|
Adolph, Count Of Ottweiler
Adolf Ludwig Karl Moritz, Count of Ottweiler (3 June 1789 in Saarbrücken, Nassau-Saarbrücken - 10 December 1812 in Vilnius, Russian Empire), was a member of the Princely House of Nassau-Saarbrücken, Count of Ottweiler, and a Lieutenant in the Army of Württemberg. He died as a volunteer in the Russian campaign. Family After the death of his first wife, Prince Louis of Nassau-Saarbrücken married on February 28, 1787 Catherine Kest, former handmaiden of his past mistress Baroness Amalie of Dorsberg. Of middle-class origin, he had been his mistress from 1774. He had her raised in 1774 to the peer status of "Lady of Ludwigsberg", in 1781 to Baroness and then in 1784 to "Countess of Ottweiler". To the opposition of the rest of the House of Nassau, Louis had coat of arms ceremoniously conferred upon Catherine, along with the title "Princess of Nassau-Saarbrücken". From their morganatic relationship before 1787 was born six children. Adolph, the seventh, was born their only leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Friedrich Dryander
Johann Friedrich Dryander (26 April 1756, in Sankt Johann, Saarbrücken – 29 March 1812, in Sankt Johann, Saarbrücken) was a German painter. Dryander created several portraits of French officers, notably: * ''French troops before Saint-Jean-lès-Sarrebruck'', on display at the Musée historique Lorrain in Nancy, 1804 * Portrait of a general, on display at the Fine Arts museum in Rouens * ''Portrait du Général Bella.'' 1795, Salon-de-Provence * ''Portrait du Citoyen Laboucly, Inspecteur de la Viande.'' 1794, Saarbrücken * ''Portrait of Dominique Joseph Garat'', 1794, Vizille, musée de la Révolution française * ''Portrait du général Jourdan Jourdan may refer to: *Carolyn Jourdan, American author *Claude Jourdan (1803–1873), French zoologist and paleontologist *David W. Jourdan, businessman *Jean-Baptiste Jourdan (1762–1833), French army commander *Murders of Jourdan Bobbish and Jac ... et de son adjudant.'' 1794, Vizille, musée de la Révolution française. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
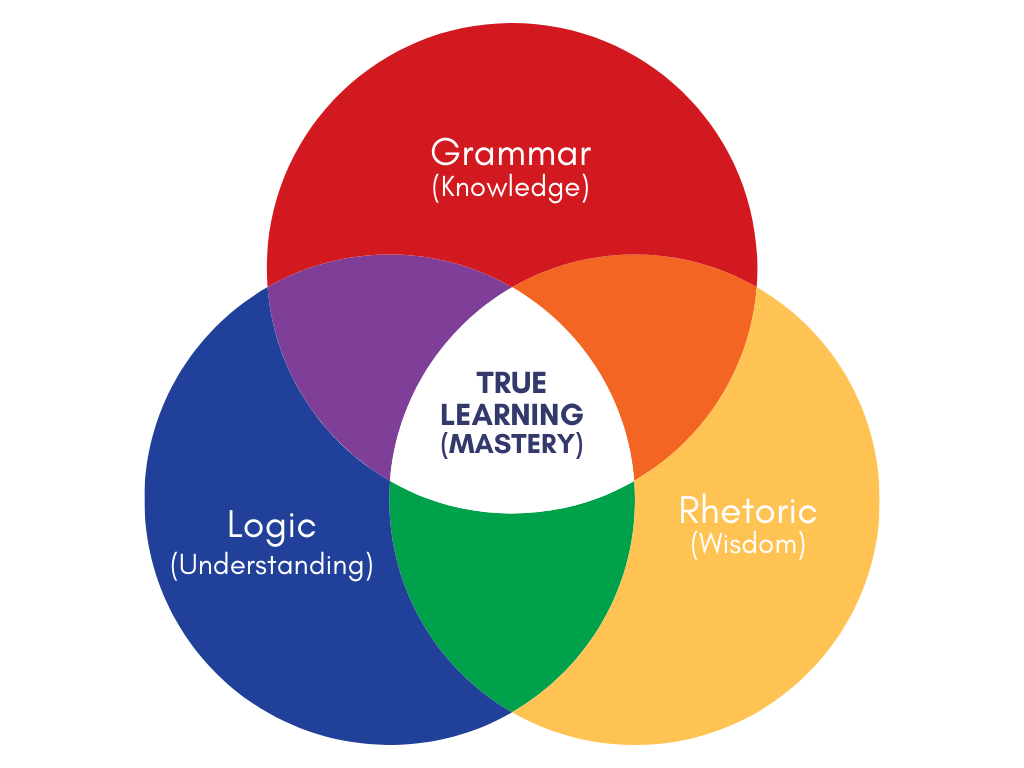
Classical Education Movement
The classical education movement includes a growing number of organizations taking renewed inspiration from a traditional and historic liberal arts education and that focuses human formation and learning on the liberal arts (including the natural sciences) as well as canons of classical literature, the fine arts, and the history of civilization. While schools in the movement vary in their use of these categories, the general goal of the classical education movement is to encourage this group of studies within the hundreds of contemporary schools involved (both independent and public charter) as well as the thousands of homeschooling communities. This movement has inspired multiple gradate programs and colleges as well as ''Principia: A Journal of Classical Education'' (a peer-reviewed scholarly journal that publishes articles, policy research, editorials, and reviews related to the history, theory, practice, and pedagogy of classic liberal arts education and contemporary classica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Erlangen
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Jena
The University of Jena, officially the Friedrich Schiller University Jena (german: Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, abbreviated FSU, shortened form ''Uni Jena''), is a public research university located in Jena, Thuringia, Germany. The university was established in 1558 and is counted among the ten oldest universities in Germany. It is affiliated with six Nobel Prize winners, most recently in 2000 when Jena graduate Herbert Kroemer won the Nobel Prize for physics. In the 2023 Times Higher Education World University Rankings, the university was awarded 189th place in the world. It was renamed after the poet Friedrich Schiller who was teaching as professor of philosophy when Jena attracted some of the most influential minds at the turn of the 19th century. With Karl Leonhard Reinhold, Johann Gottlieb Fichte, G. W. F. Hegel, F. W. J. Schelling and Friedrich Schlegel on its teaching staff, the university was at the centre of the emergence of German idealism and early Romanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannheim Palace
Mannheim Palace (german: Mannheimer Schloss) is a large Baroque palace in Mannheim, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It was originally the main residence of the Prince-electors of the Electorate of the Palatinate of the House of Wittelsbach until 1777. Part of the palace is used today by the University of Mannheim. The castle, which features tapestries, furniture, paintings, porcelain and silverware can be visited on a free-flow basis with audioguides. Origins The city of Mannheim, founded in 1606, was fortified and at the present site of the castle there was a fortress called ''Friedrichsburg'', sometimes serving as alternative residence for the Elector, one of the most important territorial princes of the Holy Roman Empire. The actual palace dates from the 18th century. When Elector Karl III Philip had confessional controversies with the inhabitants of his capital Heidelberg, he decided to make Mannheim the Palatinate's new capital in 1720. Karl Philip decided to construct a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Westphalia
The Kingdom of Westphalia was a kingdom in Germany, with a population of 2.6 million, that existed from 1807 to 1813. It included territory in Hesse and other parts of present-day Germany. While formally independent, it was a vassal state of the First French Empire and was ruled by Napoleon's brother Jérôme Bonaparte. It was named after Westphalia, but this was a misnomer since the kingdom had little territory in common with that area; rather the kingdom mostly covered territory formerly known as Eastphalia. Napoleon imposed the first written modern constitution in Germany, a French-style central administration, and agricultural reform. The Kingdom liberated the serfs and gave everyone equal rights and the right to a jury trial. In 1808 the Kingdom passed Germany's first laws granting Jews equal rights, thereby providing a model for reform in the other German states. Westphalia seemed to be progressive in immediately enacting and enforcing the new reforms. The country was re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corps Hannovera Göttingen
Bismarck 1836 The Corps Hannovera Göttingen is one of the oldest German Student Corps, a Studentenverbindung or student corporation founded on January 18, 1809 at the Georg August University of Göttingen by students like Georg Kloss. The name was chosen because the founders had their home residences in the Kingdom of Hanover. As a corps it is a founder member (1848) of the Kösener Senioren-Convents-Verband (KSCV), the oldest governing body of such student associations in both Germany and Austria. ''Hannovera'' commits itself still to the principles of academic fencing as well as the common principles of tolerance and democracy shared by all Corps of the KSCV. Its members wear red and blue couleur (red cap and tricoloured sash) on official occasions. Hannovera's Latin motto is ''Nunquam retrorsum, fortes adiuvat fortuna!'' (engl: ''Never backward, fortune favours the bold''). Corps Hannovera officially regards the 18th of January 1809 as its founding date though it can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Göttingen
The University of Göttingen, officially the Georg August University of Göttingen, (german: Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, known informally as Georgia Augusta) is a public research university in the city of Göttingen, Germany. Founded in 1734 by George II, King of Great Britain and Elector of Hanover, and starting classes in 1737, the Georgia Augusta was conceived to promote the ideals of the Enlightenment. It is the oldest university in the state of Lower Saxony and the largest in student enrollment, which stands at around 31,600. Home to many noted figures, it represents one of Germany's historic and traditional institutions. According to an official exhibition held by the University of Göttingen in 2002, 44 Nobel Prize winners had been affiliated with the University of Göttingen as alumni, faculty members or researchers by that year alone. The University of Göttingen was previously supported by the German Universities Excellence Initiative, holds memberships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consilium Abeundi
{{disambiguation ...
Consilium may refer to: *Consilia, a literary genre * Consilium de Emendanda Ecclesia, a 1536 report commissioned by Pope Paul III on the abuses in the Catholic Church * Consilium Place, an office complex in the Scarborough district of Toronto, Canada *''Consilium ad exsequendam Constitutionem de Sacra Liturgia'', a commission entrusted with the reform of the liturgy, including the Mass of Paul VI * Council of the European Union, or Consilium, institution in bicameral legislature of the European Union * Aulic Council or ''Consilium Aulicum'', of the Holy Roman Empire *'' Sacrosanctum Concilium'', a conciliar constitution, after the Second Vatican Council See also *Concilium (other) Concilium may refer to: * ''Concilium'' (journal), a worldwide journal of Catholic theology * Concilium Germanicum (c. 742), the first major Church synod to be held in the eastern parts of the Frankish kingdoms * Concilium Plebis, the principal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Kloss
Georg Franz Burkhard Kloss (31 July 1787 Frankfurt am Main - 10 February 1854 Frankfurt) was a German historian of freemasonry. Biography Kloss was the son of a physician and studied medicine at Heidelberg and Göttingen, where he became one of the cofounders of the Corps Hannovera Göttingen. He practiced medicine in Frankfurt. He became a book collector, and gathered a fine collection of old manuscripts, purchasing entire libraries of monasteries. Obtaining Masonic degrees, he started collecting books referring to freemasonry. His extensive library of Masonic works is now at The Hague The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of ... (Cultureel Maçonniek Centrum 'Prins Frederik'). Works His works are fundamental histories of freemasonry, and include: * ''Bibliographie der Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corps Rhenania Heidelberg
Corps Rhenania Heidelberg is a member Corps of the Kösener Senioren-Convents-Verband, the oldest association of student fraternities in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Corps Rhenania is "pflichtschlagend", which refers to the fact that it requires of its members, that they participate in several ritual, organised duels with members of other specific student fraternities. Eligible applicants are those students, both current and former, of the Ruprecht Karl University in Heidelberg, Germany. Members of Corps Rhenania are colloquially referred to as "Rhenane". General Rhenania Heidelberg is one of the oldest fraternities in Heidelberg. In its current form it was founded on January 15, 1849; its roots and predecessor fraternities date back to 1802, if not earlier. Rhenania means "area of the Rhine", where most of the founding members came from. Consequently, they chose the colors of their home area, which are blue, white and red. Following the open-minded principles of Corps, Rhena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |