|
Adolph Kohut
Adolph Kohut (10 November 1848 – 21 or 22 November 1917) was a German-Hungarian journalist, literature and cultural historian, biographer, recitator and translator from Hungarian origin. Life Born in Mindszent, Kohut was born as one of thirteen children of the very poor, pious Talmud scholar Jacob Kohut. He studied from 1866 to 1868 at the Jewish Theological Seminary of Breslau as well as his older brother Alexander. Then he studied two semesters new philology and art history at the Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität in Breslau and afterwards at the Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Berlin. In Vienna he lectured for three years at the University of Vienna and received his PhD from the University of Jena in 1878. In 1872 he was called by Karl von Holtei to the editorial office of the ''Breslauer Nachrichten''. In 1873 he was editor of the ''Düsseldorfer Zeitung''. Leopold Ullstein hired him in 1878 at the ''Tribüne'' in Berlin and later at the ''Berliner Zeitung''. Afterwards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literary Historian
The history of literature is the historical development of writings in prose or poetry that attempt to provide entertainment, enlightenment, or instruction to the reader/listener/observer, as well as the development of the literary techniques used in the communication of these pieces. Not all writings constitute literature. Some recorded materials, such as compilations of data (e.g., a check register) are not considered literature, and this article relates only to the evolution of the works defined above. Ancient (Bronze Age–5th century) Early literature is derived from stories told in hunter-gatherer bands through oral tradition, including myth and folklore. Storytelling emerged as the human mind evolved to apply causal reasoning and structure events into a narrative and language allowed early humans to share information with one another. Early storytelling provided opportunity to learn about dangers and social norms while also entertaining listeners. Myth can be expanded t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Stöcker
Adolf Stoecker (December 11, 1835 – February 2, 1909) was a German court chaplain to Kaiser Wilhelm I, a politician, leading antisemite, and a Lutheran theologian who founded the Christian Social Party to lure members away from the Social Democratic Workers' Party. Early life Stoecker was born in Halberstadt, Province of Saxony, in the Kingdom of Prussia. Stoecker's father was a blacksmith turned prison guard, and despite his poverty, Stoecker was able to attend university, which was unusual for a working-class man in the 19th century.Telman, Jeffrey "Adolf Stoecker: Anti-Semite with a Christian Mission" pages 93-112 from ''Jewish History'', Volume 9, Issue # 2. Fall 1995 page 99. An energetic and hardworking Protestant pastor who wrote widely on various social and political issues, Stoecker had a charismatic personality which made him one of Germany's best loved and most respected Lutheran clergyman.Green Harold "Adolf Stoecker: Portrait of a Demagogue" pages 106-12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Karl Theodor Zarncke
Friedrich Karl Theodor Zarncke (7 July 182515 October 1891), German philologist, was born in Zahrensdorf, Mecklenburg-Schwerin, the son of a country pastor. He was educated at the Rostock gymnasium, and studied (1844–1847) at the universities of Rostock, Leipzig and Berlin. In 1848 he was employed in arranging the valuable library of Old German literature of Freiherr Karl Hartwig von Meusebach (1781–1847), and superintending its removal from Baumgartenbrück, near Potsdam, to the Royal Library at Berlin. This work cites: *''Zur Erinnerung an den Heimgang von Dr Friedrich Zarncke'' (1891) * Franz Vogt in ''Zeitschrift für deutsche Philologie'' * Eduard Zarncke in ''Biographisches Jahrbuch für Altertumswissenschaft'' (1895) * E. Sievers in '' Allgemeine deutsche Biographie'' In 1850 he founded the ''Literarisches Centralblatt für Deutschland'' in Leipzig. In 1852 he established himself as '' privatdozent'' at Leipzig University. In 1858 he was appointed full professor. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Kirchbach
Ernst Wolfgang Kirchbach (18 September 1857, in London, England – 8 September 1906, in Bad Nauheim) was a German critic and writer. Biography He was the son of German artist Ernst Kirchbach and his wife Emma née Schmitthenner-Stockhausen. He studied philosophy and history in Dresden and Leipzig. Settling in Dresden in 1888, he was editor of the ''Magazin für Litteratur des In- und Auslandes'' (Magazine for domestic and foreign literature). Beginning 1896, he lived in Berlin. and became a leading member of the "Giordano Bruno Bund" of freethinking intellectuals.Andreas W. Daum Andreas W. Daum is a German-American historian who specializes in modern German and transatlantic history, as well as the history of knowledge and global exploration. Daum received his Ph.D. summa cum laude in 1995 from the Ludwig Maximilian Unive ..., ''Wissenschaftspopularisierung im 19. Jahrhundert: Bürgerliche Kultur, naturwissenschaftliche Bildung und die deutsche Öffentlichkeit, 1848–1914''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Kretschmer
Carl Franz Edmund Kretschmer (31 August 1830 – 13 September 1908) was a German organist and composer who worked for the Dresden Court and composed several operas and masses. Career Born in Ostritz, Lausitz, the son of the rector of the municipal school, Kretschmer received first musical instruction from his father. From 1846, he studied in Dresden, composition with Ernst Julius Otto and organ with Johann Gottlieb Schneider. He first worked as a teacher, and in 1854 became the organist of the Katholische Hofkirche. In 1863, he was appointed ''Hoforganist'' (Court Organist) and instructor of the Kapellknabeninstitut, and in 1880 also choral conductor of the Hofkirche. He composed around 80 stage works and several orchestral works, including four operas and four Mass (music), masses. The King awarded him the title of ''Hofkirchen-Componist''. His composition ''Die Geisterschlacht'' won a prize at the first Deutsches Sängerfest in 1865. He received a prize for a mass at an int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facsimile
A facsimile (from Latin ''fac simile'', "to make alike") is a copy or reproduction of an old book, manuscript, map, Old master print, art print, or other item of historical value that is as true to the original source as possible. It differs from other forms of reproduction by attempting to replicate the source as accurately as possible in scale, color, condition, and other material qualities. For books and manuscripts, this also entails a complete copy of all pages; hence, an incomplete copy is a "partial facsimile". Facsimiles are sometimes used by scholars to research a source that they do not have access to otherwise, and by museums and archives for media preservation and Art conservation and restoration, conservation. Many are sold commercially, often accompanied by a volume of commentary. They may be produced in limited editions, typically of 500–2,000 copies, and cost the equivalent of a few thousand United States dollars. The term "fax" is a shortened form of "facsimile" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
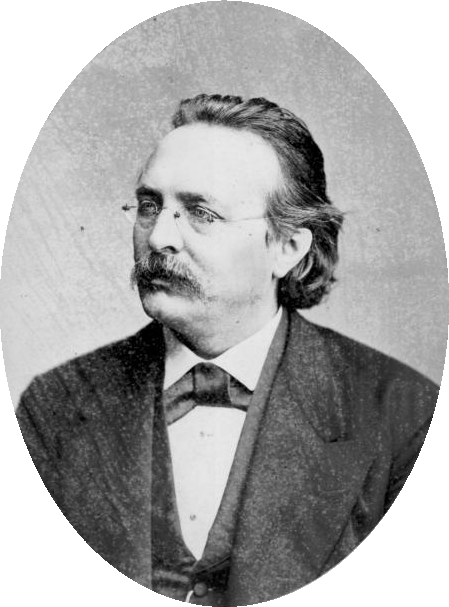
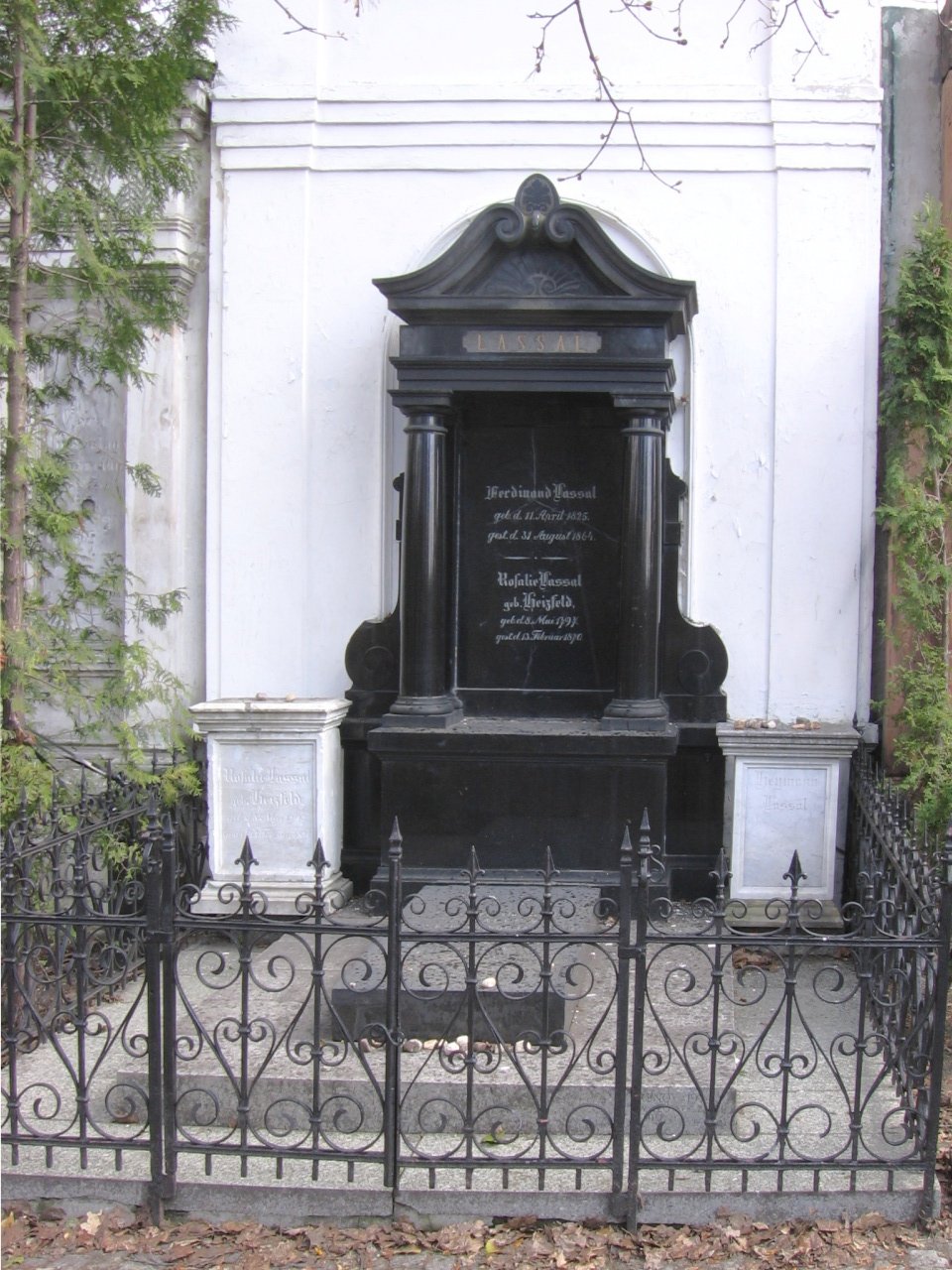
Ferdinand Lassalle
Ferdinand Lassalle (; 11 April 1825 – 31 August 1864) was a Prussian-German jurist, philosopher, socialist and political activist best remembered as the initiator of the social democratic movement in Germany. "Lassalle was the first man in Germany, the first in Europe, who succeeded in organising a party of socialist action", or, as Rosa Luxemburg put it: "Lassalle managed to wrestle from history in two years of flaming agitation what needed many decades to come about." As agitator he coined the terms night-watchman state and iron law of wages. Biography Early life Lassalle was born Ferdinand Johann Gottlieb Lassal on 11 April 1825 in Breslau, Silesia (now Wrocław, Poland). His father Heyman Lassal was a Jewish silk merchant and intended his son for a business career, sending him to the commercial school at Leipzig. However, Lassalle soon transferred to university, studying first in the University of Breslau and later at the University of Berlin. There, Lassalle studied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sándor Petőfi
Sándor Petőfi ( []; né Petrovics; sk, Alexander Petrovič; sr, Александар Петровић; 1 January 1823 – most likely 31 July 1849) was a Hungarian poet of Serbian origin and liberal revolutionary. He is considered Hungary's national poet, and was one of the key figures of the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. He is the author of the ''Nemzeti dal'' (National Song), which is said to have inspired the revolution in the Kingdom of Hungary that grew into a war for independence from the Austrian Empire. It is most likely that he died in the Battle of Segesvár, one of the last battles of the war. Early life Petőfi was born on the New Year's morning of 1823, in the town of Kiskőrös, Kingdom of Hungary. The population of Kiskőrös was predominantly of Slovak origin as a consequence of the Habsburgs' reconstruction policy designed to settle, where possible, non-Hungarians in areas devastated during the Turkish wars. His birth certificate, in Latin, gives his name as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Language
Hungarian () is an Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungarian communities in southern Slovakia, western Ukraine ( Subcarpathia), central and western Romania (Transylvania), northern Serbia (Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia (Prekmurje), and eastern Austria. It is also spoken by Hungarian diaspora communities worldwide, especially in North America (particularly the United States and Canada) and Israel. With 17 million speakers, it is the Uralic family's largest member by number of speakers. Classification Hungarian is a member of the Uralic language family. Linguistic connections between Hungarian and other Uralic languages were noticed in the 1670s, and the family itself (then called Finno-Ugric) was established in 1717. Hungarian has traditionally been assigned to the Ugric alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Karl Friedrich Zöllner
Johann Karl Friedrich Zöllner (8 November 1834, Berlin25 April 1882, Leipzig) was a German astrophysicist who studied optical illusions. He was also an early psychical investigator. Biography From 1872 he held the chair of astrophysics at Leipzig University. He wrote numerous papers on photometry and spectrum analysis in Poggendorff's '' Annalen'' and ''Berichte der k. sächsischen Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften'', two works on celestial photometry (''Grundzüge einer allgemeinen Photometrie des Himmels'', Berlin, 1861, 4to, and ''Photometrische Untersuchungen'', Leipzig, 1865, 8vo), and a curious book, ''Ueber die Natur der Cometen'' (Leipzig, 1872, 3rd ed. 1883). He discovered the Zöllner illusion where lines that are parallel appear diagonal. He also successfully proved Christian Doppler's theory on the effect of motion of the color of stars, and the resulting shift of absorption lines, via the invention of a very sensitive spectroscope which he named "Reversionspectros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Georg Conrad
Michael Georg Conrad (5 April 1846 – 20 December 1927) was a German writer and philosopher. He was the founder and editor of ''Die Gesellschaft ''Die Gesellschaft'' (German: ''Society'') was a magazine which was published in German Empire between 1885 and 1902. It billed itself as the "organ of contemporary literary youth". It is known for its strong support for naturalism and its found ...''. External links * * * 1846 births 1927 deaths People from Marktbreit People from the Kingdom of Bavaria German Lutherans German People's Party (1868) politicians Members of the 9th Reichstag of the German Empire German male writers German-language writers German philosophers German magazine founders {{Germany-philosopher-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Von Dönhoff
August Karl Graf von Dönhoff-Friedrichstein (26 January 1845 – 9 September 1920) was a Prussian nobleman and politician. Life Born in Frankfurt Dönhoff descended from the East Prussian branch of the Dönhoff. His father was the diplomat and Prussian foreign minister August Heinrich Hermann von Dönhoff, his mother Pauline, ''née Countess'' von Lehndorff. Dönhoff grew up on the family castle Friedrichstein not far from Königsberg and attended the Kneiphof Gymnasium. After the Abitur he studied law at the Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn. In 1865 he became a member of the Corps Borussia Bonn. As a Prussian major he took part in the Austro-Prussian War at the age of 21. From 1868 to 1870 he was an articled clerk at the Kammergericht and then served again as a major in the Franco-Prussian War. Like his father, Dönhoff also embarked on a diplomatic career and worked as secretary of legation for the Empire in Paris, Vienna, London, Saint Petersburg and Washin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |