|
Acinar
An acinus (; plural, acini; adjective, acinar or acinous) refers to any cluster of cells that resembles a many-lobed "berry," such as a raspberry (''acinus'' is Latin for "berry"). The berry-shaped termination of an exocrine gland, where the secretion is produced, is acinar in form, as is the alveolar sac containing multiple alveoli in the lungs. Exocrine glands Acinar exocrine glands are found in many organs, including: * the stomach * the sebaceous gland of the scalp * the salivary glands of the tongue * the liver * the lacrimal glands * the mammary glands * the pancreas * the bulbourethral (Cowper's) glands The thyroid follicles can also be considered of acinar formation but in this case the follicles, being part of an ''endocrine'' gland, act as a hormonal deposit rather than to facilitate secretion. Mucous acini usually stain pale, while serous acini usually stain dark. Lungs The end of the terminal bronchioles in the lungs mark the beginning of a pulmonary acinus that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acinus
An acinus (; plural, acini; adjective, acinar or acinous) refers to any cluster of cells that resembles a many-lobed "berry," such as a raspberry ('' acinus'' is Latin for "berry"). The berry-shaped termination of an exocrine gland, where the secretion is produced, is acinar in form, as is the alveolar sac containing multiple alveoli in the lungs. Exocrine glands Acinar exocrine glands are found in many organs, including: * the stomach * the sebaceous gland of the scalp * the salivary glands of the tongue * the liver * the lacrimal glands * the mammary glands * the pancreas * the bulbourethral (Cowper's) glands The thyroid follicles can also be considered of acinar formation but in this case the follicles, being part of an ''endocrine'' gland, act as a hormonal deposit rather than to facilitate secretion. Mucous acini usually stain pale, while serous acini usually stain dark. Lungs The end of the terminal bronchioles in the lungs mark the beginning of a pulmonary acinus tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocrine Gland
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstream. The liver and pancreas are both exocrine and endocrine glands; they are exocrine glands because they secrete products—bile and pancreatic juice—into the gastrointestinal tract through a series of ducts, and endocrine because they secrete other substances directly into the bloodstream. Exocrine sweat glands are part of the integumentary system; they have eccrine and apocrine types. Classification Structure Exocrine glands contain a glandular portion and a duct portion, the structures of which can be used to classify the gland. * The duct portion may be branched (called compound) or unbranched (called simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Gland
Alveolar glands, also called saccular glands are glands with a saclike secretory portion, in conrast with tubular glands. They typically have an enlarged lumen (cavity), hence the name: they have a shape similar to alveoli, the very small air sacs in the lungs. Some sources draw a clear distinction between acinar and alveolar glands, based upon the size of the lumen. A further complication in the case of the alveolar glands may occur in the form of still smaller saccular diverticuli growing out from the main sacculi. The term "racemose gland" is used to describe a "compound alveolar gland" or "compound acinar gland." Branched alveolar glands are classified as follows: Additional images File:Gray897.png, Alveoli of lacrimal gland. File:Gray1026.png, Human submaxillary gland The paired submandibular glands (historically known as submaxillary glands) are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. They each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acinar Cells
Centroacinar cells are spindle-shaped cells in the exocrine pancreas. They represent an extension of the intercalated duct into each pancreatic acinus. These cells are commonly known as duct cells, and secrete an aqueous bicarbonate solution under stimulation by the hormone secretin. They also secrete mucin. The intercalated ducts take the bicarbonate to intralobular ducts which become lobular ducts. These lobular ducts finally converge to form the main pancreatic duct. See also *List of human cell types derived from the germ layers This is a list of cells in humans derived from the three embryonic germ layers – ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Cells derived from ectoderm Surface ectoderm Skin * Trichocyte * Keratinocyte Anterior pituitary * Gonadotrope * Corticotro ... References External links * - "Pancreas" * - "Liver, Gall Bladder, and Pancreas: pancreas, centroacinar cells" * Digestive system {{cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic alcohol use and gallstones. Becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salivary Glands
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary glands can be classified as serous, mucous, or seromucous (mixed). In serous secretions, the main type of protein secreted is alpha-amylase, an enzyme that breaks down starch into maltose and glucose, whereas in mucous secretions, the main protein secreted is mucin, which acts as a lubricant. In humans, 1200 to 1500 ml of saliva are produced every day. The secretion of saliva (salivation) is mediated by parasympathetic stimulation; acetylcholine is the active neurotransmitter and binds to muscarinic receptors in the glands, leading to increased salivation. The fourth pair of salivary glands, the tubarial glands discovered in 2020, are named for their location, being positioned in front and over the torus tubarius. However, this finding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercalated Duct
In anatomy and physiology, a duct is a circumscribed channel leading from an exocrine gland or organ. Types of ducts Examples include: Duct system As ducts travel from the acinus which generates the fluid to the target, the ducts become larger and the epithelium becomes thicker. The parts of the system are classified as follows: Some sources consider "lobar" ducts to be the same as "interlobar ducts", while others consider lobar ducts to be larger and more distal from the acinus. For sources that make the distinction, the interlobar ducts are more likely to classified with simple columnar epithelium (or pseudostratified epithelium), reserving the stratified columnar for the lobar ducts. File:Gray1025.png, Section of submaxillary gland of kitten. Duct semidiagrammatic. X 200. File:Gray1173.png, Section of portion of mamma. Intercalated duct The intercalated duct, also called intercalary duct (ducts of Boll), is the portion of an exocrine gland leading directly from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacrimal Glands
The lacrimal glands are paired exocrine glands, one for each eye, found in most terrestrial vertebrates and some marine mammals, that secrete the aqueous layer of the tear film. In humans, they are situated in the upper lateral region of each orbit, in the lacrimal fossa of the orbit formed by the frontal bone. Inflammation of the lacrimal glands is called dacryoadenitis. The lacrimal gland produces tears which are secreted by the lacrimal ducts, and flow over the ocular surface, and then into canals that connect to the lacrimal sac. From that sac, the tears drain through the lacrimal duct into the nose. Anatomists divide the gland into two sections, a palpebral lobe, or portion, and an orbital lobe or portion. The smaller ''palpebral lobe'' lies close to the eye, along the inner surface of the eyelid; if the upper eyelid is everted, the palpebral portion can be seen. The orbital lobe of the gland, contains fine interlobular ducts that connect the orbital lobe and the palpebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
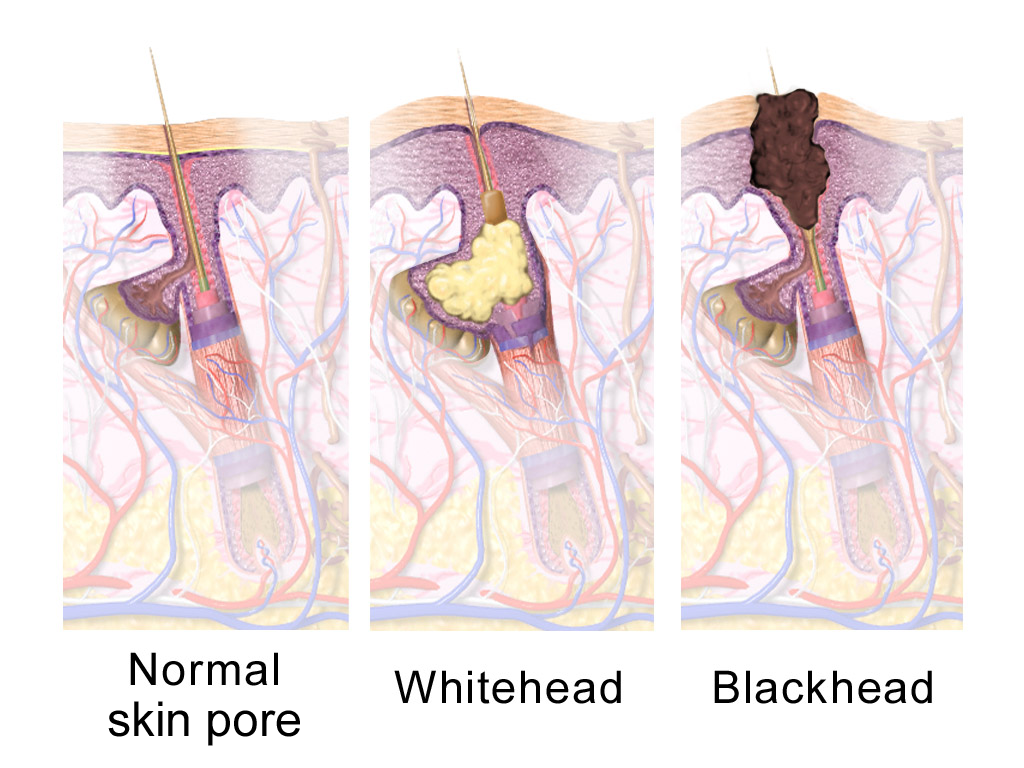
Sebaceous Gland
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipple, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipple. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location Sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands, those connected to hair follicles and those that exist independently. Sebaceous glands are found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raspberry
The raspberry is the edible fruit of a multitude of plant species in the genus ''Rubus'' of the rose family, most of which are in the subgenus '' Idaeobatus''. The name also applies to these plants themselves. Raspberries are perennial with woody stems. World production of raspberries in 2020 was 895,771 tonnes, led by Russia with 20% of the total. Description A raspberry is an aggregate fruit, developing from the numerous distinct carpels of a single flower. What distinguishes the raspberry from its blackberry relatives is whether or not the torus ( receptacle or stem) "picks with" (i.e., stays with) the fruit. When picking a blackberry fruit, the torus stays with the fruit. With a raspberry, the torus remains on the plant, leaving a hollow core in the raspberry fruit. Raspberries are grown for the fresh fruit market and for commercial processing into individually quick frozen (IQF) fruit, purée, juice, or as dried fruit used in a variety of grocery products such as raspb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)