|
Aelurillus Dubatolovi
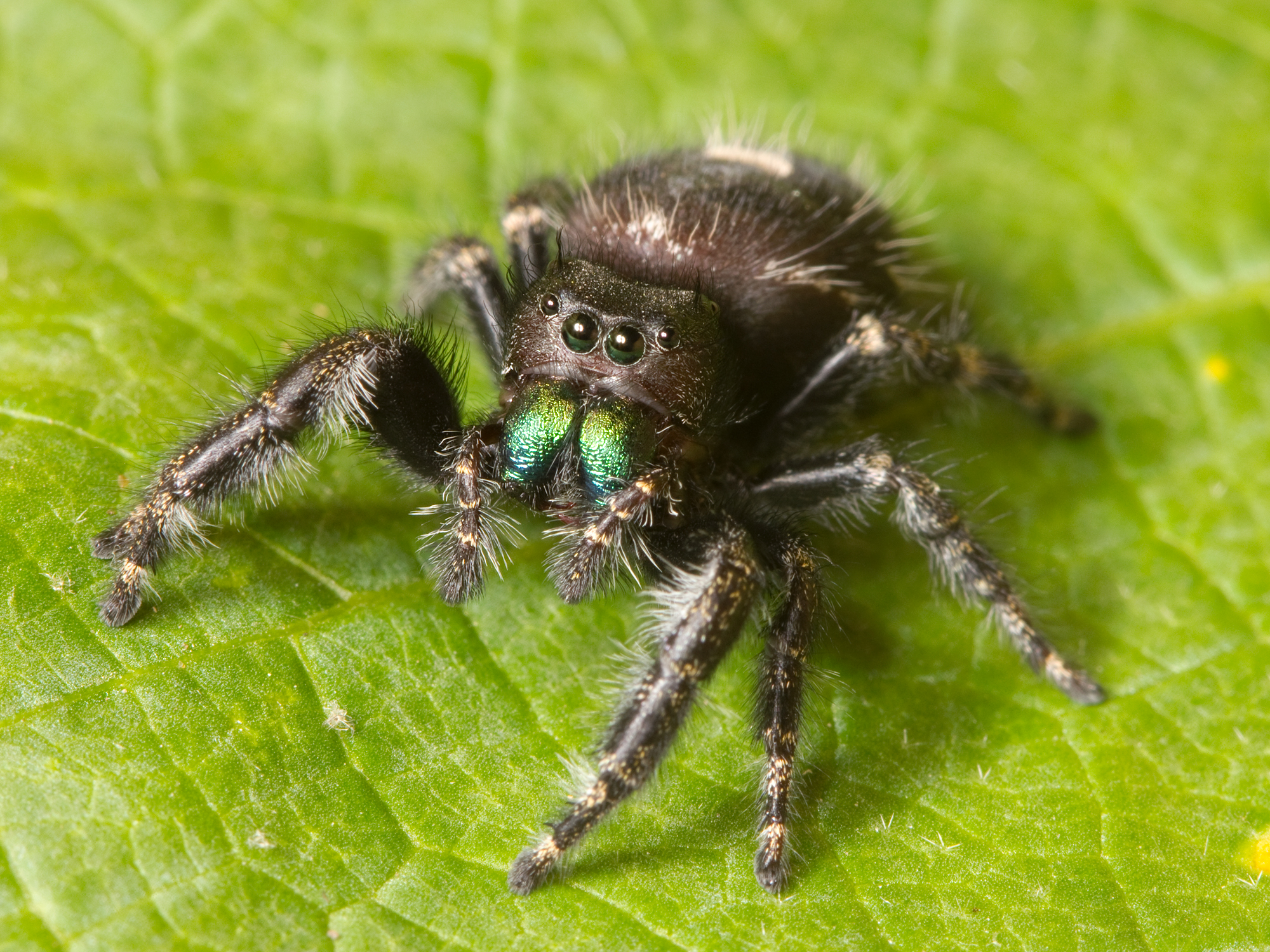
''Aelurillus dubatolovi'' is a species of jumping spider in the genus ''Aelurillus'' that lives in Central Asia. First identified in 2003 in Turkmenistan, it has a distribution that extends from Caspian Sea to Lake Balkhash and includes Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. The spider itself is small, the male being smaller than the female, with a carapace measuring between in length and an abdomen between long. The carapace is dark brown, with long hairs along the side that distinguish the species from the similar ''Aelurillus brutus'' and '' Aelurillus lutosus''. It also has a hairy clypeus and palpal femora, which enables it to be identified as not being the otherwise similar ''Aelurillus ater''. The female has a net-like pattern on the abdomen. This is clearer on examples found towards the northeast of the species distribution. The spiders found towards the northeast are also smaller, lighter and less hairy, but these are insufficient differences to ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessarily "typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigyne
The epigyne or epigynum is the external genital structure of female spiders. As the epigyne varies greatly in form in different species, even in closely related ones, it often provides the most distinctive characteristic for recognizing species. It consists of a small, hardened portion of the exoskeleton located on the underside of the abdomen, in front of the epigastric furrow and between the epigastric plates. Functions The primary function of the epigyne is to receive and direct the palpal organ of the male during copulation. The various specific forms of epigynes are correlated, in each case, with corresponding specific differences in the palpus of the male. This specialization prevents individuals of different species from mating. The epigyne covers or accompanies the openings of the spermathecae, which are pouches for receiving and retaining sperm. Frequently, the openings of the spermathecae are on the outer face of the epigyne and can be easily seen. A secondary functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles: the coxa, the trochanter, the femur, the short patella, the tibia, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spiders, or chelate weapons ( pincers) of great size, as in scorpions. The pedipalps of Solifugae are covered in setae, but have not been studied in detail. Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Distribution
Species distribution —or species dispersion — is the manner in which a biological taxon is spatially arranged. The geographic limits of a particular taxon's distribution is its range, often represented as shaded areas on a map. Patterns of distribution change depending on the scale at which they are viewed, from the arrangement of individuals within a small family unit, to patterns within a population, or the distribution of the entire species as a whole (range). Species distribution is not to be confused with dispersal, which is the movement of individuals away from their region of origin or from a population center of high density. Range In biology, the range of a species is the geographical area within which that species can be found. Within that range, distribution is the general structure of the species population, while dispersion is the variation in its population density. Range is often described with the following qualities: * Sometimes a distinction is made betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
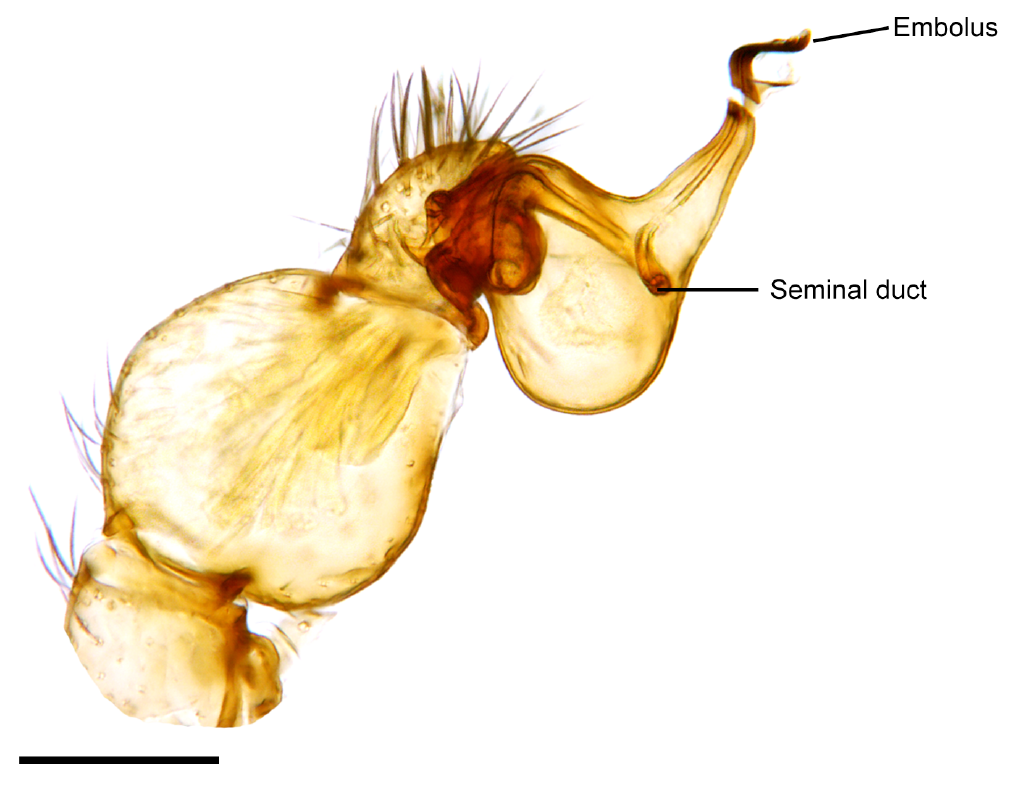
Palpal Bulb
The two palpal bulbs – also known as palpal organs and genital bulbs – are the copulatory organs of a male spider. They are borne on the last segment of the pedipalps (the front "limbs" of a spider), giving the spider an appearance often described as like wearing boxing gloves. The palpal bulb does not actually produce sperm, being used only to transfer it to the female. Palpal bulbs are only fully developed in adult male spiders and are not completely visible until after the final moult. In the majority of species of spider, the bulbs have complex shapes and are important in identification. Structure The palpal bulb of a mature male spider is borne on the last segment of the pedipalp. This segment usually has touch-sensitive hairs (setae) with nerves leading to them. The bulb itself is entirely without nerves, and hence without sensory organs and muscles, since these depend on nerves for their functioning, although some spiders have one or two muscles external to the bulb and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Leg
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plural ''coxae''), ''trochanter'', ''femur'' (plural ''femora''), ''tibia'' (plural ''tibiae''), ''tarsus'' (plural ''tarsi''), ''ischium'' (plural ''ischia''), ''metatarsus'', ''carpus'', ''dactylus'' (meaning finger), ''patella'' (plural ''patellae''). Homologies of leg segments between groups are difficult to prove and are the source of much argument. Some authors posit up to eleven segments per leg for the most recent common ancestor of extant arthropods but modern arthropods have eight or fewer. It has been argued that the ancestral leg need not have been so complex, and that other events, such as successive loss of function of a ''Hox''-gene, could result in parallel gains of leg segments. In arthropods, each of the leg segments ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicerae
The chelicerae () are the mouthparts of the subphylum Chelicerata, an arthropod group that includes arachnids, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. Commonly referred to as "jaws", chelicerae may be shaped as either articulated fangs, or similarly to pincers. Some chelicerae, such as those found on nearly all spiders, are hollow and contain (or are connected to) venom glands, and are used to inject venom into prey or a perceived threat. In ''Pisaurina mira'', also known as the nursery web spider, the chelicerae are utilized to snatch the prey once it becomes within reach, facilitating the "sit-and-wait ambush predator" behavior. Both pseudoscorpions and harvestmen have structures on their chelicerae that are used for grooming (papillae in pseudoscorpions, cheliceral teeth in Opiliones). Types Chelicerae can be divided into three kinds: jackknife chelicerae, scissor chelicerae, and 3-segmented chelate chelicerae. Jackknife chelicerae The jackknife chelicera is subchelate (with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinneret
A spinneret is a silk-spinning organ of a spider or the larva of an insect. Some adult insects also have spinnerets, such as those borne on the forelegs of Embioptera. Spinnerets are usually on the underside of a spider's opisthosoma, and are typically segmented. While most spiders have six spinnerets, some have two, four, or eight. They can move both independently and in concert. Most spinnerets are not simple structures with a single orifice producing a single thread, but complex structures of many microscopic spigots, each producing one filament. This produces the necessary orientation of the protein molecules, without which the silk would be weak and useless. Spigots can be singular or found in groups, which also permits spiders to combine multiple filaments in different ways to produce many kinds of silk for various purposes. Spinneret morphology can help arachnologists identify the taxon of a specimen and the specific morphology of a spigot can determine its use as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spider Vision
The eyes of spiders vary significantly in their structure, arrangement, and function. They usually have eight, each being a simple eye with a single lens (optics), lens rather than multiple units as in the compound eyes of insects. The specific arrangement and structure of the eyes is one of the features used in the identification and classification of different species, genera, and families. Most Haplogynae, haplogynes have six eyes, although some have eight (Plectreuridae), four (e.g., ''Tetrablemma'') or even two (most Caponiidae). In some cave species, there are no eyes at all (e.g. Stalita taenaria). Sometimes one pair of eyes is better developed than the rest. Several families of hunting spiders, such as jumping spiders and wolf spiders, have fair to excellent vision. The main pair of eyes in jumping spiders even sees in colour. Structure and anatomy Spiders' eyes are Simple eye in invertebrates, simple eyes, or ''ocelli'' (singular ''ocellus''), meaning their eyes have a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade (biology)
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayne Maddison
Wayne Paul Maddison , is a professor and Canada Research Chair at the departments of zoology and botany at the University of British Columbia, and the Director of the Spencer Entomological Collection at the Beaty Biodiversity Museum. His research concerns the phylogeny, biodiversity, and evolution of jumping spiders (Salticidae), of which he has discovered new species and genera. He has also done research in phylogenetic theory, developing and perfecting various methods used in comparative biology, such as character state inference in internal nodes through Maximum parsimony (phylogenetics), maximum parsimony, squared-change parsimony, or character correlation through the concentrated changes test or pairwise comparisons. In collaboration with David R. Maddison, he worked on thMesquiteopen-source phylogeny software, thMacCladeprogram, and the Tree of Life Web Project. His research has led him to discover new species of jumping spiders in Sarawak and Papua New Guinea. Selected pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |