|
Aelurillus Brutus
''Aelurillus brutus'' is a species of jumping spider in the genus ''Aelurillus'' that lives in Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan. The female was first described by Wanda Wesołowska in 1996 and the male by Galina Azarkina in 2003. The spider is small with a carapace that is between long and an abdomen between in length. The female is larger than the male. The spider is generally dark brown and hairy, but the male abdomen has a pattern of grey-yellow wavy lines. The difference between this species and others in the genus are subtle. The females are particularly difficult to distinguish. However, there are three distinctive stripes on the eye field and a pattern on the bottom of the abdomen. Taxonomy ''Aelurillus brutus'' is a jumping spider species first described by Wanda Wesołowska in 1996. It was one of over 500 species identified by the Polish arachnologist during her career. She placed it in the genus ''Aelurillus'' that was first circumscribed by Eugène Simon in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aelurillus V-insignitus
''Aelurillus v-insignitus'' is a species of jumping spiders. Appearance The male has v-shaped rows of hairs on its head and a pronounced white median stripe on its abdomen. The female is mottled brown. The spider can reach a length of . Name ''Insignitus'' is Latin for "signed", because of the white chevron on the back of the male spider, which is in the form of the letter "V". This letter was originally spelled one v above another V, which could also be interpreted as a double V or W, but usually is interpreted as "V". Distribution ''A. v-insignitus'' occurs in the Palaearctic. It is the only ''Aelurillus'' species that occurs in northwestern Europe. References External links *Photography of male and female Salticidae Spiders of Europe Spiders described in 1757 Palearctic spiders Taxa named by Carl Alexander Clerck {{Salticidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clypeus (arthropod Anatomy)
The clypeus is one of the sclerites that make up the face of an arthropod. In insects, the clypeus delimits the lower margin of the face, with the labrum articulated along the ventral margin of the clypeus. The mandibles bracket the labrum, but do not touch the clypeus. The dorsal margin of the clypeus is below the antennal sockets. The clypeus is often well-defined by sulci ("grooves") along its lateral and dorsal margins, and is most commonly rectangular or trapezoidal in overall shape. The post-clypeus is a large nose-like structure that lies between the eyes and makes up much of the front of the head in cicadas. In spiders, the clypeus is generally the area between the anterior edge of the carapace A carapace is a Dorsum (biology), dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tor ... and the anterior eyes. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessarily "typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ustyurt Plateau
The Ustyurt or Ust-Yurt (from kk, Үстірт; uz, Ustyurt; tk, Üstyurt; — flat hill, plateau) is a transboundary clay desert shared by Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan. The plateau's semi-nomadic population raises sheep, goats, and camels. Geography The Ustyurt is located between the Dead Kultuk, Mangyshlak Peninsula and Kara-Bogaz-Gol of the Caspian Sea to the west, and the Aral Sea, Amudarya Delta and Sarygamysh Lake to the east. It extends roughly , with an average altitude of . Its highest point rises to in the south-west. At its northeastern edge it drops steeply to the Aral Sea and the surrounding plain. Protected areas Kazakhstan created the Ustyurt Nature Reserve (223,300 hectares) in July, 1984 in the south of Mangystausky district in Eralievsky region. It preserves rare fauna and flora such as the Ustyurt Mountain sheep and the Saiga antelope. Among its features are Sherkala Mountain and the concretions found in the Torysh ('Valley of Balls') near t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaplaňgyr Nature Reserve
Gaplaňgyr or Kaplankyr is a mountain plateau and nature reserve (''zapovednik'') of northern Turkmenistan. It was established in 1979. It is a place for the protection and restoration of indigenous flora and fauna, it is located on the Gaplaňgyr Plateau at the southern spur of the Ustyurt Plateau at the border with Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan in the north-west of Daşoguz Province. It covers an area of 2822 km². Fauna and flora 26 species of mammals, 147 species of birds, and 918 species of higher plants have been recorded in Kaplankyr reserve. Protected rare species of animals found in the reserve include, Central Asian gazelle, the Ustyurt mountain sheep, ratel as well as substantial populations of saiga antelopes that migrate here from Karakalpakstan in the winter are also protected in the nature reserve. Plants include the Khiva thistle, Turkmen tulip, Antonia's gypsophila, Karelin sand acacia, and 55 other endemic species. The Gaplaňgyr nature reserve also incorpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aelurillus Dubatolovi
''Aelurillus dubatolovi'' is a species of jumping spider in the genus ''Aelurillus'' that lives in Central Asia. First identified in 2003 in Turkmenistan, it has a distribution that extends from Caspian Sea to Lake Balkhash and includes Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. The spider itself is small, the male being smaller than the female, with a carapace measuring between in length and an abdomen between long. The carapace is dark brown, with long hairs along the side that distinguish the species from the similar ''Aelurillus brutus'' and '' Aelurillus lutosus''. It also has a hairy clypeus and palpal femora, which enables it to be identified as not being the otherwise similar ''Aelurillus ater''. The female has a net-like pattern on the abdomen. This is clearer on examples found towards the northeast of the species distribution. The spiders found towards the northeast are also smaller, lighter and less hairy, but these are insufficient differences to ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aelurillus Ater
''Aelurillus'' is a genus of spiders in the family Salticidae (jumping spiders). Description Species of the genus ''Aelurillus'' are typically about 7 mm long in females, and up to five mm in males. They are stout, squat-shaped and rather furry, with females often uniformly mottled sandy brown, while males are often black, sometimes with a pattern and with light, annulated legs.Murphy & Murphy 2000: 273 Habits Spiders in this genus mainly catch and feed on ants ( myrmecophagy). A Southeast Asian species of the genus ''Aelurillus'' has been observed to jump around 30-40 times its body length straight onto the back of a large gnaphosid spider and kill it. They like hot, dry, stony places or small bare open areas with dead twigs or similar amongst low vegetation. Distribution Species of the genus ''Aelurillus'' occur in the Palaearctic and Africa, with a few species known from India (''A. improvisus'', ''A. minimontanus'') and Sri Lanka (''A. kronestedti'', ''A. quadri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aelurillus Helvanacius
''Aelurillus'' is a genus of spiders in the family Salticidae (jumping spiders). Description Species of the genus ''Aelurillus'' are typically about 7 mm long in females, and up to five mm in males. They are stout, squat-shaped and rather furry, with females often uniformly mottled sandy brown, while males are often black, sometimes with a pattern and with light, annulated legs.Murphy & Murphy 2000: 273 Habits Spiders in this genus mainly catch and feed on ants ( myrmecophagy). A Southeast Asian species of the genus ''Aelurillus'' has been observed to jump around 30-40 times its body length straight onto the back of a large gnaphosid spider and kill it. They like hot, dry, stony places or small bare open areas with dead twigs or similar amongst low vegetation. Distribution Species of the genus ''Aelurillus'' occur in the Palaearctic and Africa, with a few species known from India (''A. improvisus'', ''A. minimontanus'') and Sri Lanka (''A. kronestedti'', ''A. quadri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
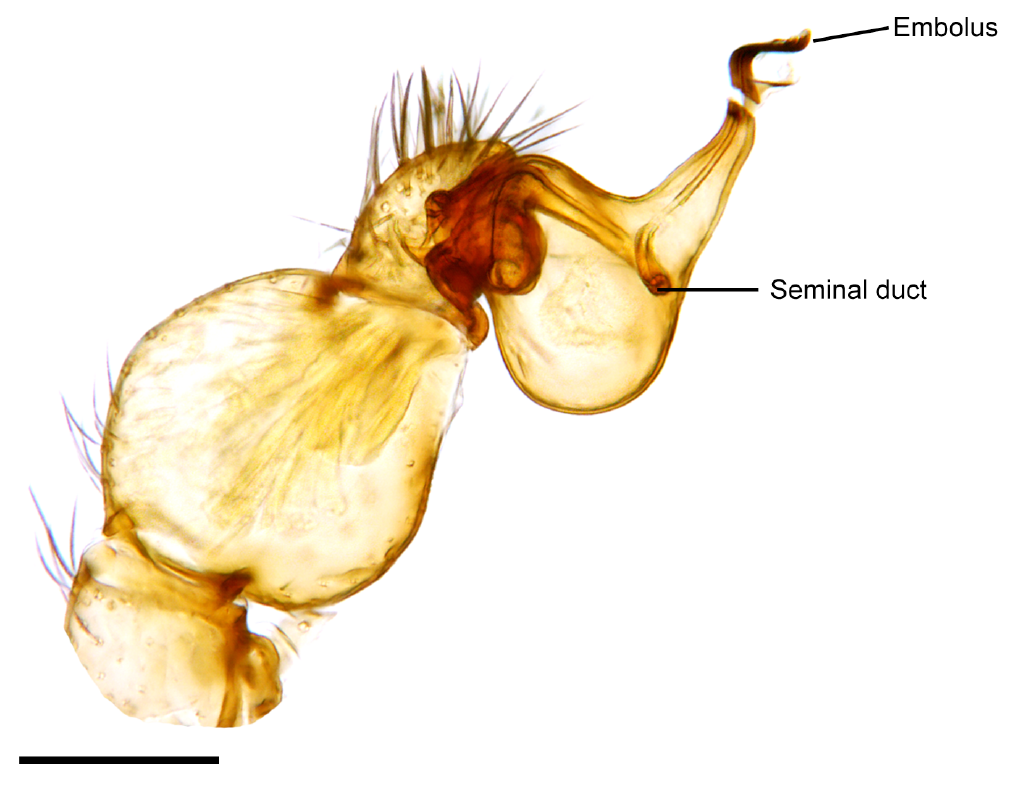
Embolus (spider Anatomy)
The two palpal bulbs – also known as palpal organs and genital bulbs – are the copulatory organs of a male spider. They are borne on the last segment of the pedipalps (the front "limbs" of a spider), giving the spider an appearance often described as like wearing boxing gloves. The palpal bulb does not actually produce sperm, being used only to transfer it to the female. Palpal bulbs are only fully developed in adult male spiders and are not completely visible until after the final moult. In the majority of species of spider, the bulbs have complex shapes and are important in identification. Structure The palpal bulb of a mature male spider is borne on the last segment of the pedipalp. This segment usually has touch-sensitive hairs (setae) with nerves leading to them. The bulb itself is entirely without nerves, and hence without sensory organs and muscles, since these depend on nerves for their functioning, although some spiders have one or two muscles external to the bulb and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palpal Bulb
The two palpal bulbs – also known as palpal organs and genital bulbs – are the copulatory organs of a male spider. They are borne on the last segment of the pedipalps (the front "limbs" of a spider), giving the spider an appearance often described as like wearing boxing gloves. The palpal bulb does not actually produce sperm, being used only to transfer it to the female. Palpal bulbs are only fully developed in adult male spiders and are not completely visible until after the final moult. In the majority of species of spider, the bulbs have complex shapes and are important in identification. Structure The palpal bulb of a mature male spider is borne on the last segment of the pedipalp. This segment usually has touch-sensitive hairs (setae) with nerves leading to them. The bulb itself is entirely without nerves, and hence without sensory organs and muscles, since these depend on nerves for their functioning, although some spiders have one or two muscles external to the bulb and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigyne
The epigyne or epigynum is the external genital structure of female spiders. As the epigyne varies greatly in form in different species, even in closely related ones, it often provides the most distinctive characteristic for recognizing species. It consists of a small, hardened portion of the exoskeleton located on the underside of the abdomen, in front of the epigastric furrow and between the epigastric plates. Functions The primary function of the epigyne is to receive and direct the palpal organ of the male during copulation. The various specific forms of epigynes are correlated, in each case, with corresponding specific differences in the palpus of the male. This specialization prevents individuals of different species from mating. The epigyne covers or accompanies the openings of the spermathecae, which are pouches for receiving and retaining sperm. Frequently, the openings of the spermathecae are on the outer face of the epigyne and can be easily seen. A secondary functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles: the coxa, the trochanter, the femur, the short patella, the tibia, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spiders, or chelate weapons ( pincers) of great size, as in scorpions. The pedipalps of Solifugae are covered in setae, but have not been studied in detail. Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |