|
Aeruginascin
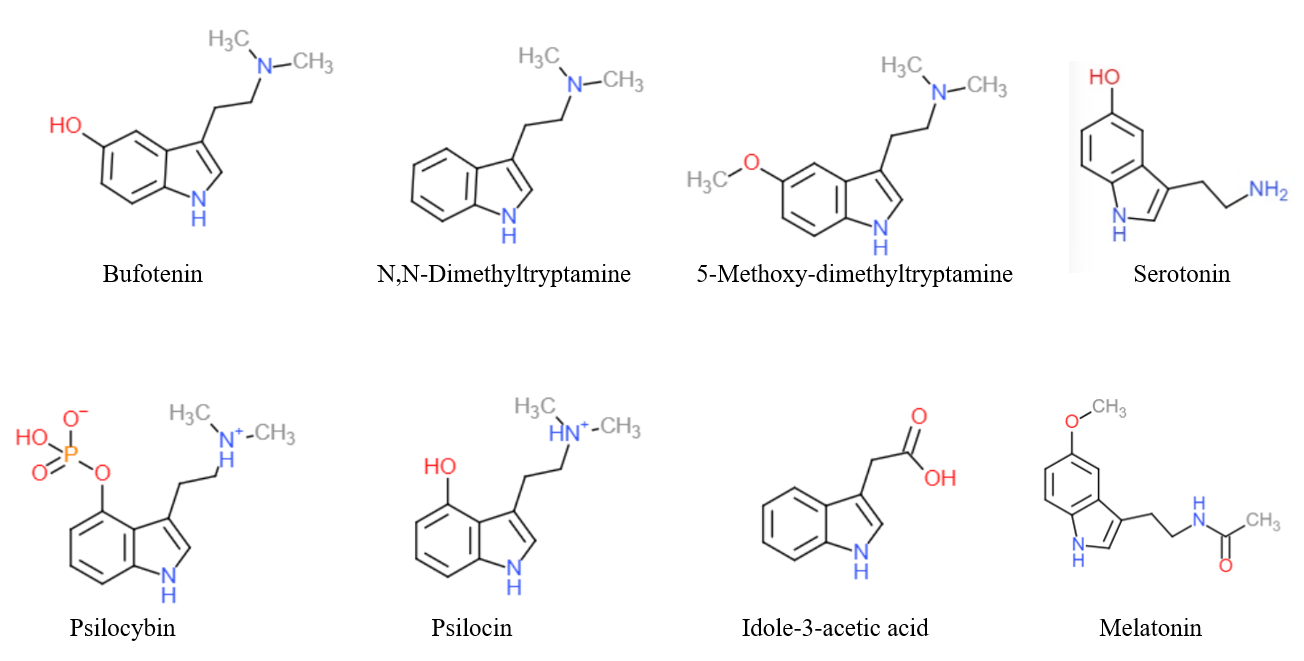
Aeruginascin or ''N,N,N''-trimethyl-4-phosphoryloxytryptamine is an indoleamine derivative which occurs naturally within the mushroom ''Inocybe aeruginascens'' and ''Pholiotina cyanopus''. Aeruginascin is the ''N''-trimethyl analogue of psilocybin. It is closely related to the frog skin toxin bufotenidine (5-HTQ), a potent 5-HT3 receptor agonist, but the aeruginascin metabolite 4-HO-TMT shows strong binding at the 5-HT2 receptors similar to psilocin Psilocin (also known as 4-HO-DMT, 4-hydroxy DMT, psilocine, psilocyn, or psilotsin) is a substituted tryptamine alkaloid and a serotonergic psychedelic substance. It is present in most psychedelic mushrooms together with its phosphorylated counte .... The first scientific literature about the pharmacological effects of aeruginascin is from a study published by Gartz in 1989. Across 23 analyzed cases of accidental hallucinogenic mushroom poisonings, people who had ingested the mushroom ''Inocybe aeruginascens'' reported only euphor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
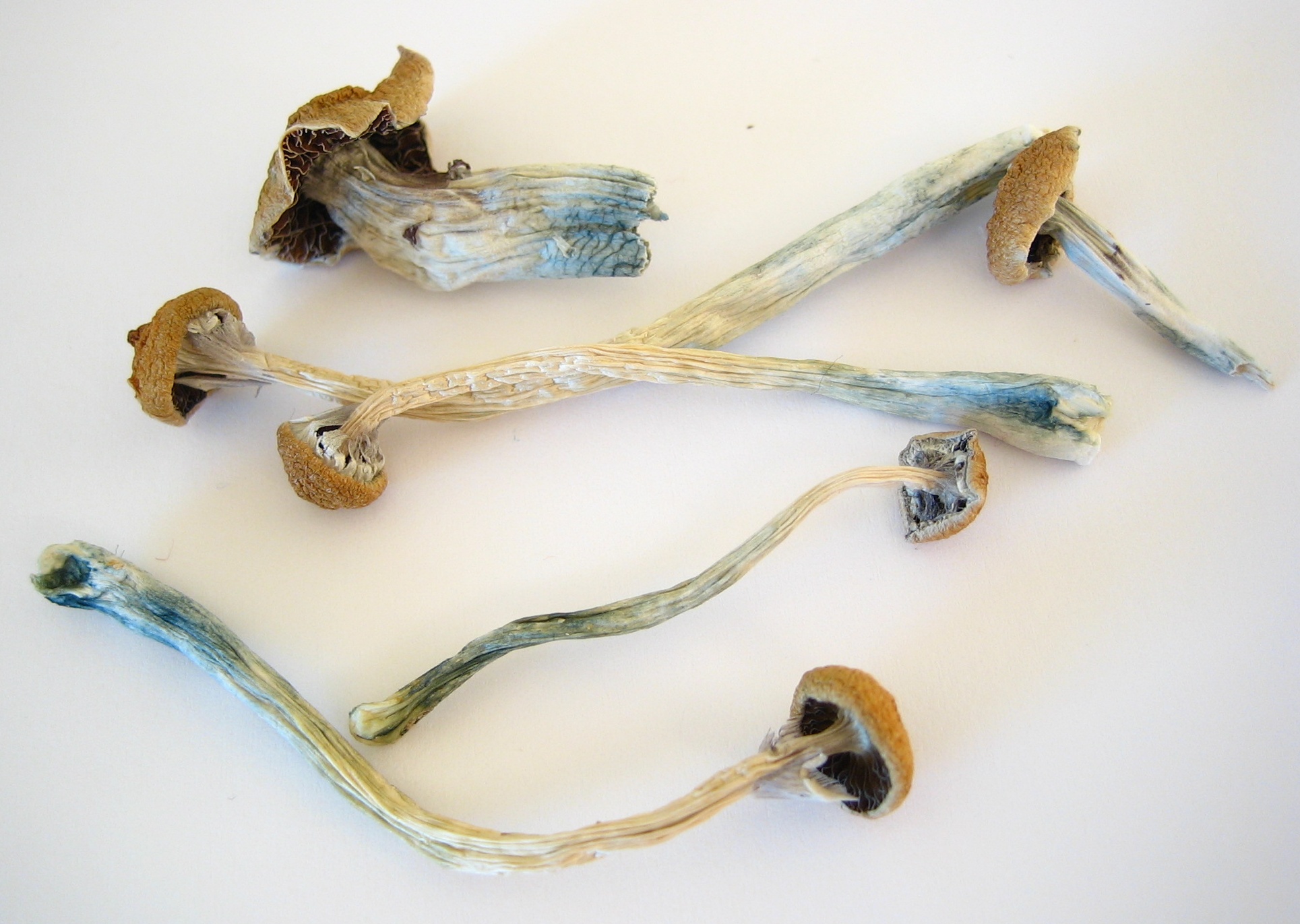
Inocybe Aeruginascens
''Inocybe aeruginascens'' is a member of the genus ''Inocybe'' which is widely distributed in Europe. The species was first documented by I. Ferencz in Ócsa, Hungary on June 15, 1965. Description ''Inocybe aeruginascens'' is a small mycorrhizal mushroom with a conic to convex cap which becomes plane in age and is often fibrillose near the margin. It is usually less than 5 cm across, has a slightly darker blunt umbo and an incurved margin when young. The cap color varies from buff to light yellow brown, usually with greenish stains which disappear when the mushroom dries. The gills are adnate to nearly free, numerous, colored pale brown, grayish brown, or tobacco brown. The fruit body has greenish tones and bruises blue where damaged. The spores are smooth and ellipsoid, measuring 6–9.5 x 4.5 micrometres and forming a clay brown spore print. The stem is 2–7 cm long, 3 to 8 mm thick, and is equal width for the whole length, sometimes with some swelling at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pholiotina Cyanopus
''Pholiotina cyanopus'' is a species of fungus that contains psychoactive compounds including psilocybin and the uncommon aeruginascin. Originally described as ''Galerula cyanopus'' by American mycologist George Francis Atkinson in 1918. It was transferred to ''Conocybe'' by Robert Kühner in 1935 before being transferred to ''Pholiotina'' by Rolf Singer in 1950. A 2013 molecular phylogenetics study found it to belong to a group of species currently assigned to ''Pholiotina'' that are more closely related to ''Galerella nigeriensis'' than to ''Pholiotina'' or ''Conocybe''. It is likely that it will be moved to a different genus in the future, but this has not happened yet. It is very similar to '' Pholiotina smithii'', a species known only from North America, from which it differs slightly in the color of its cap and gills and the width of its cheilocystidia. Some authors have speculated that the ''P. smithii'' could be a junior synonym of ''P. cyanopus'', but this has not been c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indoleamine
Indolamines are a family of neurotransmitters that share a common molecular structure (namely, indolamine). Indolamines are a classification of monoamine neurotransmitter, along with catecholamines and ethylamine derivatives. A common example of an indolamine is the tryptophan derivative serotonin, a neurotransmitter involved in mood and sleep. Another example of an indolamine is melatonin. In biochemistry, indolamines are substituted indole compounds that contain an amino group. Examples of indolamines include the lysergamides. Synthesis Indolamines are biologically synthesized from the essential amino acid tryptophan. Tryptophan is synthesized into serotonin through the addition of a hydroxyl group by the enzyme ''tryptophan hydroxylase'' and the subsequent removal of the carboxyl group by the enzyme ''5-HTP decarboxylase''.Carlson, Neil R. ''Physiology of Behavior''. 11th ed. Vol. 1. N.p.: Pearson Education, n.d. Print. See also *Indole *Tryptamine Tryptamine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bounded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For example, protonation of methanol gives an elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog (chemistry)
A structural analog (analogue in modern traditional English; Commonwealth English), also known as a chemical analog or simply an analog, is a compound having a structure similar to that of another compound, but differing from it in respect to a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced with other atoms, groups, or substructures. A structural analog can be imagined to be formed, at least theoretically, from the other compound. Structural analogs are often isoelectronic. Despite a high chemical similarity, structural analogs are not necessarily functional analogs and can have very different physical, chemical, biochemical, or pharmacological properties. In drug discovery, either a large series of structural analogs of an initial lead compound are created and tested as part of a structure–activity relationship study or a database is screened for structural analogs of a lead compound. Chemical analogues of il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocybin
Psilocybin ( , ) is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug compound produced by more than 200 species of fungi. The most potent are members of the genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P. cyanescens'', but psilocybin has also been isolated from about a dozen other genera. Psilocybin is itself biologically inactive but is quickly converted by the body to psilocin, which has mind-altering effects similar, in some aspects, to those of LSD, mescaline, and DMT. In general, the effects include euphoria, visual and mental hallucinations, changes in perception, a distorted sense of time, and perceived spiritual experiences. It can also cause adverse reactions such as nausea and panic attacks. Imagery found on prehistoric murals and rock paintings of modern-day Spain and Algeria suggests that human usage of psilocybin mushrooms predates recorded history. In Mesoamerica, the mushrooms had long been consumed in spiritual and div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bufotenidine
Bufotenidine, also known as 5-hydroxy-''N'',''N'',''N''-trimethyltryptammonium (5-HTQ), is a toxin related to bufotenin, serotonin, and other tryptamines which is found in the venom of a variety of toads. It acts as a selective 5-HT3 receptor agonist, and has been used in scientific research The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientific m ... to study the function of the 5-HT3 receptor, though this use has been limited by the fact that, as a quaternary amine, it is unable to readily cross the blood-brain-barrier. See also * 2-Methyl-5-HT * Chlorophenylbiguanide References 5-HT3 agonists Emetics Tryptamines Vertebrate toxins Drugs with no legal status {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
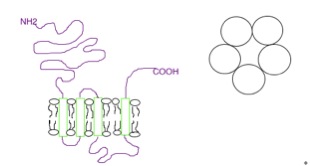
5-HT3 Receptor
The 5-HT3 receptor belongs to the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) and therefore differs structurally and functionally from all other 5-HT receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine, or serotonin receptors) which are G protein-coupled receptors. This ion channel is cation-selective and mediates neuronal depolarization and excitation within the central and peripheral nervous systems. As with other ligand gated ion channels, the 5-HT3 receptor consists of five subunits arranged around a central ion conducting pore, which is permeable to sodium (Na), potassium (K), and calcium (Ca) ions. Binding of the neurotransmitter 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) to the 5-HT3 receptor opens the channel, which, in turn, leads to an excitatory response in neurons. The rapidly activating, desensitizing, inward current is predominantly carried by sodium and potassium ions. 5-HT3 receptors have a negligible permeability to anions. They are most closely related by homology to the nicotinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT Receptor
5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand. The serotonin receptors modulate the release of many neurotransmitters, including glutamate, GABA, dopamine, epinephrine / norepinephrine, and acetylcholine, as well as many hormones, including oxytocin, prolactin, vasopressin, cortisol, corticotropin, and substance P, among others. Serotonin receptors influence various biological and neurological processes such as aggression, anxiety, appetite, cognition, learning, memory, mood, nausea, sleep, and thermoregulation. They are the target of a variety of pharmaceutical and recreational drugs, including many antidepressants, antipsychotics, anorectics, antiemetics, gast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocin
Psilocin (also known as 4-HO-DMT, 4-hydroxy DMT, psilocine, psilocyn, or psilotsin) is a substituted tryptamine alkaloid and a serotonergic psychedelic substance. It is present in most psychedelic mushrooms together with its phosphorylated counterpart psilocybin. Psilocin is a Schedule I drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. Acting on the 5-HT2A receptors, psilocin modulates the production and reuptake of serotonin. The mind-altering effects of psilocin are highly variable and subjective and resemble those of LSD and DMT. Chemistry Psilocin and its phosphorylated cousin, psilocybin, were first isolated and named in 1958 by Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann. Hofmann obtained the chemicals from laboratory-grown specimens of the entheogenic mushroom ''Psilocybe mexicana''. Hofmann also succeeded in finding synthetic routes to these chemicals. Psilocin can be obtained by dephosphorylation of natural psilocybin under strongly acidic or under alkaline conditions (hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptamine Alkaloids
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychedelic Tryptamines
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary states of consciousness (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips").Pollan, Michael (2018). ''How to Change Your Mind: What the New Science of Psychedelics Teaches Us About Consciousness, Dying, Addiction, Depression, and Transcendence'' Sometimes, they are called classic hallucinogens, serotonergic hallucinogens, or serotonergic psychedelics, and the term ''psychedelics'' is used more broadly to include all hallucinogens; this article uses the narrower definition of ''psychedelics''. Psychedelics cause specific psychological, visual, and auditory changes, and often a substantially altered state of consciousness.Leary, Timothy; Metzner, Ralph (1964). ''The Psychedelic Experience: A Manual Based on The Tibetan Book of the Dead'' Psychedelic states are often compared to meditative, psychodynamic or transcendental types of alterations of mind. The "classical" psychedelics, the psyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |