|
Actuators
An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving and controlling a mechanism or system, for example by opening a valve. In simple terms, it is a "mover". An actuator requires a control device (controlled by control signal) and a source of energy. The control signal is relatively low energy and may be electric voltage or current, pneumatic, or hydraulic fluid pressure, or even human power. Its main energy source may be an electric current, hydraulic pressure, or pneumatic pressure. The Control device is usually a valve. When it receives a control signal, an actuator responds by converting the source's energy into mechanical motion. In the ''electric'', ''hydraulic'', and ''pneumatic'' sense, it is a form of automation or automatic control. History The history of the pneumatic actuation system and the hydraulic actuation system dates to around the time of World War II (1938). It was first created by Xhiter Anckeleman who used his knowledge of engines and brake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
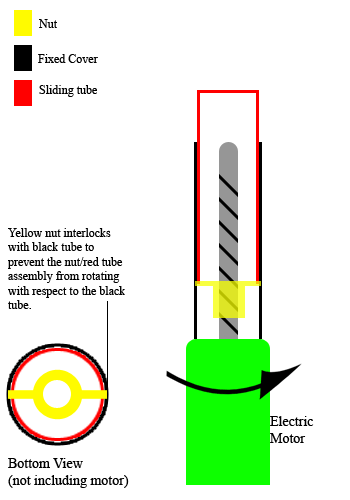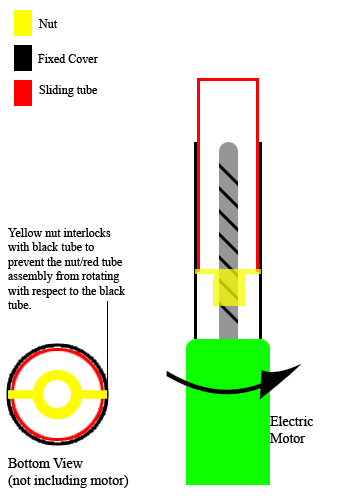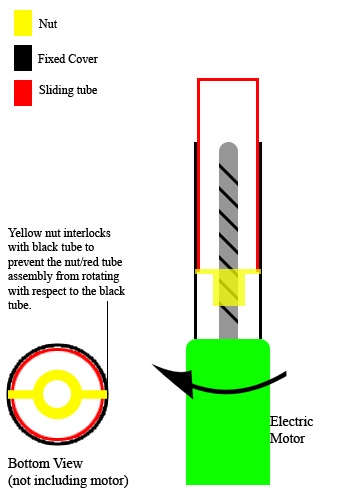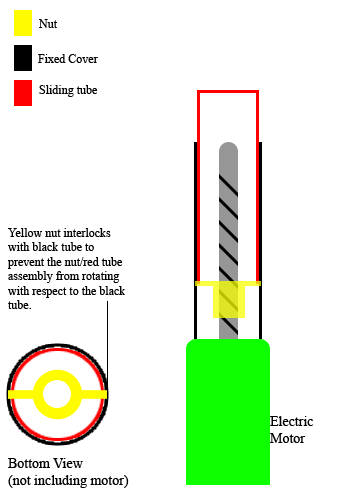
Linear Actuator
A linear actuator is an actuator that creates motion in a straight line, in contrast to the circular motion of a conventional electric motor. Linear actuators are used in machine tools and industrial machinery, in computer Peripheral, peripherals such as disk drives and printers, in Valve, valves and Damper (flow), dampers, and in many other places where linear motion is required. Hydraulics, Hydraulic or Pneumatics, pneumatic cylinders inherently produce linear motion. Many other mechanisms are used to generate linear motion from a rotating motor. Types Mechanical actuators Machine, Mechanical linear actuators typically operate by conversion of rotary motion into linear motion. Conversion is commonly made via a few simple types of mechanism: * Screw (simple machine), Screw: leadscrew, screw jack, ball screw and roller screw actuators all operate on the principle of the simple machine known as the screw. By rotating the actuator's nut, the screw shaft moves in a line. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shape-memory Alloy
In metallurgy, a shape-memory alloy (SMA) is an alloy that can be deformed when cold but returns to its pre-deformed ("remembered") shape when heated. It may also be called memory metal, memory alloy, smart metal, smart alloy, or muscle wire. Parts made of shape-memory alloys can be lightweight, solid-state alternatives to conventional actuators such as hydraulic, pneumatic, and motor-based systems. They can also be used to make hermetic joints in metal tubing. Overview The two most prevalent shape-memory alloys are copper-aluminium-nickel and nickel-titanium (NiTi), but SMAs can also be created by alloying zinc, copper, gold and iron. Although iron-based and copper-based SMAs, such as Fe-Mn-Si, Cu-Zn-Al and Cu-Al-Ni, are commercially available and cheaper than NiTi, NiTi-based SMAs are preferable for most applications due to their stability and practicability as well as their superior thermo-mechanic performance. SMAs can exist in two different phases, with three different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical System
A machine is a physical system using Power (physics), power to apply Force, forces and control Motion, movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecules, such as molecular machines. Machines can be driven by Animal power, animals and Human power, people, by natural forces such as Wind power, wind and Water power, water, and by Chemical energy, chemical, Thermal energy, thermal, or electricity, electrical power, and include a system of mechanism (engineering), mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement. They can also include computers and sensors that monitor performance and plan movement, often called mechanical systems. Renaissance natural philosophers identified six simple machines which were the elementary devices that put a load into motion, and calculated the ratio of output force to input fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rack And Pinion
A rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that comprises a circular gear (the '' pinion'') engaging a linear gear (the ''rack''). Together, they convert rotational motion into linear motion. Rotating the pinion causes the rack to be driven in a line. Conversely, moving the rack linearly will cause the pinion to rotate. A rack and pinion drive can use both straight and helical gears. Though some suggest helical gears are quieter in operation, no hard evidence supports this theory. Helical racks, while being more affordable, have proven to increase side torque on the datums, increasing operating temperature leading to premature wear. Straight racks require a lower driving force and offer increased torque and speed per percentage of gear ratio which allows lower operating temperature and lessens viscal friction and energy use. The maximum force that can be transmitted in a rack and pinion mechanism is determined by the tooth pitch and the size of the pinion as well as the gear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Shape-memory Alloy
Magnetic shape memory alloys (MSMAs), also called ferromagnetic shape memory alloys (FSMA), are particular shape memory alloys which produce forces and deformations in response to a magnetic field. The thermal shape memory effect has been obtained in these materials, too. Introduction MSM alloys are ferromagnetic materials that can produce motion and forces under moderate magnetic fields. Typically, MSMAs are alloys of Nickel, Manganese and Gallium (Ni-Mn-Ga). A ''magnetically induced deformation'' of about 0.2% was presented in 1996 by Dr. Kari Ullakko and co-workers at MIT. Since then, improvements on the production process and on the subsequent treatment of the alloys have led to deformations of up to 6% for commercially available ''single crystalline'' Ni-Mn-Ga MSM elements, as well as up to 10-12 % and 20% for new alloys in R&D stage. The large magnetically induced strain, as well as the short response times make the MSM technology very attractive for the design of innovat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines. Automation has been achieved by various means including mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, electronic devices, and computers, usually in combination. Complicated systems, such as modern factories, airplanes, and ships typically use combinations of all of these techniques. The benefit of automation includes labor savings, reducing waste, savings in electricity costs, savings in material costs, and improvements to quality, accuracy, and precision. Automation includes the use of various equipment and control systems such as machinery, processes in factories, boilers, and heat-treating ovens, switching on telephone networks, steering, and stabilization of ships, aircraft, and other applications and vehicles with reduced hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Fluid
A hydraulic fluid or hydraulic liquid is the medium by which power is transferred in hydraulic machinery. Common hydraulic fluids are based on mineral oil or water. Examples of equipment that might use hydraulic fluids are excavators and backhoes, hydraulic brakes, power steering systems, automatic transmissions, garbage trucks, aircraft flight control systems, lifts, and industrial machinery. Hydraulic systems like the ones mentioned above will work most efficiently if the hydraulic fluid used has zero compressibility. Functions and properties The primary function of a hydraulic fluid is to convey power. In use, however, there are other important functions of hydraulic fluid such as protection of the hydraulic machine components. The table below lists the major functions of a hydraulic fluid and the properties of a fluid that affect its ability to perform that function: Composition Base stock The original hydraulics fluid, dating back to the time of ancient Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Motor
A linear motor is an electric motor that has had its stator and rotor "unrolled", thus, instead of producing a torque (rotation), it produces a linear force along its length. However, linear motors are not necessarily straight. Characteristically, a linear motor's active section has ends, whereas more conventional motors are arranged as a continuous loop. A typical mode of operation is as a Lorentz-type actuator, in which the applied force is linearly proportional to the current and the magnetic field (\vec F = I \vec L \times \vec B). Linear motors are by far most commonly found in high accuracy engineering applications. It is a thriving field of applied research with dedicated scientific conferences and engineering text books. Many designs have been put forward for linear motors, falling into two major categories, low-acceleration and high-acceleration linear motors. Low-acceleration linear motors are suitable for maglev trains and other ground-based transportation applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
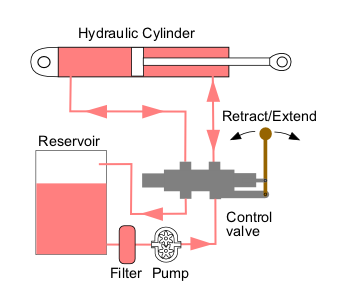
Hydraulic Machinery
Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and becomes pressurized according to the resistance present. The fluid is controlled directly or automatically by control valves and distributed through hoses, tubes, or pipes. Hydraulic systems, like pneumatic systems, are based on Pascal's law which states that any pressure applied to a fluid inside a closed system will transmit that pressure equally everywhere and in all directions. A hydraulic system uses an incompressible liquid as its fluid, rather than a compressible gas. The popularity of hydraulic machinery is due to the very large amount of power that can be transferred through small tubes and flexible hoses, the high power density and a wide array of actuators that can make use of this power, and the huge multiplication of forces t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Motor
An electric motor is an Electric machine, electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a Electromagnetic coil, wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates with a reversed flow of power, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries, or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, Inverter (electrical), inverters or electrical generators. Electric motors may be classified by considerations such as power source type, construction, application and type of motion output. They can be powered by AC or DC, be Brushed motor, brushed or Brushless motor, brushless, single-phase, Two-phase electric power, two-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Motion
Linear motion, also called rectilinear motion, is one-dimensional motion along a straight line, and can therefore be described mathematically using only one spatial dimension. The linear motion can be of two types: uniform linear motion, with constant velocity (zero acceleration); and non-uniform linear motion, with variable velocity (non-zero acceleration). The motion of a particle (a point-like object) along a line can be described by its position x, which varies with t (time). An example of linear motion is an athlete running a 100-meter dash along a straight track. Linear motion is the most basic of all motion. According to Newton's first law of motion, objects that do not experience any net force will continue to move in a straight line with a constant velocity until they are subjected to a net force. Under everyday circumstances, external forces such as gravity and friction can cause an object to change the direction of its motion, so that its motion cannot be described as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotary Motion
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed-axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's rotation theorem, simultaneous rotation along a number of stationary axes at the same time is impossible; if two rotations are forced at the same time, a new axis of rotation will appear. This article assumes that the rotation is also stable, such that no torque is required to keep it going. The kinematics and dynamics of rotation around a fixed axis of a rigid body are mathematically much simpler than those for free rotation of a rigid body; they are entirely analogous to those of linear motion along a single fixed direction, which is not true for ''free rotation of a rigid body''. The expressions for the kinetic energy of the object, and for the forces on the parts of the object, are also simpler for rotation around a fixed axis, than for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |