|
Adenanthos Cygnorum
''Adenanthos cygnorum'', commonly known as common woollybush or just woollybush, is a tall shrub in the family Proteaceae. It is endemic to Western Australia, commonly occurring in the south west of the State from north of Geraldton south to Kojonup. It is very common on road verges and in disturbed areas of Perth. Description Common woollybush grows as a tall shrub up to three metres high. It has soft grey-green or grey-blue foliage, consisting of closely packed, small, hairy leaves on pliable, hairy stems. It is woolly both in appearance and feel, hence the common name. The leaves have nectaries at the tips; these attract ants, which play a role in the distribution of seed. The nectar filled cups are taken by the ants to their nests to be consumed, the seeds becoming inaccessible to birds, etc. Like most other ''Adenanthos'' species, but unusually for Proteaceae, the flowers of common woollybush are not large and showy, but are rather small, dull, and hidden within the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Diels
Dr. Friedrich Ludwig Emil Diels (24 September 1874 – 30 November 1945) was a German botanist. Diels was born in Hamburg, the son of the classical scholar Hermann Alexander Diels. From 1900 to 1902 he traveled together with Ernst Georg Pritzel through South Africa, Java, Australia and New Zealand. Shortly before the First World War he travelled New Guinea and in the 1930s in Ecuador. Especially his collections of plants from Australia and Ecuador, which contained numerous holotypes, enriched the knowledge of the concerning floras. His monography on the Droseraceae from 1906 is still a standard. The majority of his collections were stored at the botanical garden in Berlin-Dahlem, whose vicedirector he had been since 1913, becoming its director in 1921 until 1945. His collections were destroyed there during an air raid in 1943. He died in Berlin on 30 November 1945. Honours Several genus of plants have been named after him including; ''Dielsantha'' (from ''Campanulaceae' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allan Cunningham (botanist)
Allan Cunningham (13 July 1791 – 27 June 1839) was an English botany, botanist and List of explorers, explorer, primarily known for his travels in Australia to collect plants. Early life Cunningham was born in Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon, Surrey, England, the son of Allan Cunningham (head gardener at Wimbledon Park House), who came from Renfrewshire, Scotland, and his English wife Sarah (née Juson/Jewson née Dicken). Allan Cunningham was educated at a Putney private school, Reverend John Adams (educational writer), John Adams Academy and then went into a solicitor's office (a Lincoln's Inn Conveyancer). He afterwards obtained a position with William Townsend Aiton superintendent of Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Kew Gardens, and this brought him in touch with Robert Brown (Scottish botanist from Montrose), Robert Brown and Joseph Banks, Sir Joseph Banks. Brazil and Australia (New South Wales) On Banks' recommendation, Cunningham went to Brazil with James Bowie (botani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
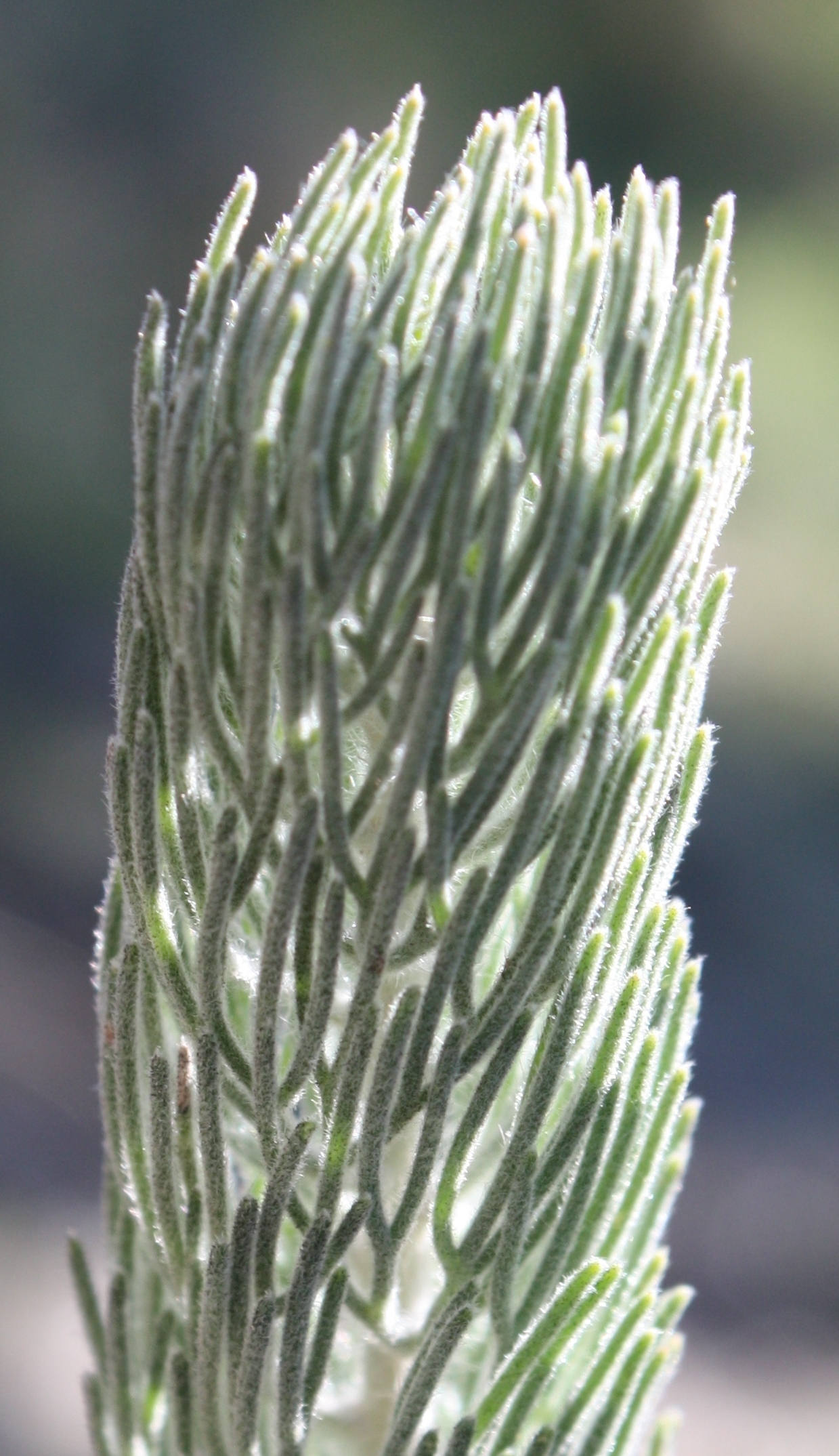
Adenanthos Cygnorum Foliage
''Adenanthos'' is a genus of Australian native shrubs in the flowering plant family Proteaceae. Variable in habit and leaf shape, it is the only genus in the family where solitary flowers are the norm. It was discovered in 1791, and formally published by Jacques Labillardière in 1805. The type species is ''Adenanthos cuneatus'', and 33 species are recognised. The genus is placed in subfamily Proteoideae, and is held to be most closely related to several South African genera. Endemic to Australia, its centre of diversity is southwest Western Australia, where 31 species occur. The other two species occur in South Australia and western Victoria (Australia). They are mainly pollinated by birds. Description Habit The growth habits of ''Adenanthos'' species range from prostrate shrubs to small trees, with most species occurring as erect shrubs. There are two basic growth forms. Plants that lack a lignotuber have a single stem. Such plants usually grow into fairly erect shrubs; and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of The Environment And Heritage
The Department of the Environment and Heritage was an Australian government The Australian Government, also known as the Commonwealth Government, is the national government of Australia, a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy. Like other Westminster-style systems of government, the Australian Government ... department that existed between October 1998 and December 2007. Scope Information about the department's functions and/or government funding allocation could be found in the Administrative Arrangements Orders, the annual Portfolio Budget Statements, in the department's annual reports and on the department's website. At its creation, the department was responsible for: *Environment and conservation *Meteorology *Administration of the Australian Antarctic Territory and the Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands *Natural and built heritage *Greenhouse policy coordination Structure The department was an Australian Public Service departme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytophthora Cinnamomi
''Phytophthora cinnamomi'' is a soil-borne water mould that produces an infection which causes a condition in plants variously called "root rot", "dieback", or (in certain '' Castanea'' species), "ink disease". The plant pathogen is one of the world's most invasive species and is present in over 70 countries around the world. Host range and symptoms The host range for ''Phytophythora cinnamomi'' is very broad. It is distributed worldwide and causes disease on hundreds of hosts. The disease affects a range of economic groups, including food crops such as avocado and pineapple as well as trees and woody ornamentals such as Fraser firs, shortleaf pines, loblolly pines, azaleas, camellia, boxwood, causing root rot and dieback. It is a root pathogen that causes root rot and death of host plants. Some symptoms include: wilting, decreased fruit size, decrease in yield, collar rot, gum exudation, necrosis, leaf chlorosis, leaf curl, and stem cankers. Another symptom is that it can cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Honeyeater
The brown honeyeater (''Lichmera indistincta'') is a species of bird in the family Meliphagidae. It belongs to the honeyeaters, a group of birds which have highly developed brush-tipped tongues adapted for nectar feeding. Honeyeaters are found mainly in Australia, New Guinea, and parts of Indonesia, but the brown honeyeater is unique in that it also occurs on the island of Bali, making it the only honeyeater to be found west of the Wallace Line, the biogeographical boundary between the Australian-Papuan and Oriental zoogeographical regions. It is a medium-small brownish bird, with yellow-olive panels in the tail and wing, and a yellow tuft behind the eye. It is widespread across western, northern and eastern Australia, New Guinea and surrounding islands, and the Lesser Sundas of Indonesia. Throughout this range, the brown honeyeater occupies a range of habitats from mangroves to eucalypt woodlands. It is seasonally nomadic within its local area, following flowering food plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenanthos Cygnorum Chamaephyton
''Adenanthos'' is a genus of Australian native shrubs in the flowering plant family Proteaceae. Variable in habit and leaf shape, it is the only genus in the family where solitary flowers are the norm. It was discovered in 1791, and formally published by Jacques Labillardière in 1805. The type species is ''Adenanthos cuneatus'', and 33 species are recognised. The genus is placed in subfamily Proteoideae, and is held to be most closely related to several South African genera. Endemic to Australia, its centre of diversity is southwest Western Australia, where 31 species occur. The other two species occur in South Australia and western Victoria (Australia). They are mainly pollinated by birds. Description Habit The growth habits of ''Adenanthos'' species range from prostrate shrubs to small trees, with most species occurring as erect shrubs. There are two basic growth forms. Plants that lack a lignotuber have a single stem. Such plants usually grow into fairly erect shrubs; and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenanthos Cygnorum Cygnorum
''Adenanthos'' is a genus of Australian native shrubs in the flowering plant family Proteaceae. Variable in habit and leaf shape, it is the only genus in the family where solitary flowers are the norm. It was discovered in 1791, and formally published by Jacques Labillardière in 1805. The type species is ''Adenanthos cuneatus'', and 33 species are recognised. The genus is placed in subfamily Proteoideae, and is held to be most closely related to several South African genera. Endemic to Australia, its centre of diversity is southwest Western Australia, where 31 species occur. The other two species occur in South Australia and western Victoria (Australia). They are mainly pollinated by birds. Description Habit The growth habits of ''Adenanthos'' species range from prostrate shrubs to small trees, with most species occurring as erect shrubs. There are two basic growth forms. Plants that lack a lignotuber have a single stem. Such plants usually grow into fairly erect shrubs; and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Locality (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is almost a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swan River, Western Australia
The Swan River () is a river in the south west of Western Australia. The river runs through the metropolitan area of Perth, Western Australia's capital and largest city. Course of river The Swan River estuary flows through the city of Perth. Its lower reaches are relatively wide and deep, with few constrictions, while the upper reaches are usually quite narrow and shallow. The Swan River drains the Avon and coastal plain catchments, which have a total area of about . It has three major tributaries, the Avon River, Canning River and Helena River. The latter two have dams (Canning Dam and Mundaring Weir) which provide a sizeable part of the potable water requirements for Perth and the regions surrounding. The Avon River contributes the majority of the freshwater flow. The climate of the catchment is Mediterranean, with mild wet winters, hot dry summers, and the associated highly seasonal rainfall and flow regime. The Avon rises near Yealering, southeast of Perth: it meand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Botanical Province
Southwest Australia is a ecoregion, biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna. The region is also known as the Southwest Australia Global Diversity Hotspot, as well as Kwongan. Geography The region includes the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregions of Western Australia. The region covers 356,717 km2, consisting of a broad coastal plain 20-120 kilometres wide, transitioning to gently undulating uplands made up of weathered granite, gneiss and laterite. Bluff Knoll in the Stirling Range is the highest peak in the region, at 1,099 metres (3,606 ft) elevation. Deserts and xeric shrublands, Desert and xeric shrublands lie to the north and east across the centre of Australia, separating Southwest Australia from the other Mediterranean and humid-climate regions of the continent. Climate The region has a wet-wint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)