|
Adiposity
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and insulates the body. Previously treated as being hormonally inert, in recent years adipose tissue has been recognized as a major endocrine organ, as it produces hormones such as leptin, estrogen, resistin, and cytokines (especially TNFα). In obesity, adipose tissue is implicated in the chronic release of pro-inflammatory markers known as adipokines, which are responsible for the development of metabolic syndromea constellation of diseases including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. Adipose tissue is derived from preadipocytes and its formation appears to be con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Metabolic syndrome is associated with the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. In the U.S., about 25% of the adult population has metabolic syndrome, a proportion increasing with age, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. Insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and prediabetes are closely related to one another and have overlapping aspects. The syndrome is thought to be caused by an underlying disorder of energy utilization and storage, but the cause of the syndrome is an area of ongoing medical research. Researchers debate whether a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome implies differential treatment or increases risk of cardiovascular disease beyond what is suggested by the sum of its individual components. Signs and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visceral Fat
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of White blood cell, immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and Thermal insulation, insulates the body. Previously treated as being hormonally inert, in recent years adipose tissue has been recognized as a major endocrine organ, as it produces hormones such as leptin, estrogen, resistin, and cytokines (especially TNF-alpha, TNFα). In obesity, adipose tissue is implicated in the chronic release of pro-inflammatory markers known as adipokines, which are responsible for the development of metabolic syndromea constellation of diseases including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. Adipose tissue is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistin
Resistin, also known as adipose tissue-specific secretory factor (ADSF) or C/EBP-epsilon-regulated myeloid-specific secreted cysteine-rich protein (XCP1), is a cysteine-rich peptide hormone that is derived from adipose tissue and, in humans, is encoded by the ''RETN'' gene. In primates, pigs, and dogs, resistin is secreted primarily by immune and epithelial cells, whereas in rodents, it is mainly secreted by adipose tissue. The human resistin pre-peptide consists of 108 amino acid residues, while in mice and rats it is 114 amino acids in length; the molecular weight is approximately 12.5 kDa. Resistin is classified as an adipose-derived hormone (similar to a cytokine), and its physiological role has been widely debated, particularly regarding its involvement in obesity and type II diabetes mellitus ( T2DM). Discovery Resistin was discovered in 2001 and identified as a hormone produced by adipose tissue, with a role in promoting insulin resistance. Elevated resistin levels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptin
Leptin (from Ancient Greek, Greek λεπτός ''leptos'', "thin" or "light" or "small"), also known as obese protein, is a protein hormone predominantly made by adipocytes (cells of adipose tissue). Its primary role is likely to regulate long-term Energy homeostasis, energy balance. As one of the major signals of energy status, leptin levels influence appetite, Hunger (physiology), satiety, and motivated behaviors oriented toward the maintenance of energy reserves (e.g., feeding, foraging behaviors). The amount of circulating leptin correlates with the amount of energy reserves, mainly Triglyceride, triglycerides stored in adipose tissue. High leptin levels are interpreted by the brain that energy reserves are high, whereas low leptin levels indicate that energy reserves are low, in the process adapting the organism to Starvation response, starvation through a variety of metabolic, endocrine, neurobiochemical, and behavioral changes. Leptin is coded for by the ''LEP'' gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipokines
The adipokines, or adipocytokines (Greek ', fat; ', cell; and ', movement) are cytokines (cell signaling proteins) secreted by adipose tissue. Some contribute to an obesity-related low-grade state of inflammation or to the development of metabolic syndrome, a constellation of diseases including, but not limited to, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. The first adipokine to be discovered was leptin in 1994. Since that time, hundreds of adipokines have been discovered. Members include: * Leptin * Adiponectin * Apelin * chemerin * interleukin-6 (IL-6) * CCL2, monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) * plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) * retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4) * tumor necrosis factor * visfatin * omentin * vaspin (SERPINA12) * progranulin * CTRP-4 Interleukin 8 (IL-8), interleukin 10 (IL-10), interferon gamma (IFN-γ) and inducible protein 10 (IP-10 or CXCL10) have been shown to be associated with excessive body weight. See also * Adipose t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Fat
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, or superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's dermatome region. It consists primarily of loose connective tissue and contains larger blood vessels and nerves than those found in the dermis. It is a major site of fat storage in the body. In arthropods, a hypodermis can refer to an epidermal layer of cells that secretes the chitinous cuticle. The term also refers to a layer of cells lying immediately below the epidermis of plants. Structure * Fibrous bands anchoring the skin to the deep fascia * Collagen and elastin fibers attaching it to the dermis * Fat is absent from the eyelids, clitoris, penis, much of pinna, and scrotum * Blood vessels on route to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Adipose Tissue
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) or brown fat makes up the adipose organ together with white adipose tissue (or white fat). Brown adipose tissue is found in almost all mammals. Classification of brown fat refers to two distinct cell populations with similar functions. The first shares a common embryological origin with muscle cells, found in larger "classic" deposits. The second develops from white adipocytes that are stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system. These adipocytes are found interspersed in white adipose tissue and are also named 'beige' or 'brite' (for "brown in white"). Brown adipose tissue is especially abundant in newborns and in hibernation, hibernating mammals. It is also present and metabolically active in adult humans, but its prevalence decreases as humans age. Its primary function is thermoregulation. In addition to heat produced by shivering muscle, brown adipose tissue produces heat by non-shivering thermogenesis. The therapeutic targeting of brown fat for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Adipose Tissue
White adipose tissue or white fat is one of the two types of adipose tissue found in mammals. The other kind is brown adipose tissue. White adipose tissue is composed of monolocular Adipocyte, adipocytes. In humans, the healthy body fat percentage, amount of white adipose tissue varies with age, but composes between 6–25% of body weight in adult men and 14–35% in adult women. Its cells contain a single large Lipid droplet, fat droplet, which forces the nucleus to be squeezed into a thin rim at the periphery. They have receptors for insulin, sex hormones, norepinephrine, and glucocorticoids. White adipose tissue is used for energy storage. Upon release of insulin from the pancreas, white adipose cells' insulin receptors cause a dephosphorylation cascade that leads to the inactivation of hormone-sensitive lipase. It was previously thought that upon release of glucagon from the pancreas, glucagon receptors cause a phosphorylation cascade that activates hormone-sensitive lipase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ (anatomy)
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of Tissue (biology), tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the biological organization, hierarchy of life, an organ lies between Tissue (biology), tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type Cell (biology), cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma (tissue), stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerve t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
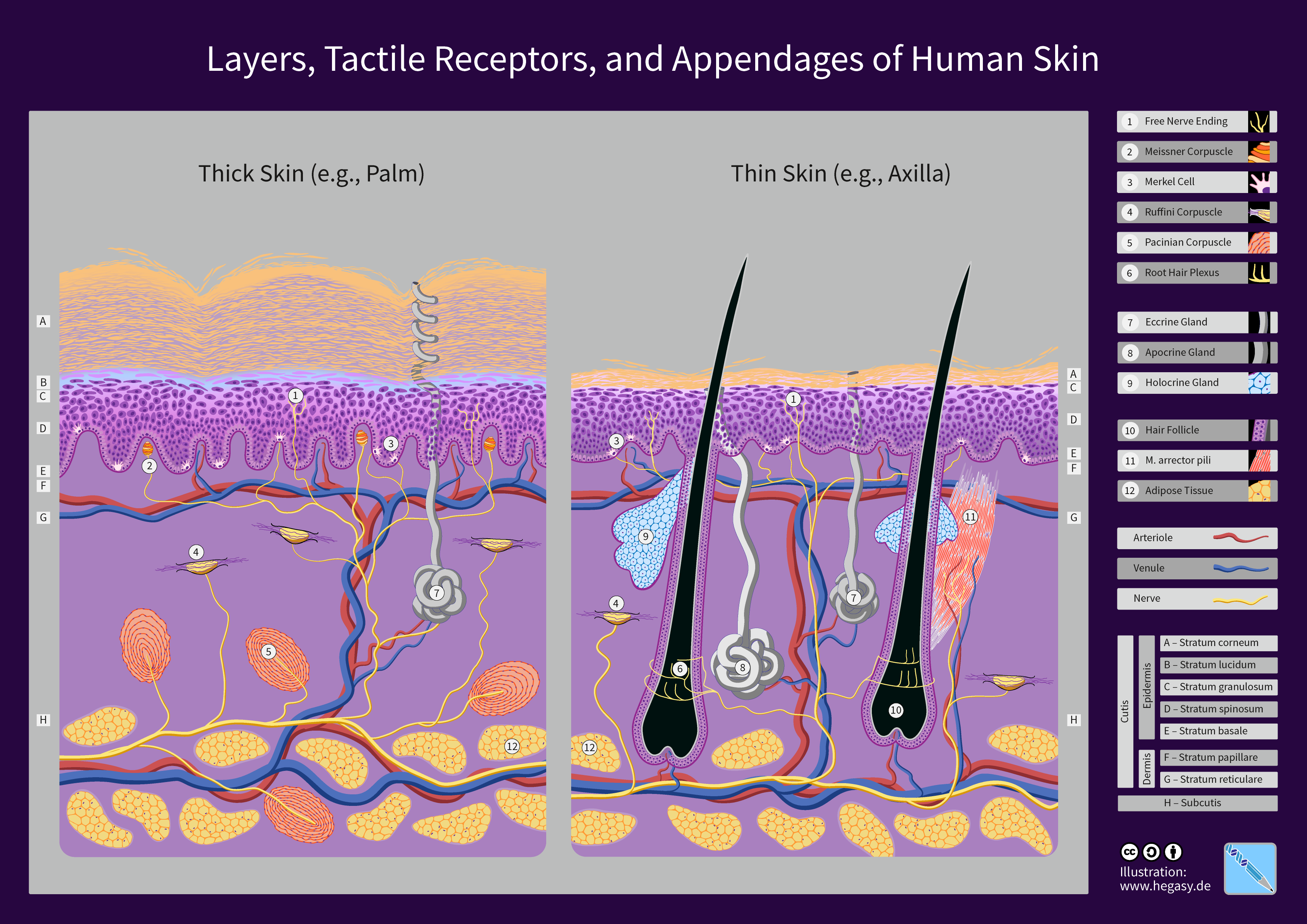
Human Skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue guarding Skeletal muscle, muscles, bones, ligaments and organ (anatomy), internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear Nudity#Evolution of hairlessness, hairless. There are two general types of skin: hairy and glabrous skin (hairless). The adjective List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes#C, ''cutaneous'' literally means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'', skin). Skin plays an important immunity (medical), immunity role in protecting the body against pathogens and excessive transepidermal water loss, water loss. Its other functions are Thermal insulation, insulation, thermoregulation, temperature regulation, sensation, synthesis of vitamin D, and the protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Adipose Distribution In The Body
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on television and computer screens is created by a mixture of red, blue, and green light. The color white can be given with white pigments, especially titanium dioxide. In ancient Egypt and ancient Rome, priestesses wore white as a symbol of purity, and Romans wore white togas as symbols of citizenship. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance a white unicorn symbolized chastity, and a white lamb sacrifice and purity. It was the royal color of the kings of France as well as the flag of monarchist France from 1815 to 1830, and of the monarchist movement that opposed the Bolsheviks during the Russian Civil War (1917–1922). Greek temples and Roman temples were faced with white marble, and beginning in the 18th century, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conrad Gessner
Conrad Gessner (; ; 26 March 1516 – 13 December 1565) was a Swiss physician, naturalist, bibliographer, and philologist. Born into a poor family in Zürich, Switzerland, his father and teachers quickly realised his talents and supported him through university, where he studied classical languages, theology and medicine. He became Zürich's city physician, but was able to spend much of his time on collecting, research and writing. Gessner compiled monumental works on bibliography ('' Bibliotheca universalis'' 1545–1549) and zoology ( 1551–1558) and was working on a major botanical text at the time of his death from plague at the age of 49. He is regarded as the father of modern scientific bibliography, zoology and botany. He was frequently the first to describe species of plants or animals in Europe, such as the tulip in 1559. A number of plants and animals have been named after him. Life Conrad Gessner was born on 26 March 1516, in Zürich, Switzerland, the son of Ursus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |