|
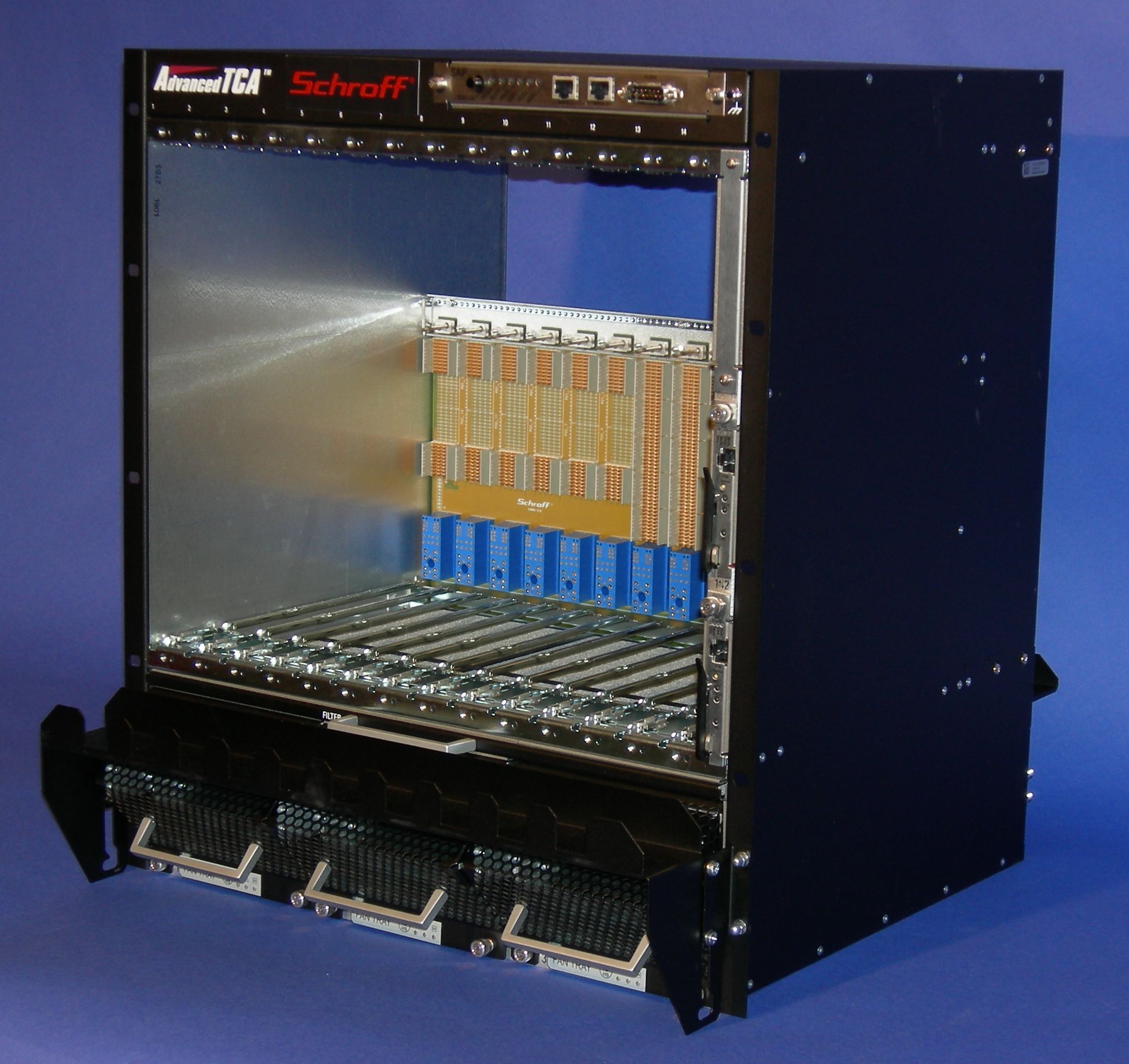
AdvancedTCA
Advanced Telecommunications Computing Architecture (ATCA or AdvancedTCA) is the largest specification effort in the history of the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group (PICMG), with more than 100 companies participating. Known as AdvancedTCA, the official specification designation PICMG 3.''x'' (see below) was ratified by the PICMG organization in December 2002. AdvancedTCA is targeted primarily to requirements for " carrier grade" communications equipment, but has recently expanded its reach into more ruggedized applications geared toward the military/aerospace industries as well. This series of specifications incorporates the latest trends in high speed interconnect technologies, next-generation processors, and improved Reliability, Availability and Serviceability (RAS). Mechanical specifications An AdvancedTCA board (blade) is 280 mm deep and 322 mm high. The boards have a metal front panel and a metal cover on the bottom of the printed circuit board to limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PICMG
PICMG, or PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group, is a consortium of over 140 companies. Founded in 1994, the group was originally formed to adapt PCI technology for use in high-performance telecommunications, military, and industrial computing applications, but its work has grown to include newer technologies. PICMG is distinct from the similarly named and adjacently-focused PCI Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG). PICMG currently focuses on developing and implementing specifications and guidelines for open standards-based computer architectures from a wide variety of interconnects. Background PICMG is a standards development organization in the embedded computing industry. Members work collaboratively to develop new specifications and enhancements to existing ones. The members benefit from participating in standards development, gain early access to leading-edge technology, and forging relationships with thought leaders and suppliers in the industry. The original PICMG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Mezzanine Card
Advanced Mezzanine Cards are printed circuit boards (PCBs) that follow a specification of the PCI Industrial Computers Manufacturers Group (PICMG). Known as AdvancedMC or AMC, the official specification designation is AMC.''x''. Originally AMC was targeted to requirements for carrier grade communications equipment, but later used in other markets. AMC modules are designed to work standalone, hot pluggable on any carrier card (base boards and system carrier boards in AdvancedTCA Systems) or as a hot pluggable board into a backplane directly as defined by MicroTCA specifications. The AMC standard differs from other mezzanine card standards such as PCI Mezzanine Card (PMC), PCIexpress Mezzanine Card XMC and FMC – FPGA Mezzanine Card by the 0 degree instead of 90 degree orientation of its connector enabling hot plug of the AMC. Specifications *AMC.0 is the "base" or "core" specification. The AdvancedMC definition alone defines a protocol agnostic connector to connect to a carr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
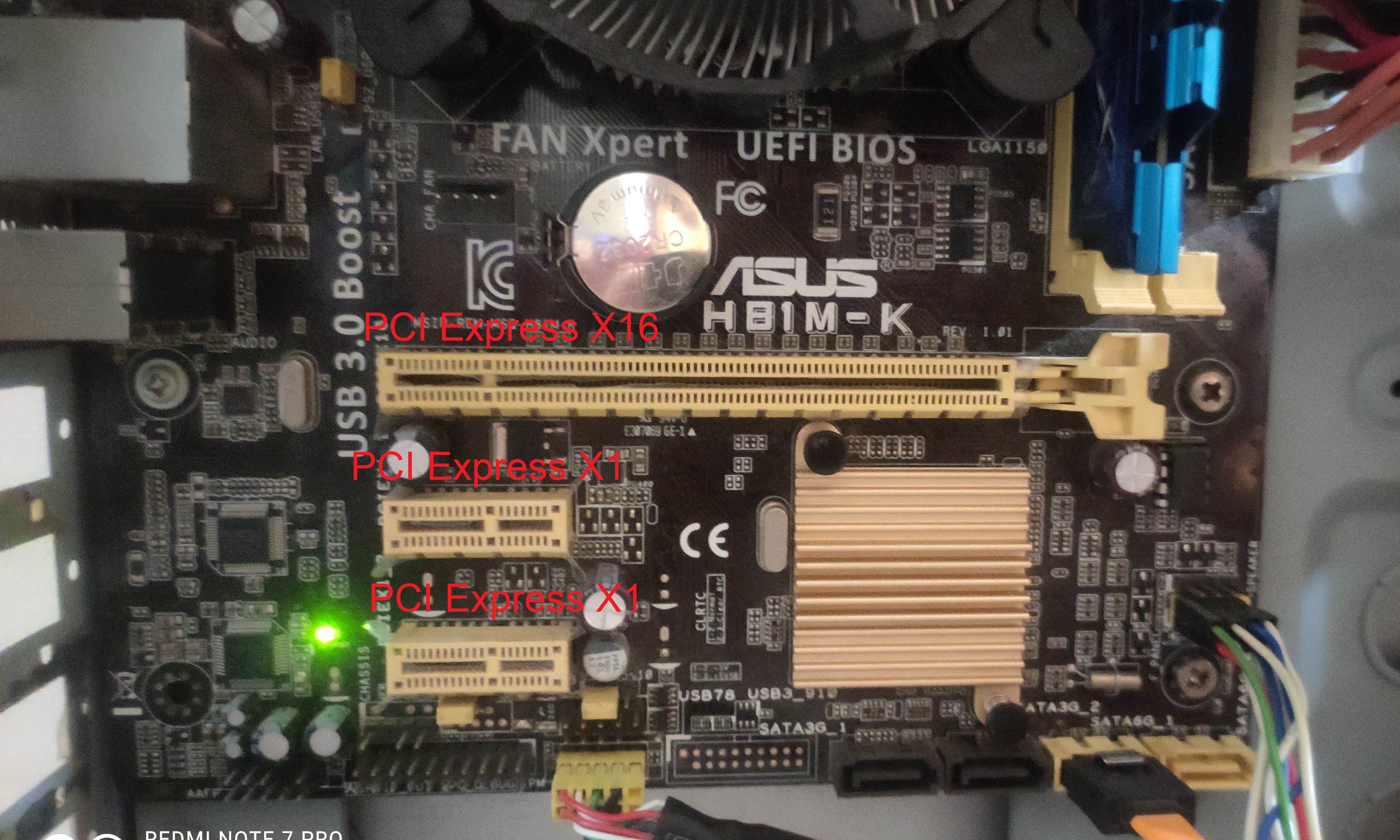
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism (Advanced Error Reporting, AER), and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization. The PCI Express electrical interface is measured by the number of simultaneous lanes. (A lane is a single send/receive line of data. The analogy is a highway with traffic in both direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I²C
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit, ), alternatively known as I2C or IIC, is a synchronous, multi-controller/multi-target (master/slave), packet switched, single-ended, serial communication bus invented in 1982 by Philips Semiconductors. It is widely used for attaching lower-speed peripheral ICs to processors and microcontrollers in short-distance, intra-board communication. Several competitors, such as Siemens, NEC, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics, Motorola, Nordic Semiconductor and Intersil, have introduced compatible I2C products to the market since the mid-1990s. System Management Bus (SMBus), defined by Intel in 1995, is a subset of I2C, defining a stricter usage. One purpose of SMBus is to promote robustness and interoperability. Accordingly, modern I2C systems incorporate some policies and rules from SMBus, sometimes supporting both I2C and SMBus, requiring only minimal reconfiguration either by commanding or output pin use. Applications I2C is appropriate f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MLVDS
Low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS), also known as TIA/EIA-644, is a technical standard that specifies electrical characteristics of a differential, serial signaling standard. LVDS operates at low power and can run at very high speeds using inexpensive twisted-pair copper cables. LVDS is a physical layer specification only; many data communication standards and applications use it and add a data link layer as defined in the OSI model on top of it. LVDS was introduced in 1994, and has become popular in products such as LCD-TVs, in-car entertainment systems, industrial cameras and machine vision, notebook and tablet computers, and communications systems. The typical applications are high-speed video, graphics, video camera data transfers, and general purpose computer buses. Early on, the notebook computer and LCD display vendors commonly used the term LVDS instead of FPD-Link when referring to their protocol, and the term ''LVDS'' has mistakenly become synonymous with ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Interference
Electromagnetic interference (EMI), also called radio-frequency interference (RFI) when in the radio frequency spectrum, is a disturbance generated by an external source that affects an electrical circuit by electromagnetic induction, electrostatic coupling, or conduction. The disturbance may degrade the performance of the circuit or even stop it from functioning. In the case of a data path, these effects can range from an increase in error rate to a total loss of the data. Both man-made and natural sources generate changing electrical currents and voltages that can cause EMI: ignition systems, cellular network of mobile phones, lightning, solar flares, and auroras (northern/southern lights). EMI frequently affects AM radios. It can also affect mobile phones, FM radios, and televisions, as well as observations for radio astronomy and atmospheric science. EMI can be used intentionally for radio jamming, as in electronic warfare. History Since the earliest days o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel (FC) is a high-speed data transfer protocol providing in-order, lossless delivery of raw block data. Fibre Channel is primarily used to connect computer data storage to servers in storage area networks (SAN) in commercial data centers. Fibre Channel networks form a switched fabric because the switches in a network operate in unison as one big switch. Fibre Channel typically runs on optical fiber cables within and between data centers, but can also run on copper cabling. Supported data rates include 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, and 128 gigabit per second resulting from improvements in successive technology generations. The industry now notates this as Gigabit Fibre Channel (GFC). There are various upper-level protocols for Fibre Channel, including two for block storage. Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) is a protocol that transports SCSI commands over Fibre Channel networks. FICON is a protocol that transports ESCON commands, used by IBM mainframe computers, over F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Network Management Protocol
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet Standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and for modifying that information to change device behaviour. Devices that typically support SNMP include cable modems, routers, switches, servers, workstations, printers, and more. SNMP is widely used in network management for network monitoring. SNMP exposes management data in the form of variables on the managed systems organized in a management information base (MIB) which describe the system status and configuration. These variables can then be remotely queried (and, in some circumstances, manipulated) by managing applications. Three significant versions of SNMP have been developed and deployed. SNMPv1 is the original version of the protocol. More recent versions, SNMPv2c and SNMPv3, feature improvements in performance, flexibility and security. SNMP is a component of the Internet Protocol Suite as defined by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTTP
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include hyperlinks to other resources that the user can easily access, for example by a mouse click or by tapping the screen in a web browser. Development of HTTP was initiated by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN in 1989 and summarized in a simple document describing the behavior of a client and a server using the first HTTP protocol version that was named 0.9. That first version of HTTP protocol soon evolved into a more elaborated version that was the first draft toward a far future version 1.0. Development of early HTTP Requests for Comments (RFCs) started a few years later and it was a coordinated effort by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), with work later moving t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATCA Shelf Manager , a radio telescope in New South Wales
{{disambig ...
ATCA may refer to: * Atça, a town in Turkey * Advanced Telecommunications Computing Architecture, a specification for communications equipment * Aid to the civil authority, military aid to the civil power * Alien Tort Claims Act, a U.S. statue on jurisdiction * All Tripura Chess Association, an Indian organisation * American Theatre Critics Association * Association of Turkish Cypriots Abroad * Australia Telescope Compact Array The Australia Telescope Compact Array (ATCA) is a radio telescope operated by CSIRO at the Paul Wild Observatory, twenty five kilometres (16 mi) west of the town of Narrabri in New South Wales, Australia. Its opening ceremony took place on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10 Gigabit Ethernet
10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GE, 10GbE, or 10 GigE) is a group of computer networking technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of 10 gigabits per second. It was first defined by the IEEE 802.3ae-2002 standard. Unlike previous Ethernet standards, 10 Gigabit Ethernet defines only full-duplex point-to-point links which are generally connected by network switches; shared-medium CSMA/CD operation has not been carried over from the previous generations Ethernet standards so half-duplex operation and repeater hubs do not exist in 10GbE. The 10 Gigabit Ethernet standard encompasses a number of different physical layer (PHY) standards. A networking device, such as a switch or a network interface controller may have different PHY types through pluggable PHY modules, such as those based on SFP+. Like previous versions of Ethernet, 10GbE can use either copper or fiber cabling. Maximum distance over copper cable is 100 meters but because of its bandwidth requirements, hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)