|
Accidents And Incidents Involving The McDonnell Douglas DC-10 Family
The McDonnell Douglas DC-10 is an American trijet wide-body aircraft manufactured by McDonnell Douglas. The DC-10 was intended to succeed the DC-8 for long-range flights. It first flew on August 29, 1970; it was introduced on August 5, 1971, by American Airlines. The trijet has two turbofans on underwing pylons and a third one at the base of the vertical stabilizer. The twin-aisle layout has a typical seating for 270 in two classes. The initial DC-10-10 had a range for transcontinental flights. The DC-10-15 had more powerful engines for hot and high airports. The DC-10-30 and −40 models (with a third main landing gear leg to support higher weights) each had intercontinental ranges of up to . The KC-10 Extender (based on the DC-10-30) is a U.S. Air Force tanker. A design flaw in the original cargo doors caused a poor safety record in early operations. Following the American Airlines Flight 191 crash (the deadliest aviation accident in US history), the US Federal Aviatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Range (aeronautics)
The maximal total range is the maximum distance an aircraft can fly between takeoff and landing. Powered aircraft range is limited by the aviation fuel energy storage capacity (chemical or electrical) considering both weight and volume limits. Unpowered aircraft range depends on factors such as cross-country speed and environmental conditions. The range can be seen as the cross-country ground speed multiplied by the maximum time in the air. The fuel time limit for powered aircraft is fixed by the available fuel (considering reserve fuel requirements) and rate of consumption. Some aircraft can gain energy while airborne through the environment (e.g. collecting solar energy or through rising air currents from mechanical or thermal lifting) or from in-flight refueling. These aircraft could theoretically have an infinite range. Ferry range means the maximum range that an aircraft engaged in ferry flying can achieve. This usually means maximum fuel load, optionally with extra fuel tan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
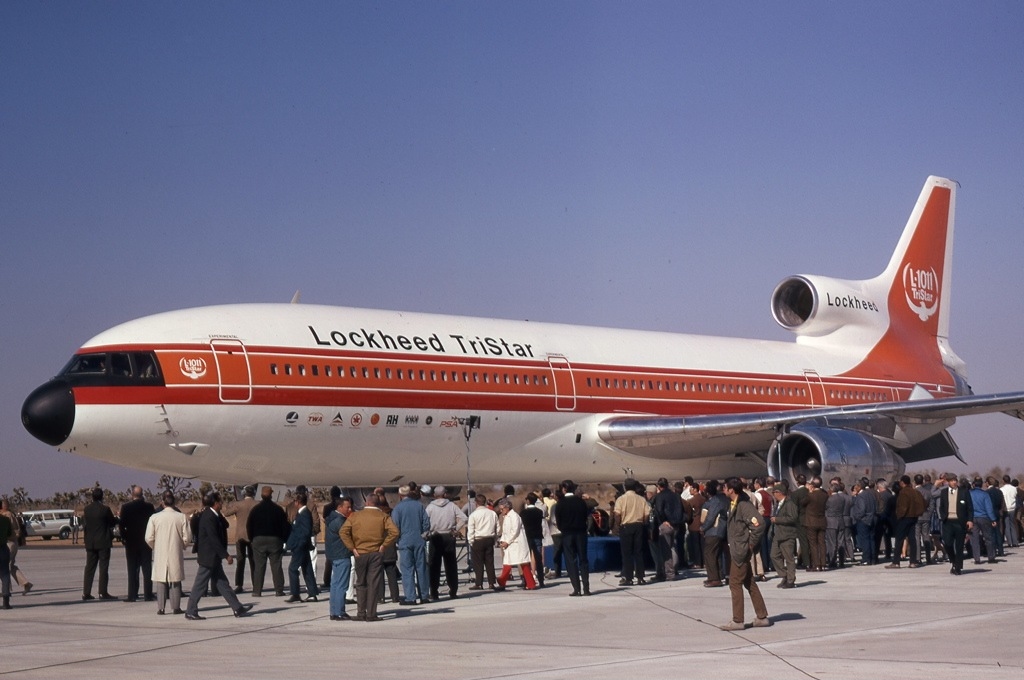
Lockheed L-1011 TriStar
The Lockheed L-1011 TriStar, also known as the L-1011 (pronounced "El-ten-eleven") and TriStar, is an American medium-to-long-range, wide-body trijet airliner built by the Lockheed Corporation. It was the third wide-body airliner to enter commercial operations, after the Boeing 747 and the McDonnell Douglas DC-10. The airliner has a seating capacity of up to 400 passengers and a range of over . Its trijet configuration has three Rolls-Royce RB211 engines with one engine under each wing, along with a third engine center-mounted with an S-duct air inlet embedded in the tail and the upper fuselage. The aircraft has an autoland capability, an automated descent control system, and available lower deck galley and lounge facilities. The L-1011 TriStar was produced in two fuselage lengths. The original L-1011-1 first flew in November 1970 and entered service with Eastern Air Lines in 1972. The shortened, longer range L-1011-500 first flew in 1978 and entered service with British Airways ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanker Aircraft
This is a list of tanker aircraft used for aerial refuelling of another aircraft whilst in powered flight. Refueling methods ;Looped hose: The first commercial method employed a hose which was held slack in a trailing half-loop behind both aircraft. The receiving aircraft flew just below the tanker and deployed a steel line, which the tanker caught with its own grappling line and drew in. The tanker then connected the first steel line to the refueling hose and paid it out as the receiving aircraft reeled it back in. ;Probe-and-drogue: The tanker trails a flexible hose with a stabilising drogue on the end and the receiving aircraft manoeuvers to insert a short probe into the receptacle in the drogue. ;Flying boom: The tanker extends a hinged telescopic boom with aerodynamic control surfaces on its end. An operator "flies" it to match up with a receptacle on the receiving aircraft, which then moves forwards to make the connection. ;Wing-to-wing: A hybrid method in which the tanker t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
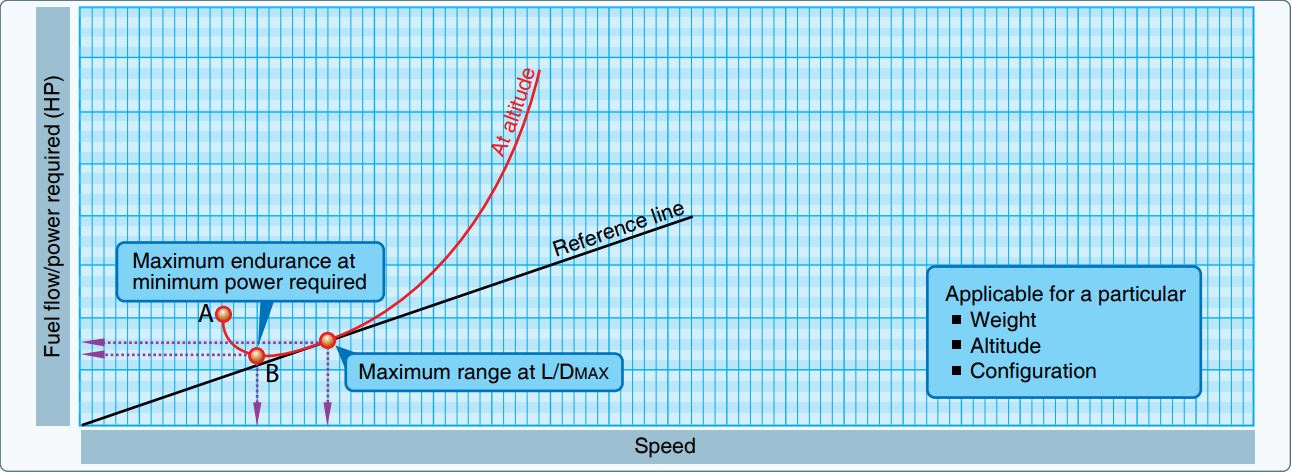
Fuel Economy In Aircraft
The fuel economy in aircraft is the measure of the transport energy efficiency of aircraft. Efficiency is increased with better aerodynamics and by reducing weight, and with improved engine BSFC and propulsive efficiency or TSFC. Endurance and range can be maximized with the optimum airspeed, and economy is better at optimum altitudes, usually higher. An airline efficiency depends on its fleet fuel burn, seating density, air cargo and passenger load factor, while operational procedures like maintenance and routing can save fuel. Average fuel burn of new aircraft fell 45% from 1968 to 2014, a compounded annual reduction 1.3% with a variable reduction rate. In 2018, CO₂ emissions totalled 747 million tonnes for passenger transport, for 8.5 trillion revenue passenger kilometres (RPK), giving an average of 88 gram CO₂ per RPK. A 88 gCO₂/km represents g of fuel per km, or a fuel consumption. New technology can reduce engine fuel consumption, like higher pressure a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic management, certification of personnel and aircraft, setting standards for airports, and protection of U.S. assets during the launch or re-entry of commercial space vehicles. Powers over neighboring international waters were delegated to the FAA by authority of the International Civil Aviation Organization. Created in , the FAA replaced the former Civil Aeronautics Administration (CAA) and later became an agency within the U.S. Department of Transportation. Major functions The FAA's roles include: *Regulating U.S. commercial space transportation *Regulating air navigation facilities' geometric and flight inspection standards *Encouraging and developing civil aeronautics, including new aviation technology *Issuing, suspending, or revoking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Airlines Flight 191
American Airlines Flight 191 was a regularly scheduled domestic passenger flight in the United States operated by American Airlines from Chicago O'Hare International Airport to Los Angeles International Airport. On the afternoon of May 25, 1979, the McDonnell Douglas DC-10-10 operating this flight was taking off from runway 32R when its left engine detached, causing loss of control, and it crashed less than from the end of the runway. All 258 passengers and 13 crew on board were killed, along with two people on the ground. With 273 fatalities, it is the deadliest aviation accident to have occurred in the United States. The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) found that as the aircraft was beginning its takeoff rotation, engine number one (the left engine) separated from the left wing, flipping over the top of the wing and landing on the runway. As the engine separated from the aircraft, it severed hydraulic fluid lines that lock the wing's leading-edge slats in pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation Safety
Aviation safety is the study and practice of managing risks in aviation. This includes preventing aviation accidents and incidents through research, educating air travel personnel, passengers and the general public, as well as the design of aircraft and aviation infrastructure. The aviation industry is subject to significant regulation and oversight. Aviation security is focused on protecting air travelers, aircraft and infrastructure from intentional harm or disruption, rather than unintentional mishaps. Statistics Evolution In 1926 and 1927, there were a total of 24 fatal commercial airline crashes, a further 16 in 1928, and 51 in 1929 (killing 61 people), which remains the worst year on record at an accident rate of about 1 for every flown. Based on the current numbers flying, this would equate to 7,000 fatal incidents per year. For the ten-year period 2002 to 2011, 0.6 fatal accidents happened per one million flights globally, 0.4 per million hours flown, 22.0 fatal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Door
A door is a hinged or otherwise movable barrier that allows ingress (entry) into and egress (exit) from an enclosure. The created opening in the wall is a ''doorway'' or ''portal''. A door's essential and primary purpose is to provide security by controlling access to the doorway (portal). Conventionally, it is a panel that fits into the doorway of a building, room, or vehicle. Doors are generally made of a material suited to the door's task. They are commonly attached by hinges, but can move by other means, such as slides or counterbalancing. The door may be able to move in various ways (at angles away from the doorway/portal, by sliding on a plane parallel to the frame, by folding in angles on a parallel plane, or by spinning along an axis at the center of the frame) to allow or prevent ingress or egress. In most cases, a door's interior matches its exterior side. But in other cases (e.g., a vehicle door) the two sides are radically different. Many doors incorporate locking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Flaw
A product defect is any characteristic of a product which hinders its usability for the purpose for which it was designed and manufactured. Product defects arise most prominently in legal contexts regarding product safety, where the term is applied to "anything that renders the product not reasonably safe".Patricia A. Robinson, ''Writing and Designing Manuals and Warnings'' (2009), p. 234. The field of law that addresses injuries caused by defective products is called ''product liability''. A wide range of circumstances can render a product defective. The product may have a design defect or design flaw, resulting from the product having been poorly designed or tested, so that the design itself yields a product that can not perform its desired function. Even if the design is correct, the product may have a manufacturing defect if it was incorrectly manufactured, for example if the wrong materials are used. A product may also be considered legally defective if it lacks appropriate i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KC-10 Extender
The McDonnell Douglas KC-10 Extender is an American aerial refueling tanker aircraft operated by the United States Air Force (USAF). A military version of the three-engine DC-10 airliner, the KC-10 was developed from the Advanced Tanker Cargo Aircraft Program. It incorporates military-specific equipment for its primary roles of transport and aerial refueling. It was developed to supplement the KC-135 Stratotanker following experiences in Southeast Asia and the Middle East. The KC-10 was the second McDonnell Douglas transport aircraft to be selected by the Air Force following the C-9. A total of 60 KC-10s were produced for the USAF. The Royal Netherlands Air Force operated two similar tankers designated ''KDC-10'' that were converted from DC-10s. The KC-10 plays a key role in the mobilization of US military assets, taking part in overseas operations far from home. These aircraft performed airlift and aerial refueling during the 1986 bombing of Libya (Operation Eldorado Canyon), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
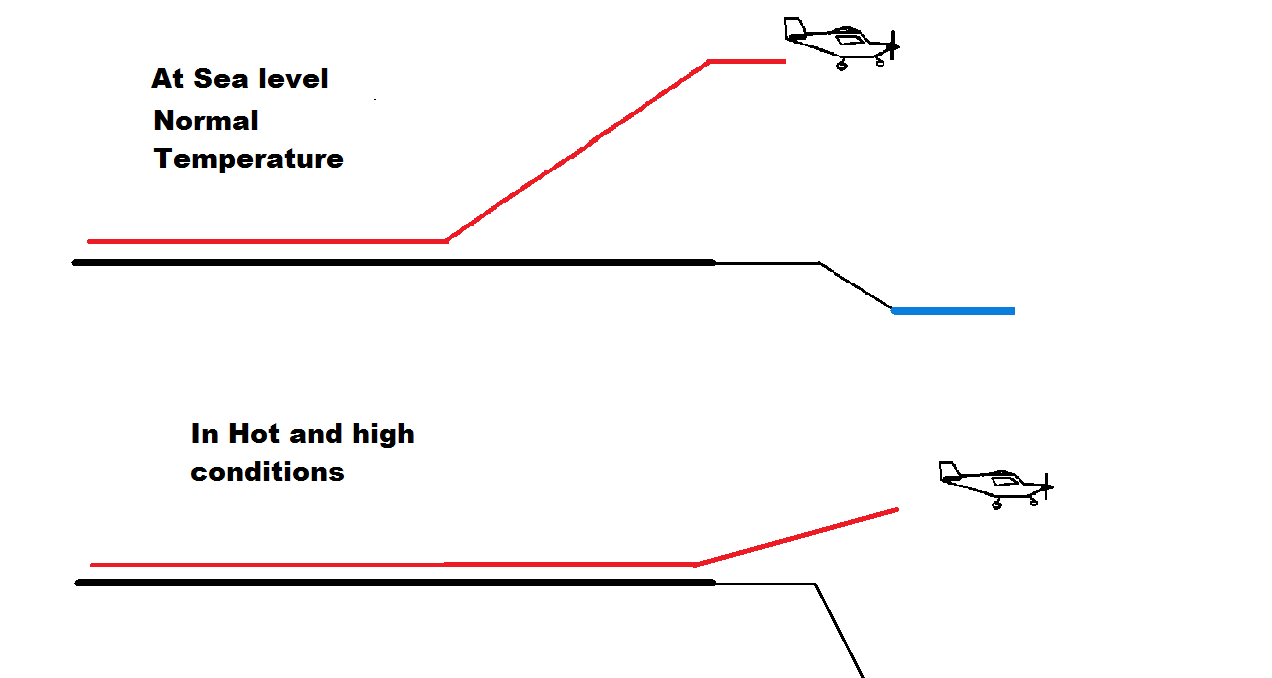
Hot And High
In aviation, hot and high is a condition of low air density due to high ambient temperature and high airport elevation. Air density decreases with increasing temperature and altitude. The lower air density reduces the power output from the aircraft's engine and also requires a higher true airspeed before the aircraft can become airborne. Aviators gauge air density by calculating the density altitude. An airport may be especially hot ''or'' high, without the other condition being present. Temperature and pressure altitude can change from one hour to the next. The fact that temperature decreases as altitude increases mitigates the "hot and high" effect to a small extent. Negative effects of reduced engine power due to hot and high conditions * Airplanes require a longer takeoff run, potentially exceeding the amount of available runway. * Reduced take-off power hampers an aircraft's ability to climb. In some cases, an aircraft may be unable to climb rapidly enough to clear terrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |