituto Cardenal Cisneros in Madrid in 1949. Two years later, he became a professor at the University of Barcelona and the next year, he moved to the Complutense University of Madrid, where he worked until his retirement. He worked as a translator of Ancient Greek and Sanskrit texts. He was considered to be an expert on Ancient Greek. Rodríguez Adrados died on 21 July 2020 in Madrid, aged 98. Awards and honor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Young Man And The Swallow
The young man and the swallow (which also has the Victorian title of "The spendthrift and the swallow") is one of Aesop's Fables and is numbered 169 in the Perry Index. It is associated with the ancient proverb 'One swallow doesn't make a summer'. The fable The story appears only in Greek sources in ancient times and may have been invented to explain the proverb 'One swallow does not make a spring' (μία γὰρ χελιδὼν ἔαρ οὐ ποιεῖ), which is recorded in Aristotle's Nicomachean Ethics (I.1098a18). Other instances of where fables appear to derive from proverbs include The Mountain in Labour, recorded by Phaedrus, and Jumping from the frying pan into the fire by Laurentius Abstemius. The fable is about a young man who spends all his money on gambling and luxurious living until he has only a cloak to keep off the weather. Seeing an unusually early swallow fly by, the man concludes that spring has come and sells his cloak so as to use the proceeds to mend h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Town Mouse And The Country Mouse
"The Town Mouse and the Country Mouse" is one of Aesop's Fables. It is number 352 in the Perry Index and type 112 in Aarne–Thompson's folk tale index. Like several other elements in Aesop's fables, 'town mouse and country mouse' has become an English idiom. Story In the original tale, a proud town mouse visits his cousin in the country. The country mouse offers the city mouse a meal of simple country cuisine, at which the visitor scoffs and invites the country mouse back to the city for a taste of the "fine life" and the two cousins dine on white bread and other fine foods. But their rich feast is interrupted by a cat which forces the rodent cousins to abandon their meal and retreat back into their mouse hole for safety. Town mouse tells country mouse that the cat killed his mother and father and that he is frequently the target of attacks. After hearing this, the country mouse decides to return home, preferring security to opulence or, as the 13th-century preacher Odo of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Frogs And The Sun
The Frogs and the Sun is one of Aesop's Fables and is numbered 314 in the Perry Index. It has been given political applications since Classical times. The fable There are both Greek and Latin versions of the fable. Babrius tells it unadorned and leaves hearers to draw their own conclusion, but Phaedrus gives the story a context. While people are rejoicing at the wedding of a thief, Aesop tells a story of frogs who lament at the marriage of the sun. This would mean the birth of a second sun and the frogs suffer already from the drying up of the ponds and marshes in which they live. Though the story appears to have an ecological meaning, it was believed that the real target was Sejanus, the powerful aide of the Roman Emperor Tiberius, who had attempted to marry into the imperial family. Certainly the fable was used in a similar way to criticize overweening lords during the Middle Ages. Marie de France's ''Ysopet'' contains a version of the story which was to influence later writers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
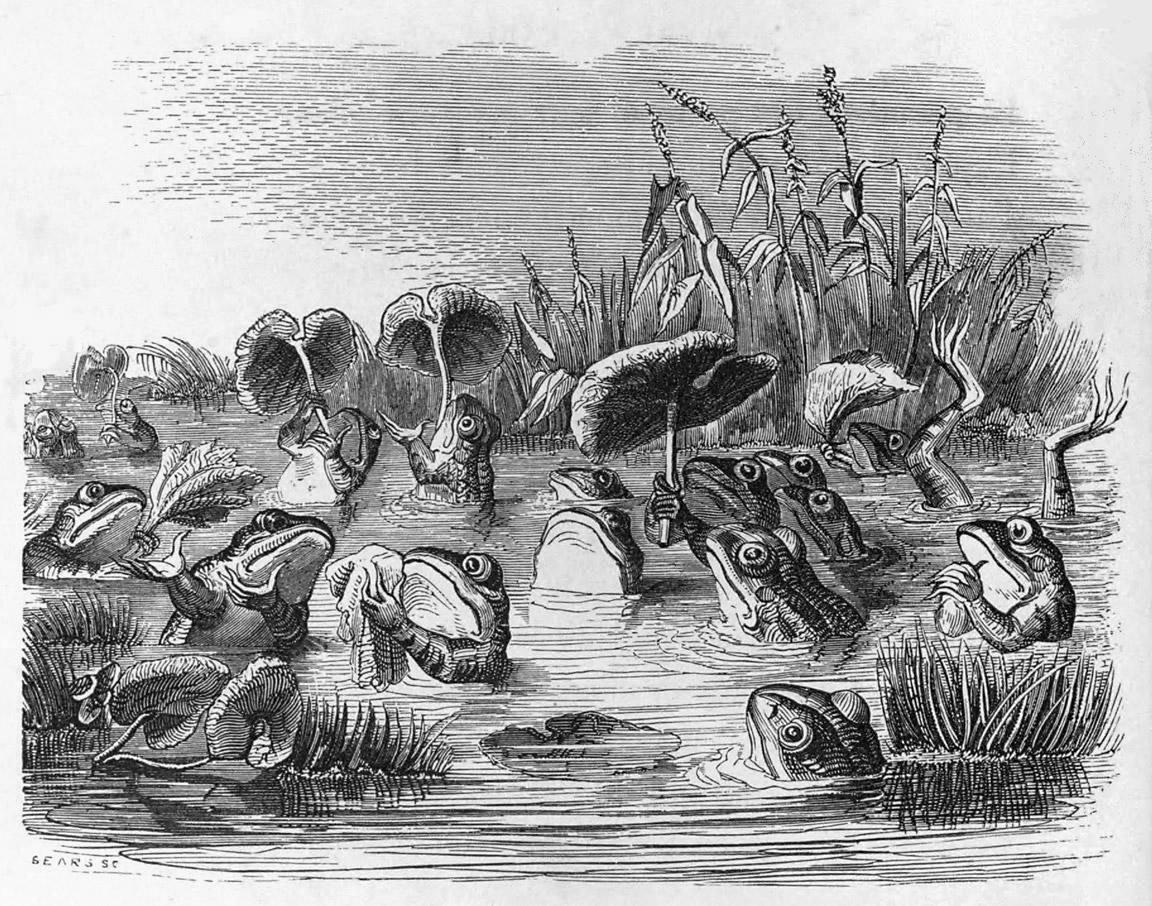
The Frogs Who Desired A King
The Frogs Who Desired a King is one of Aesop's Fables and numbered 44 in the Perry Index. Throughout its history, the story has been given a political application. The fable According to the earliest source, Phaedrus, the story concerns a group of frogs who called on the great god Zeus to send them a king. He threw down a log, which fell in their pond with a loud splash and terrified them. Eventually one of the frogs peeped above the water and, seeing that it was no longer moving, soon all hopped upon it and made fun of their king. Then the frogs made a second request for a real king and were sent down a water snake that started eating them. Once more the frogs appealed to Zeus, but this time he replied that they must face the consequences of their request. In later variations of the story, the water snake is often replaced with a stork or heron. Commentary, analysis and depiction The original context of the story, as related by Phaedrus, makes it clear that people feel t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_Foto_G._Dall'Orto_5_ago_2006.jpg)