|
Adobe Voco
Adobe Voco is an unreleased audio editing and generating prototype software by Adobe that enables novel editing and generation of audio. Dubbed "Photoshop-for-voice", it was first previewed at the Adobe MAX event in November 2016. The technology shown at Adobe MAX was a preview that could potentially be incorporated into Adobe Creative Cloud. It was later revealed that Voco was never meant to be released and was meant to be a research prototype. Technical details As the demo showed, the software takes approximately 20 minutes of the desired target's speech and generates a sound-alike voice including phonemes that were not present in the target example material. Adobe stated Voco would lower the cost of audio production. Concerns Ethical and security concerns were raised over the ability to alter an audio recording to include words and phrases the original speaker never spoke, and the potential risk to voiceprint biometrics. Concerns also rose that it may be used in conjunct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Manipulation
Video manipulation is a type of media manipulation Media manipulation is a series of related techniques in which partisans create an image or argument that favors their particular interests. Such tactics may include the use of logical fallacies, manipulation, outright deception (disinformation) ... that targets digital video using video processing and video editing techniques. The applications of these methods range from educational videos to videos aimed at (Crowd manipulation, mass) manipulation and propaganda, a straightforward extension of the long-standing possibilities of photo manipulation. This form of computer-generated misinformation has contributed to fake news, and there have been instances when this technology was used during political campaigns. Other uses are less sinister; entertainment purposes and harmless pranks provide users with movie-quality artistic possibilities. History The concept of manipulating video can be traced back as far as the 1950s, when th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DeepMind
DeepMind Technologies is a British artificial intelligence subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. and research laboratory founded in 2010. DeepMind was acquired by Google in 2014 and became a wholly owned subsidiary of Alphabet Inc, after Google's restructuring in 2015. The company is based in London, with research centres in Canada, France, and the United States. DeepMind has created a neural network that learns how to play video games in a fashion similar to that of humans, as well as a Neural Turing machine, or a neural network that may be able to access an external memory like a conventional Turing machine, resulting in a computer that mimics the short-term memory of the human brain. DeepMind made headlines in 2016 after its AlphaGo program beat a human professional Go player Lee Sedol, a world champion, in a five-game match, which was the subject of a documentary film. A more general program, AlphaZero, beat the most powerful programs playing go, chess and shogi (Japanese chess) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-source Software
Open-source software (OSS) is computer software that is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and distribute the software and its source code to anyone and for any purpose. Open-source software may be developed in a collaborative public manner. Open-source software is a prominent example of open collaboration, meaning any capable user is able to participate online in development, making the number of possible contributors indefinite. The ability to examine the code facilitates public trust in the software. Open-source software development can bring in diverse perspectives beyond those of a single company. A 2008 report by the Standish Group stated that adoption of open-source software models has resulted in savings of about $60 billion per year for consumers. Open source code can be used for studying and allows capable end users to adapt software to their personal needs in a similar way user scripts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WaveNet
WaveNet is a deep neural network for generating raw audio. It was created by researchers at London-based AI firm DeepMind. The technique, outlined in a paper in September 2016, is able to generate relatively realistic-sounding human-like voices by directly modelling waveforms using a neural network method trained with recordings of real speech. Tests with US English and Mandarin reportedly showed that the system outperforms Google's best existing Speech synthesis#Text-to-speech systems, text-to-speech (TTS) systems, although as of 2016 its text-to-speech synthesis still was less convincing than actual human speech. WaveNet's ability to generate raw waveforms means that it can model any kind of audio, including music. History Generating speech from text is an increasingly common task thanks to the popularity of software such as Apple's Siri, Microsoft's Cortana (virtual assistant), Cortana, Amazon Alexa and the Google Assistant. Most such systems use a variation of a technique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RGB Color Model
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three additive primary colors, red, green, and blue. The main purpose of the RGB color model is for the sensing, representation, and display of images in electronic systems, such as televisions and computers, though it has also been used in conventional photography. Before the electronic age, the RGB color model already had a solid theory behind it, based in human perception of colors. RGB is a ''device-dependent'' color model: different devices detect or reproduce a given RGB value differently, since the color elements (such as phosphors or dyes) and their response to the individual red, green, and blue levels vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, or even in the same device over time. Thus an RGB value does not define the same ''color'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real-time Computing
Real-time computing (RTC) is the computer science term for hardware and software systems subject to a "real-time constraint", for example from event to system response. Real-time programs must guarantee response within specified time constraints, often referred to as "deadlines". Ben-Ari, Mordechai; "Principles of Concurrent and Distributed Programming", ch. 16, Prentice Hall, 1990, , page 164 Real-time responses are often understood to be in the order of milliseconds, and sometimes microseconds. A system not specified as operating in real time cannot usually ''guarantee'' a response within any timeframe, although ''typical'' or ''expected'' response times may be given. Real-time processing ''fails'' if not completed within a specified deadline relative to an event; deadlines must always be met, regardless of system load. A real-time system has been described as one which "controls an environment by receiving data, processing them, and returning the results sufficiently quic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
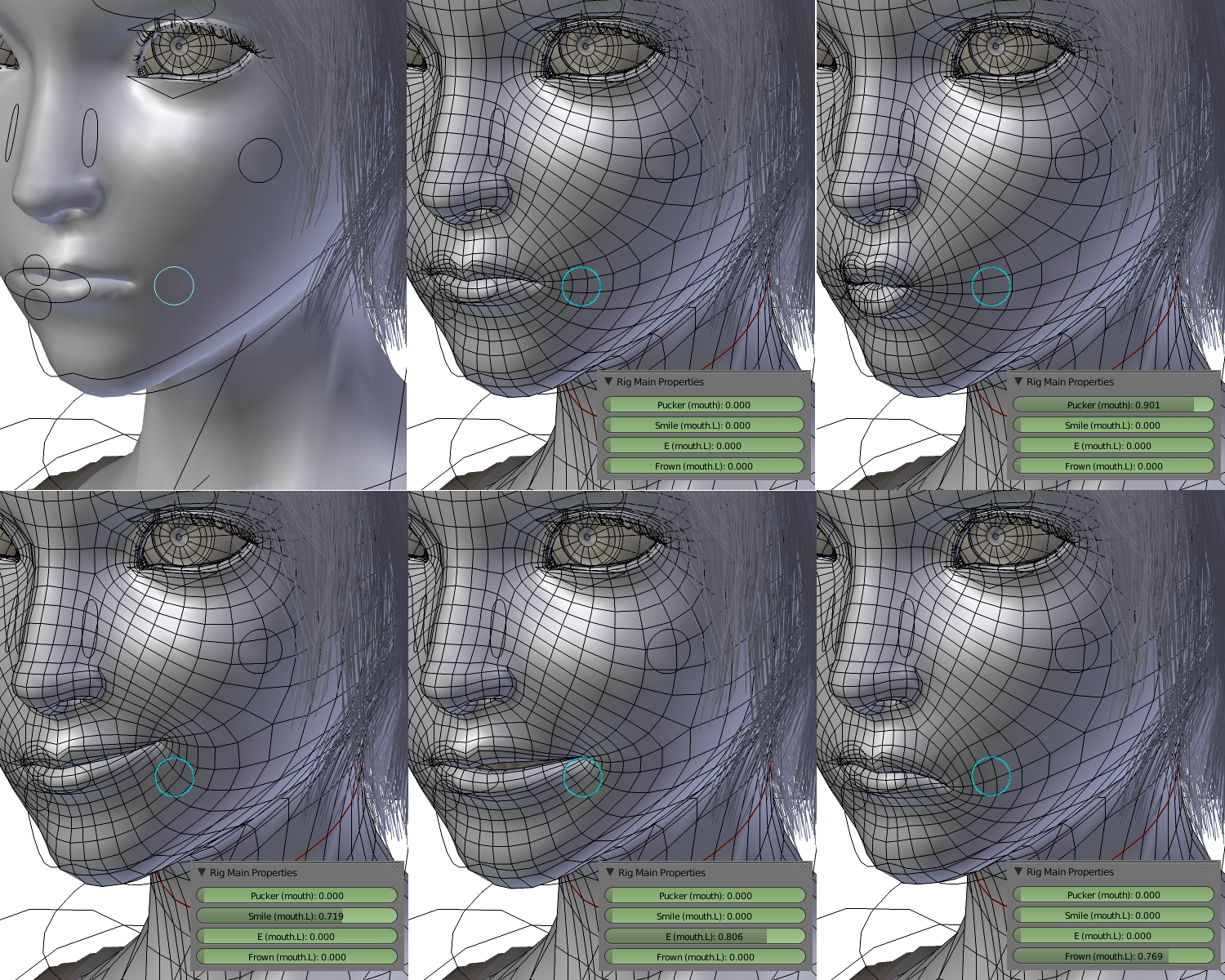
Facial Expressions
A facial expression is one or more motions or positions of the muscles beneath the skin of the face. According to one set of controversial theories, these movements convey the emotional state of an individual to observers. Facial expressions are a form of nonverbal communication. They are a primary means of conveying social information between humans, but they also occur in most other mammals and some other animal species. (For a discussion of the controversies on these claims, see Fridlund and Russell & Fernandez Dols.) Humans can adopt a facial expression voluntarily or involuntarily, and the neural mechanisms responsible for controlling the expression differ in each case. Voluntary facial expressions are often socially conditioned and follow a cortical route in the brain. Conversely, involuntary facial expressions are believed to be innate and follow a subcortical route in the brain. Facial recognition can be an emotional experience for the brain and the amygdala is highly invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2000s (decade)
File:2000s decade montage3.png, From top left, clockwise: The World Trade Center (1973–2001), World Trade Center on fire and the Statue of Liberty during the September 11 attacks, 9/11 attacks in 2001; the euro enters into European currency in 2002; a statue of Saddam Hussein being toppled during the Iraq War in 2003, and in 2006, Hussein would be Execution of Saddam Hussein, executed for crimes against humanity; U.S. troops heading toward an army helicopter in War in Afghanistan (2001–present), Afghanistan during the War on Terror; social media through the Internet spreads across the world; a Chinese soldier gazes at the 2008 Summer Olympics commencing in Beijing; the largest Financial crisis of 2007–2008, economic crisis since the Great Depression hits the world in 2008; 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami, a tsunami from the Indian Ocean earthquake kills over 230,000 in 2004, and becomes the strongest earthquake since the 1964 Alaska earthquake, 420px, thumb rect 1 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech Synthesis
Speech synthesis is the artificial production of human speech. A computer system used for this purpose is called a speech synthesizer, and can be implemented in software or hardware products. A text-to-speech (TTS) system converts normal language text into speech; other systems render symbolic linguistic representations like phonetic transcriptions into speech. The reverse process is speech recognition. Synthesized speech can be created by concatenating pieces of recorded speech that are stored in a database. Systems differ in the size of the stored speech units; a system that stores phones or diphones provides the largest output range, but may lack clarity. For specific usage domains, the storage of entire words or sentences allows for high-quality output. Alternatively, a synthesizer can incorporate a model of the vocal tract and other human voice characteristics to create a completely "synthetic" voice output. The quality of a speech synthesizer is judged by its similarit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Image Synthesis
Human image synthesis is technology that can be applied to make believable and even photorealistic renditions of human-likenesses, moving or still. It has effectively existed since the early 2000s. Many films using computer generated imagery have featured synthetic images of human-like characters digitally composited onto the real or other simulated film material. Towards the end of the 2010s deep learning artificial intelligence has been applied to synthesize images and video that look like humans, without need for human assistance, once the training phase has been completed, whereas the old school 7D-route required massive amounts of human work. Timeline of human image synthesis * In 1971 Henri Gouraud made the first CG geometry capture and representation of a human face. Modeling was his wife Sylvie Gouraud. The 3D model was a simple wire-frame model and he applied the Gouraud shader he is most known for to produce the first known representation of human-likeness on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biometrics
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics. Biometric authentication (or realistic authentication) is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used to identify individuals in groups that are under surveillance. Biometric identifiers are the distinctive, measurable characteristics used to label and describe individuals. Biometric identifiers are often categorized as physiological characteristics which are related to the shape of the body. Examples include, but are not limited to fingerprint, palm veins, face recognition, DNA, palm print, hand geometry, iris recognition, retina, odor/scent, voice, shape of ears and gait. Behavioral characteristics are related to the pattern of behavior of a person, including but not limited to mouse movement, typing rhythm, gait, signature, behavioral profiling, and credentials. Some researchers have coined the term behaviometrics to describe the latter cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |