|
Active Window
A window manager is system software that controls the placement and appearance of windows within a windowing system in a graphical user interface. Most window managers are designed to help provide a desktop environment. They work in conjunction with the underlying graphical system that provides required functionality—support for graphics hardware, pointing devices, and a keyboard—and are often written and created using a widget toolkit. Few window managers are designed with a clear distinction between the windowing system and the window manager. Every graphical user interface based on a windows metaphor has some form of window management. In practice, the elements of this functionality vary greatly. Elements usually associated with window managers allow the user to open, close, minimize, maximize, move, resize, and keep track of running windows, including window decorators. Many window managers also come with various utilities and features such as task bars, program lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schema Of The Layers Of The Graphical User Interface
Schema may refer to: Science and technology * SCHEMA (bioinformatics), an algorithm used in protein engineering * Schema (genetic algorithms), a set of programs or bit strings that have some genotypic similarity * Schema.org, a web markup vocabulary * Schema (logic) ** Axiom schema, in formal logic * Image schema, a recurring pattern of spatial sensory experience * Database schema * XML schema Other * Body schema, a neural representation of one's own bodily posture * Galant Schemata, stock phrases in Galant music * Schema (Kant), in philosophy * Schema (psychology), a mental set or representation * Schema Records, a jazz record label in Milan, Italy *, a solemn vow of asceticism of a monk in Orthodox monasticism ** Great Schema, the highest degree of Orthodox monasticism * Schema (fly), ''Schema'' (fly), a genus of insects See also * Scheme (other) * Schematic * Skema (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
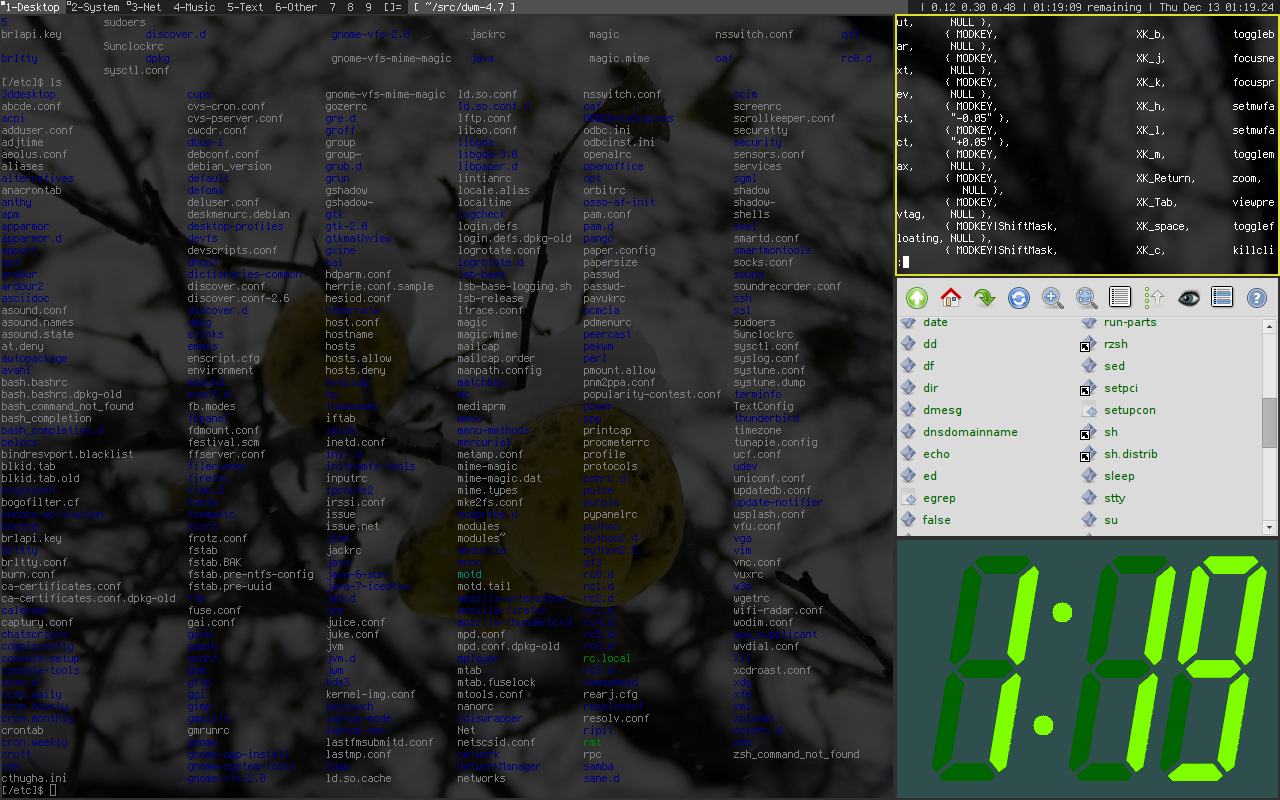
Stacking Window Manager
A stacking window manager (also called floating window manager) is a window manager that draws and allows windows to overlap, without using a compositing algorithm. All window managers that allow the overlapping of windows but are not compositing window managers are considered stacking window managers, although it is possible that not all use exactly the same methods. Other window managers that are not considered stacking window managers are those that do not allow the overlapping of windows, which are called tiling window managers. Stacking window managers allow windows to overlap using clipping to allow applications to write only to the visible parts of the windows they present. The order in which windows are to be stacked is called their z-order. History * 1970s: The Xerox Alto which contained the first working commercial GUI used a stacking window manager. * Early 1980s: The Xerox Star, successor to the Alto, used tiling for most main application windows, and used over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GEM (desktop Environment)
GEM (for Graphics Environment Manager) is a discontinued operating environment released by Digital Research in 1985. GEM is known primarily as the native graphical user interface of the Atari ST series of computers, providing a WIMP desktop. It was also available for IBM PC compatibles and shipped with some models from Amstrad. GEM is used as the core for some commercial MS-DOS programs, the most notable being Ventura Publisher. It was ported to other computers that previously lacked graphical interfaces, but never gained traction. The final retail version of GEM was released in 1988. Digital Research later produced X/GEM for their FlexOS real-time operating system with adaptations for OS/2 Presentation Manager and the X Window System under preparation as well. History GSX In late 1984, GEM started life at DRI as an outgrowth of a more general-purpose graphics library known as GSX (Graphics System Extension), written by a team led by Don Heiskell since about 1982. Lee Jay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating Environment
In computer software, an operating environment or integrated applications environment is the environment in which users run application software. The environment consists of a user interface provided by an applications manager and usually an application programming interface (API) to the applications manager. An operating environment is ''not'' a full operating system, but is a form of middleware that rests between the OS and the application. For example, the first version of Microsoft Windows, Windows 1.0, was not a full operating system, but a GUI laid over DOS albeit with an API of its own. Similarly, the IBM U2 system operates on both Unix/Linux and Windows NT. Usually the user interface is text-based or graphical, rather than a command-line interface (e.g., DOS or the Unix shell), which is often the interface of the underlying operating system. In the mid 1980s, text-based and graphical user interface operating environments surrounded DOS operating systems with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Research
Digital Research, Inc. (DR or DRI) was a privately held American software company created by Gary Kildall to market and develop his CP/M operating system and related 8-bit, 16-bit and 32-bit systems like MP/M, Concurrent DOS, FlexOS, Multiuser DOS, DOS Plus, DR DOS and Graphics Environment Manager, GEM. It was the first large software company in the microcomputer world. Digital Research was originally based in Pacific Grove, California, later in Monterey, California. History 1974–1979: Founding and incorporation In 1972, Gary Kildall, an instructor at the Naval Postgraduate School in Monterey, California, began working at Intel as a consultant under the business name Microcomputer Applications Associates (MAA). By 1974, he had developed Control Program/Monitor, or CP/M, the first disk operating system for microcomputers. In 1974 he incorporated as Intergalactic Digital Research, with his wife handling the business side of the operation. The company soon began opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GEM 1
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. Certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, jet, and pearl) may also be used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some softer minerals such as brazilianite may be used in jewelry because of their color or luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. However, generally speaking, soft minerals are not typically used as gemstones by virtue of their brittleness and lack of durability. Found all over the world, the industry of coloured gemstones (i.e. anything other than diamonds) is currently estimated at US$1.55billion and is projected to steadily increase to a value of $4.46billion by 2033. A gem expert is a gemol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ars Technica
''Ars Technica'' is a website covering news and opinions in technology, science, politics, and society, created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews, and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, science, technology policy, and video games. ''Ars Technica'' was privately owned until May 2008, when it was sold to Condé Nast Digital, the online division of Condé Nast Publications. Condé Nast purchased the site, along with two others, for $25 million and added it to the company's ''Wired'' Digital group, which also includes '' Wired'' and, formerly, Reddit. The staff mostly works from home and has offices in Boston, Chicago, London, New York City, and San Francisco. The operations of ''Ars Technica'' are funded primarily by advertising, and it has offered a paid subscription service since 2001. History Ken Fisher, who serves as the website's current editor-in-chief, and Jon Stokes created ''Ars Technica'' in 1998. Its purpose was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz Compositor
Quartz Compositor is the display server (and at the same time the compositing window manager) in macOS. It is responsible for presenting and maintaining rasterized, rendered graphics from the rest of the Core Graphics framework and other renderers in the Quartz technologies family. Overview The bitmap output from Quartz 2D, OpenGL, Core Image, QuickTime, or other process is written to a specific memory location, or ''backing store''. The Compositor then reads the data from the backing stores and assembles each into one image for the display, writing that image to the frame buffer memory of the graphics card. Quartz Compositor only accepts raster data, and is the only process that can directly access the graphics frame buffer. In managing individual windows, Quartz Compositor accepts a bitmap image of the window's contents from its renderer, along with its position. The choice of the renderer is up to the individual application, although most use Quartz 2D. Quartz Composi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mac OS X 10
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of Desktop computer, desktop and laptop computers, it is the Usage share of operating systems#Desktop and laptop computers, second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows and ahead of all Linux distributions, including ChromeOS and SteamOS. , the most recent release of macOS is MacOS Sequoia, macOS 15 Sequoia, the 21st major version of macOS. Mac OS X succeeded classic Mac OS, the primary Mac operating systems, Macintosh operating system from 1984 to 2001. Its underlying architecture came from NeXT's NeXTSTEP, as a result of NeXT#1997–2006: Acquisition by Apple, Apple's acquisition of NeXT, which also brought Steve Jobs back to Apple. The first desktop version, Mac OS X 10.0, was released on March 24, 2001. Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QuickDraw
QuickDraw was the 2D graphics library and associated application programming interface (API) which is a core part of classic Mac OS. It was initially written by Bill Atkinson and Andy Hertzfeld. QuickDraw still existed as part of the libraries of Mac OS X, but had been largely superseded by the more modern Quartz graphics system. In Mac OS X Tiger, QuickDraw has been officially deprecated. In Mac OS X Leopard applications using QuickDraw cannot make use of the added 64-bit support. In OS X Mountain Lion, QuickDraw header support was removed from the operating system. Applications using QuickDraw still ran under OS X Mountain Lion to macOS High Sierra; however, the current versions of Xcode and the macOS SDK do not contain the header files to compile such programs. Principles of QuickDraw QuickDraw was grounded in the Apple Lisa's LisaGraf of the early 1980s and was designed to fit well with the Pascal-based interfaces and development environments of the early Apple syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiling Window Manager
In computing, a tiling window manager is a window manager with the organization of the screen often dependant on mathematical formulas to organise the windows into a non-overlapping frame. This is opposed to the more common approach used by stacking window managers, which allow the user to drag windows around, instead of windows snapping into a position. This allows for a different style of organization, although it departs from the traditional desktop metaphor. History Xerox PARC The first Xerox Star system (released in 1981) tiled application windows, but allowed dialog boxes and property windows to overlap. Later, Xerox PARC also developed CEDAR (released in 1982), the first windowing system using a tiled window manager. Various vendors Next in 1983 came Andrew Project, Andrew WM, a complete tiled windowing system later replaced by X11. Microsoft's Windows 1.0 (released in 1985) also used tiling (see sections below). In 1986 came Digital Research's Graphics Environment Manag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |