|
Action Of 17 November 1865
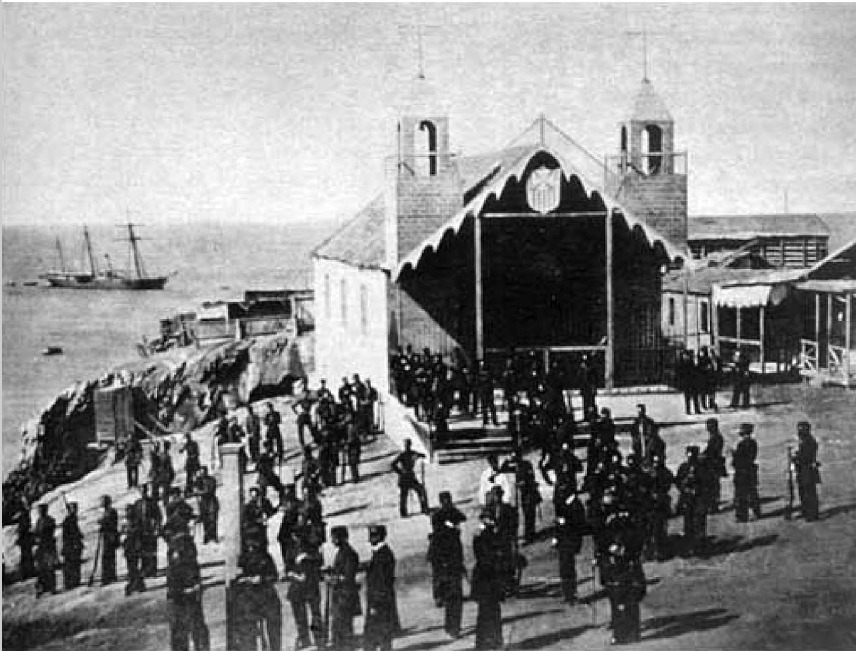
The action of 17 November 1865 was a minor naval engagement that took place off Tomé, during the Chincha Islands War. Chilean tugboat ''Independencia'' captured a Spanish gunboat who belonged to the frigate ''Resolución''. Events Background On 24 September 1865, the Spanish admiral José Manuel Pareja declared the start of hostilities against Chile, resolving to establish the blockade of its ports due to the refusal of this country to accept the Spanish demands. This caused the Chilean government to declare war on Spain the next day, in response to Pareja's hostility. The Spanish admiral wanted to blockade the entire Chilean coast with his warships, but due to its extension he had to limit himself with great difficulty to the ports of Valparaíso, Caldera, Coquimbo, La Herradura, Tomé and Talcahuano. In the first days of the war, the frigate ''Resolución'' was in charge of the blockade of the last two ports mentioned, in the bay of Concepción, where there were also small p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chincha Islands War
The Chincha Islands War, also known as Spanish–South American War ( es, Guerra hispano-sudamericana), was a series of coastal and naval battles between Spain and its former colonies of Peru, Chile, Ecuador, and Bolivia from 1865 to 1879. The conflict began with Spain's seizure of the guano-rich Chincha Islands in one of a series of attempts by Spain, under Isabella II, to reassert its influence over its former South American colonies. The war saw the use of ironclads, including the Spanish ship '' Numancia'', the first ironclad to circumnavigate the world. Background Military expenditures were greatly increased during Isabella's reign and Spain rose to a position as the world's fourth naval power. In the 1850s and 1860s Spain engaged in colonial adventures all over the world, including Morocco, Philippines, Mexico, and the Dominican Republic, the last of which it briefly reoccupied. At the end of 1862, Spain sent a scientific expedition to South American waters with the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prize (law)
In admiralty law prizes are equipment, vehicles, vessels, and cargo captured during armed conflict. The most common use of ''prize'' in this sense is the capture of an enemy ship and her cargo as a prize of war. In the past, the capturing force would commonly be allotted a share of the worth of the captured prize. Nations often granted letters of marque that would entitle private parties to capture enemy property, usually ships. Once the ship was secured on friendly territory, she would be made the subject of a prize case: an ''in rem'' proceeding in which the court determined the status of the condemned property and the manner in which the property was to be disposed of. History and sources of prize law In his book ''The Prize Game'', Donald Petrie writes, "at the outset, prize taking was all smash and grab, like breaking a jeweler's window, but by the fifteenth century a body of guiding rules, the maritime law of nations, had begun to evolve and achieve international recogn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1865 In Chile
The following lists events that happened during 1865 in Chile. Incumbents *President of Chile: José Joaquín Pérez Events November *26 November - Battle of Papudo Births *date unknown - Tomás Guevara (d. 1935) *1 April - Irene Morales (d. 1890) Deaths *date unknown - Joaquín Tocornal (b. 1788) *28 November - José Manuel Pareja (b. 1813) References {{South America topic, 1865 in 1860s in Chile Chile Chile Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ... Years of the 19th century in Chile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1865
Conflict may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Conflict'' (1921 film), an American silent film directed by Stuart Paton * ''Conflict'' (1936 film), an American boxing film starring John Wayne * ''Conflict'' (1937 film), a Swedish drama film directed by Per-Axel Branner * ''Conflict'' (1938 film), a French drama film directed by Léonide Moguy * ''Conflict'' (1945 film), an American suspense film starring Humphrey Bogart * ''Catholics: A Fable'' (1973 film), or ''The Conflict'', a film starring Martin Sheen * ''Judith'' (1966 film) or ''Conflict'', a film starring Sophia Loren * ''Samar'' (1999 film) or ''Conflict'', a 1999 Indian film by Shyam Benegal Games * ''Conflict'' (series), a 2002–2008 series of war games for the PS2, Xbox, and PC * ''Conflict'' (video game), a 1989 Nintendo Entertainment System war game * '' Conflict: Middle East Political Simulator'', a 1990 strategy computer game Literature and periodicals * ''Conflict'' (novel) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of The Chincha Islands War
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Battles Involving Chile
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface ships, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores (for example, to protect sea-lanes, deter or confront piracy, ferry troops, or attack other navies, ports, or shore installations). The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of the navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broadly divided between riverine and littoral applications (brown-water navy), open-ocean applications (blue- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Battles Involving Spain
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral zone, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface Naval ship, ships, amphibious warfare, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne naval aviation, aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is Power projection, projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores (for example, to protect Sea lane, sea-lanes, deter or confront piracy, ferry troops, or attack other navies, ports, or shore installations). The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of the navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of South America
The history of South America is the study of the past, particularly the written record, oral histories, and traditions, passed down from generation to generation on the continent of South America. The continent continues to be home to indigenous peoples, some of whom built high civilizations prior to the arrival of Europeans in the late 1400s and early 1500s. South America has a history that has a wide range of human cultures and forms of civilization. The Norte Chico civilization in Peru is the oldest civilization in the Americas and one of the first six independent civilizations in the world; it was contemporaneous with the Egyptian pyramids. It predated the Mesoamerican Olmec by nearly two millennia. Millennia of independent indigenous existence was disrupted by European colonization from Spain and Portugal, and by demographic collapse. However, the resulting culture both in continent's ''mestizos'', and in indigenous cultures remained quite distinct from those of their co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Papudo
The Naval Battle of Papudo was a naval engagement fought between Spanish and Chilean forces on November 26, 1865, during the Chincha Islands War. It was fought 55 miles north of Valparaiso, Chile, near the coastal town of Papudo. Background Until November 1865, Chile had been the only country firm in its declaration of war against Spain, which desired to recapture its lost South American colonies. Through the efforts of its president, Mariano Ignacio Prado, Peru was subsequently galvanized into action against Spain. Familiar with Spanish naval movements, the Chilean corvette '' Esmeralda'', under the command of Juan Williams Rebolledo, and whose crew included Arturo Prat, Juan José Latorre and Carlos Condell, waited for any Spanish ships to appear between Coquimbo and Valparaíso. The Chileans hoisted a British flag on their ship and maneuvered themselves close to the Spanish ship '' Virgen de Covadonga'', under the command of Luis Fery (or Ferry), who thought that the sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Mercurio
''El Mercurio'' (known online as ''El Mercurio On-Line'', ''EMOL'') is a Chilean newspaper with editions in Valparaíso and Santiago. Its Santiago edition is considered the country's newspaper of record and it is considered the oldest daily in the Spanish language currently in circulation. ''El Mercurio'' is owned by El Mercurio S.A.P. (''Sociedad Anónima Periodística'' 'joint stock news company'), which operates a network of 19 regional dailies and 32 radio stations across the country. History The Valparaíso edition of ''El Mercurio'' was founded by Pedro Félix Vicuña ( Benjamín Vicuña Mackenna's father) on September 12, 1827, and was later acquired by Agustín Edwards Ross in 1880. The Santiago edition was founded by Agustín Edwards Mac Clure, son of Edwards Ross, on June 1, 1900. In 1942 Edwards Mac Clure died and his son Agustín Edwards Budge took over as president. When Edwards Budge died in 1956, his son, Agustín Edwards Eastman, took control of the company. Edwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitución, Chile
Constitución () is a city and commune of Talca Province, Maule Region, Chile. It was historically a popular seaside resort. However, following the growth of the industrial sector (paper and pulp) tourism has since declined. Constitución is a minor port in Chile. History Before the arrival of the Spanish, the area that would later be the city of Constitución was inhabited by the Chango people and the Mapuche tribe. Both indigenous groups used the area for fishing and seasonal habitation. When the Spaniards came to the region, the European explorers, and those who followed, used the area as a port for their galleons and merchant ships on their voyages to South American and other Pacific ports. ''Nueva Bilbao'' While numerous attempts were made to establish a permanent settlement in the area, Santiago Oñederra was the first successful colonizing pioneer, circa 1791. The founding of the settlement was proposed by Oñederra to the Chilean government, and authorized by Gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)
