|
Aerobic Fermentation
Aerobic fermentation or aerobic glycolysis is a metabolic process by which cells metabolize sugars via fermentation in the presence of oxygen and occurs through the repression of normal respiratory metabolism. Preference of aerobic fermentation over aerobic respiration is referred to as the Crabtree effect in yeast, and is part of the Warburg effect in tumor cells. While aerobic fermentation does not produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in high yield, it allows proliferating cells to convert nutrients such as glucose and glutamine more efficiently into biomass by avoiding unnecessary catabolic oxidation of such nutrients into carbon dioxide, preserving carbon-carbon bonds and promoting anabolism. Aerobic fermentation in yeast Aerobic fermentation evolved independently in at least three yeast lineages (''Saccharomyces'', '' Dekkera'', '' Schizosaccharomyces''). It has also been observed in plant pollen, trypanosomatids, mutated ''E. coli'', and tumor cells. Crabtree-positive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobic Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing biological fuels using an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which stores chemical energy in a biologically accessible form. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to transfer chemical energy from nutrients to ATP, with the flow of electrons to an electron acceptor, and then release waste products. If the electron acceptor is oxygen, the process is more specifically known as aerobic cellular respiration. If the electron acceptor is a molecule other than oxygen, this is anaerobic cellular respiration. Fermentation, which is also an anaerobic process, is not respiration, as no external electron acceptor is involved. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, producing large amounts of energy (ATP). Respiration i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Selection
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together. Domesticated animals are known as breeds, normally bred by a professional breeder, while domesticated plants are known as varieties, cultigens, cultivars, or breeds. Two purebred animals of different breeds produce a crossbreed, and crossbred plants are called hybrids. Flowers, vegetables and fruit-trees may be bred by amateurs and commercial or non-commercial professionals: major crops are usually the provenance of the professionals. In animal breeding artificial selection is often combined with techniques such as inbreeding, linebreeding, and outcrossing. In plant breeding, similar methods are used. Charles Darwin discussed how selective breeding had be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wine Grapes With Dusting That Contains Yeast
Wine is an alcoholic drink made from fermented fruit. Yeast consumes the sugar in the fruit and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Wine is most often made from grapes, and the term "wine" generally refers to grape wine when used without any qualification. Even so, wine can be made from a variety of fruit crops, including plum, cherry, pomegranate, blueberry, currant, and elderberry. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are major factors in different styles of wine. These differences result from the complex interactions between the biochemical development of the grape, the reactions involved in fermentation, the grape's growing environment (terroir), and the wine production process. Many countries enact legal appellations intended to define styles and qualities of wine. These typically restrict the geographical origin and permitted varieties of grapes, as well as other aspects of wine production. Wine has been produced f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. The conversion requires the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate. Pyruvate dehydrogenase is usually encountered as a component, referred to as E1, of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC). PDC consists of other enzymes, referred to as E2 and E3. Collectively E1-E3 transform pyruvate, NAD+, coenzyme A into acetyl-CoA, CO2, and NADH. The conversion is crucial because acetyl-CoA may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration. To distinguish between this enzyme and the PDC, it is systematically called pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring). Mechanism The thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) converts to an ylide by deprotonation. The ylide attack the ketone group of pyruvate. The resulting adduct decarboxylates. The resulting 1,3-dipole reductively acetylates lipoamide-E2. In terms of details, biochem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvate Decarboxylase
Pyruvate decarboxylase is an enzyme () that catalyses the decarboxylation of pyruvic acid to acetaldehyde. It is also called 2-oxo-acid carboxylase, alpha-ketoacid carboxylase, and pyruvic decarboxylase. In anaerobic conditions, this enzyme participates in the fermentation process that occurs in yeast, especially of the genus ''Saccharomyces'', to produce ethanol by fermentation. It is also present in some species of fish (including goldfish and carp) where it permits the fish to perform ethanol fermentation (along with lactic acid fermentation) when oxygen is scarce. Pyruvate decarboxylase starts this process by converting pyruvate into acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide. Pyruvate decarboxylase depends on cofactors thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) and magnesium. This enzyme should not be mistaken for the unrelated enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase, an oxidoreductase (), that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA. Structure Pyruvate decarboxylase occurs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and NADH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes. The wide occurrence of glycolysis in other species indicates that it is an ancient metabolic pathway. Indeed, the reactions that make up glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, can occur in the Great Oxygenation Event, oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes, catalyzed by metal ions, meaning this is a plausible prebiotic pathway for abiogenesis. The most common type of glycolysis is the ''Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP) pathway'', which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol Fermentation English
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the pseudoelement symbol for ethyl. Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. As a psychoactive depressant, it is the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, and the second most consumed drug globally behind caffeine. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. Historically it was used as a general anesthetic, and has modern medical applications as an antiseptic, disinfectant, solvent for some medications, and antidote for methanol poisoning and ethylene glycol poisoning. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the synthesis of organic compounds, and as a fuel source for lamps, stoves, and internal combust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
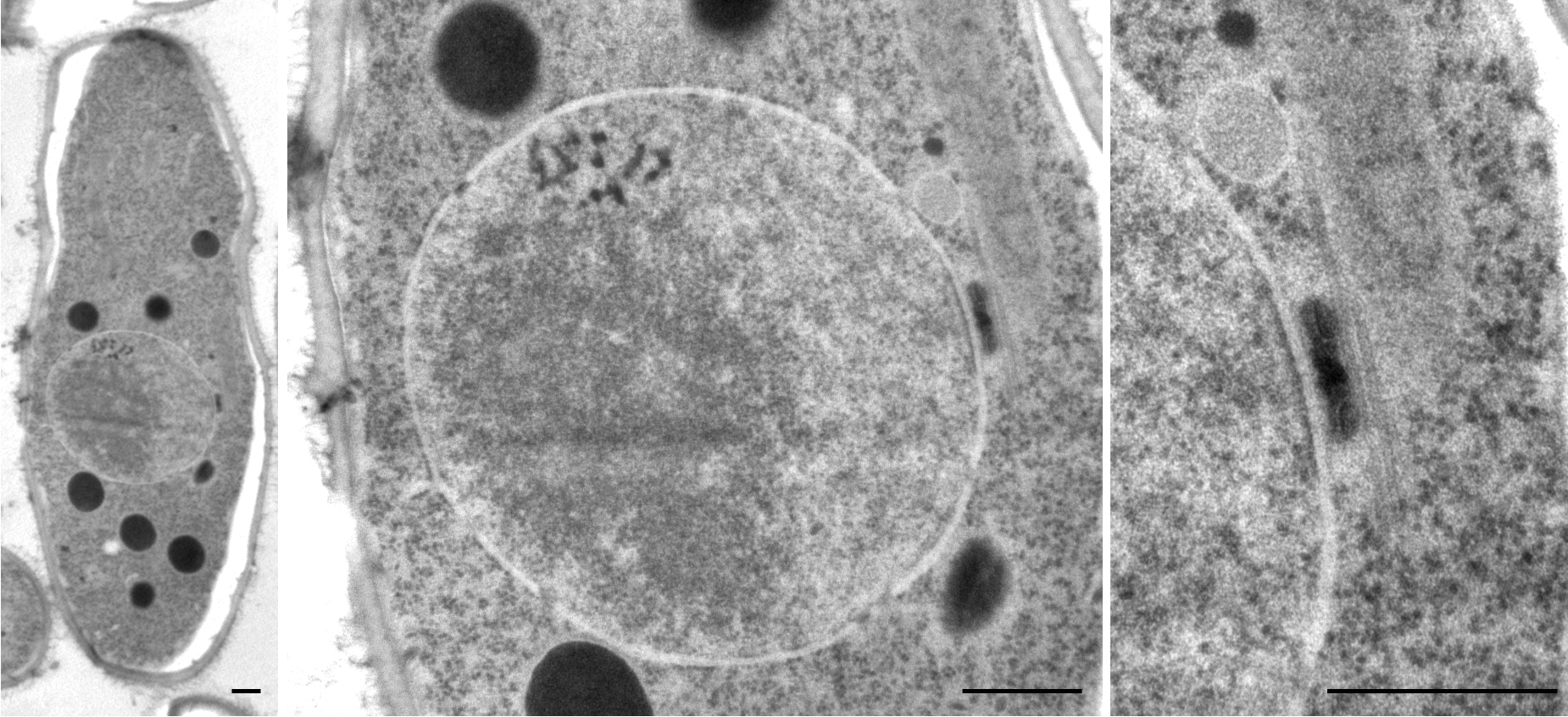
Schizosaccharomyces Pombe
''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically measure 3 to 4 micrometres in diameter and 7 to 14 micrometres in length. Its genome, which is approximately 14.1 million base pairs, is estimated to contain 4,970 protein-coding genes and at least 450 non-coding RNAs. These cells maintain their shape by growing exclusively through the cell tips and divide by medial fission to produce two daughter cells of equal size, which makes them a powerful tool in cell cycle research. Fission yeast was isolated in 1893 by Paul Lindner from East African millet beer. The species name ''pombe'' is the Swahili word for beer. It was first developed as an experimental model in the 1950s: by Urs Leupold for studying genetics, and by Murdoch Mitchison for studying the cell cycle. Paul Nurse, a fission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose Transporter
Glucose transporters are a wide group of membrane proteins that facilitate the transport of glucose across the plasma membrane, a process known as facilitated diffusion. Because glucose is a vital source of energy for all life, these transporters are present in all phyla. The GLUT or SLC2A family are a protein family that is found in most mammalian cells. 14 GLUTS are encoded by the human genome. GLUT is a type of uniporter transporter protein. Synthesis of free glucose Most non-autotrophic cells are unable to produce free glucose because they lack expression of glucose-6-phosphatase and, thus, are involved only in glucose uptake and catabolism. Usually produced only in hepatocytes, in fasting conditions, other tissues such as the intestines, muscles, brain, and kidneys are able to produce glucose following activation of gluconeogenesis. Glucose transport in yeast In ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' glucose transport takes place through facilitated diffusion. The transport p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
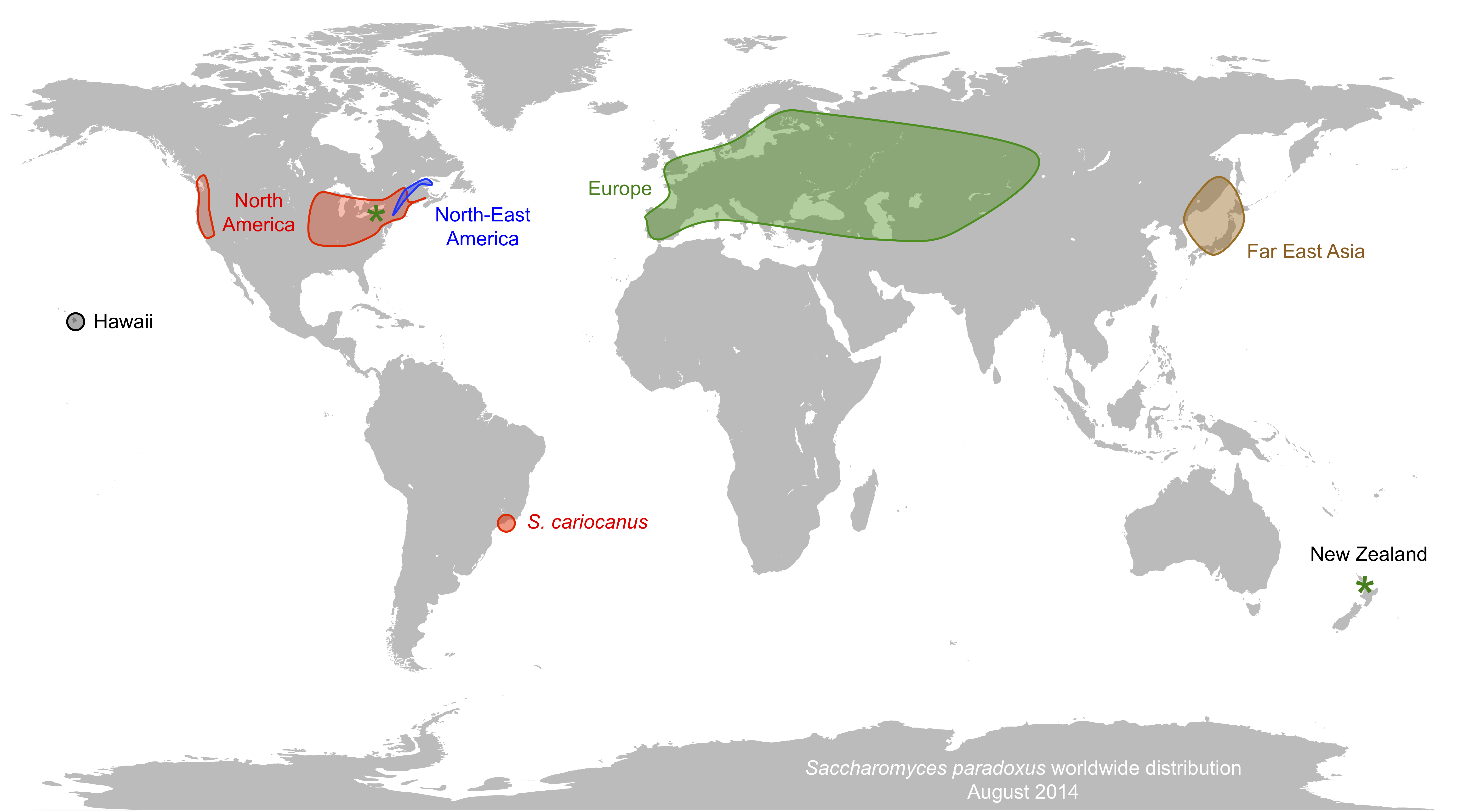
Saccharomyces Paradoxus
''Saccharomyces paradoxus'' is a wild yeast and the closest known species to the baker's yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. It is used in population genomics and phylogenetic studies to compare its wild characteristics to laboratory yeasts. Ecology ''Saccharomyces paradoxus'' is mostly isolated from deciduous trees (oak, maple, birch), and in some rare occasions on insects and fruits. It is often found in sympatry with other ''Saccharomyces'' species. Like ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', it has a worldwide distribution and it is mesophilic, which limits its natural distribution to low latitudes. However, ''Saccharomyces paradoxus'' typically grows at lower temperatures than ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', resulting in a slight shift in its distribution toward cooler regions, like British islands and Eastern Canada. Biogeography Unlike most other ''Saccharomyces'' species, there is no evidence that ''Saccharomyces paradoxus'' has been domesticated by humans. Accordingly, its bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol Dehydrogenase
Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH) () are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to NADH. In humans and many other animals, they serve to break down alcohols that are otherwise toxic, and they also participate in the generation of useful aldehyde, ketone, or alcohol groups during the biosynthesis of various metabolites. In yeast, plants, and many bacteria, some alcohol dehydrogenases catalyze the opposite reaction as part of fermentation to ensure a constant supply of NAD+. Evolution Genetic evidence from comparisons of multiple organisms showed that a glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase, identical to a class III alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH-3/ADH5), is presumed to be the ancestral enzyme for the entire ADH family. Early on in evolution, an effective method for eliminating both endogenous and exogenous fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whole Genome Duplication
Paleopolyploidy is the result of genome duplications which occurred at least several million years ago (MYA). Such an event could either double the genome of a single species ( autopolyploidy) or combine those of two species ( allopolyploidy). Because of functional redundancy, genes are rapidly silenced or lost from the duplicated genomes. Most paleopolyploids, through evolutionary time, have lost their polyploid status through a process called diploidization, and are currently considered diploids, e.g., baker's yeast, ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', and perhaps humans. Paleopolyploidy is extensively studied in plant lineages. It has been found that almost all flowering plants have undergone at least one round of genome duplication at some point during their evolutionary history. Ancient genome duplications are also found in the early ancestor of vertebrates (which includes the human lineage) near the origin of the bony fishes, and another in the stem lineage of teleost fishes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |