|
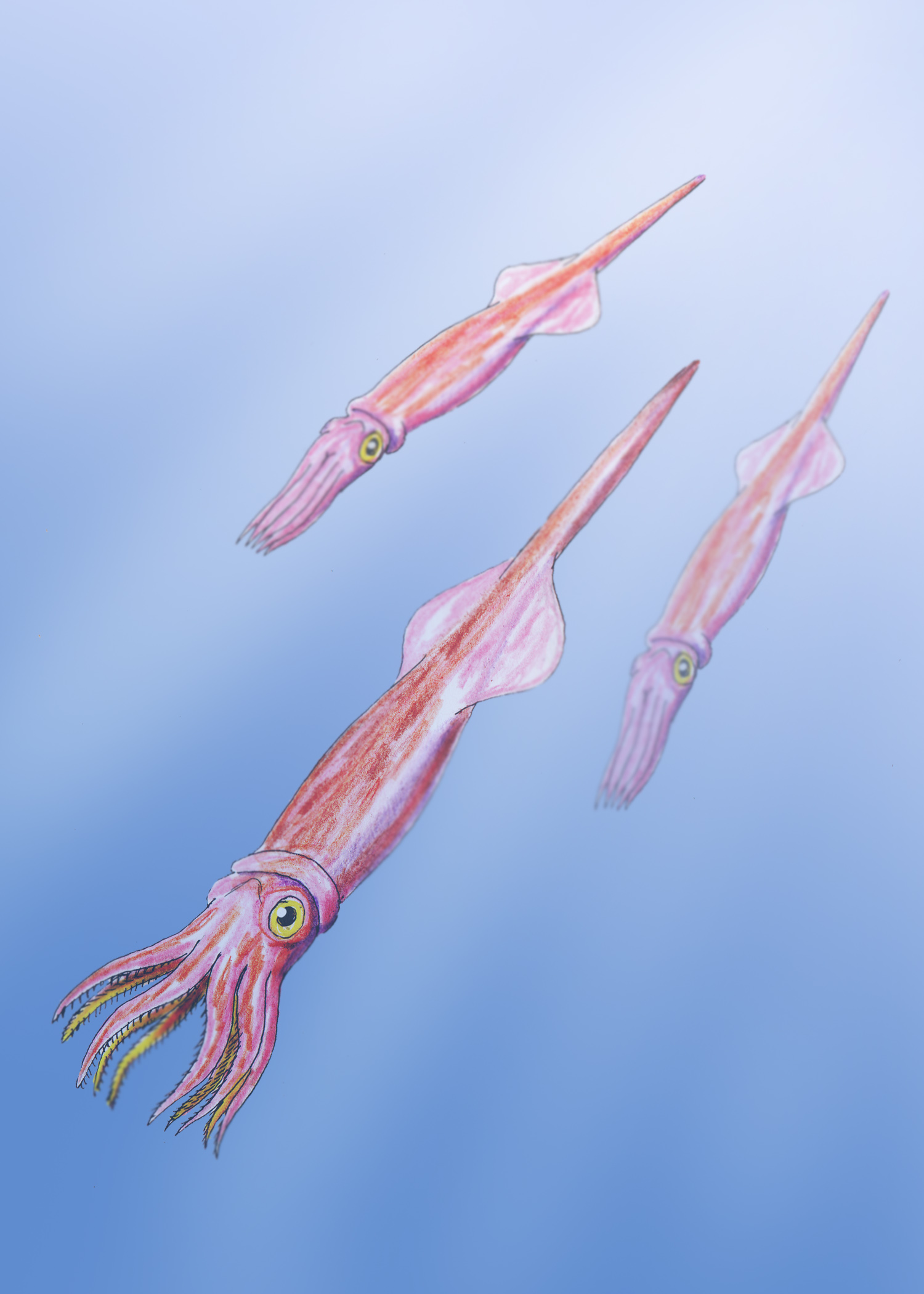
Acanthoteuthis
''Acanthoteuthis'' is a belemnite genus, a squid-like cephalopod with an internal shell from the Late Jurassic Epoch, related to modern coleoids. ''Acanthoteuthis'' belongs to the belemnoid family Belemnotheutidae in which the pointed rostrum at the back of the phragmocone is lacking. Taxonomy The genus ''Acanthoteuthis'' was founded by R. Wagner and G. Munster for belemnoids, found in the Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria, which have small hooklets on their arms, sometimes associated with more or less complete remains of the animal.G.C.Crick et al.On an Example of Acanthoteuthis ferussaci, Munst. from the Lithographic stone of Solenhofen, Bavaria,... Proceedings of the Malacological Society,Vol III Part 1,April,1898 The hooklets are typically compressed and may be beveled on either or both margins on one side. Munster characterized three species, ''A. speciosa'', ''A. ferussacii'', and ''A. lichtensteinii'', chiefly upon the forms of these hooklets. In ''A lichtensteinii'' t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belemnite
Belemnitida (or the belemnite) is an extinct order of squid-like cephalopods that existed from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous. Unlike squid, belemnites had an internal skeleton that made up the cone. The parts are, from the arms-most to the tip: the tongue-shaped pro-ostracum, the conical phragmocone, and the pointy guard. The calcitic guard is the most common belemnite remain. Belemnites, in life, are thought to have had 10 hooked arms and a pair of fins on the guard. The chitinous hooks were usually no bigger than , though a belemnite could have had between 100 and 800 hooks in total, using them to stab and hold onto prey. Belemnites were an important food source for many Mesozoic marine creatures, both the adults and the planktonic juveniles, and likely played an important role in restructuring marine ecosystems after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. They may have laid between 100 and 1,000 eggs. Some species may have been adapted to speed and swam in the tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belemnotheutis
''Belemnotheutis'' is an extinct coleoid cephalopod genus from the middle and upper Jurassic, related to but morphologically distinct from belemnites. ''Belemnotheutis'' fossils are some of the best preserved among coleoids. Remains of soft tissue are well-documented in some specimens, even down to microscopic muscle tissue. In 2008, a group of paleontologists even recovered viable ink from ink sacs found in several specimens. This genus was the subject of a dispute between several eminent 19th century British paleontologists, notably between Richard Owen and Gideon Mantell. Some authors incorrectly spell the genus ''Belemnoteuthis'' following the usual spelling ''teuthis'' (τευθίς) for 'squid'. Description The genus ''Belemnotheutis'' is characterized by an internal shell consisting of a conical phragmocone covered apically by a thin rostrum, or guard, homologous to the bullet-shaped rostrum of true belemnites, a short forward projecting proostracum, and ten hook be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Belemnites
This list of belemnite genera is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the extinct subclass Belemnoidea, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, as well as genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomina dubia''), or were not formally published (''nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered belemites. Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature as indicated. The list currently contains 100 generic names. List of belemnites See also * Belemnoidea * List of ammonites * List of nautiloids This list of nautiloids is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the subclass Nautiloidea, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered in ... References :''Unc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tithonian
In the geological timescale, the Tithonian is the latest age of the Late Jurassic Epoch and the uppermost stage of the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 152.1 ± 4 Ma and 145.0 ± 4 Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Kimmeridgian and followed by the Berriasian (part of the Cretaceous).See for a detailed version of the geologic timescale Gradstein ''et al.'' (2004) Stratigraphic definitions The Tithonian was introduced in scientific literature by German stratigrapher Albert Oppel in 1865. The name Tithonian is unusual in geological stage names because it is derived from Greek mythology. Tithonus was the son of Laomedon of Troy and fell in love with Eos, the Greek goddess of dawn. His name was chosen by Albert Oppel for this stratigraphical stage because the Tithonian finds itself hand in hand with the dawn of the Cretaceous. The base of the Tithonian stage is at the base of the ammonite biozone of '' Hybonoticeras hybonotum''. A global refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirula
''Spirula spirula'' is a species of deep-water squid-like cephalopod mollusk. It is the only extant member of the genus ''Spirula'', the family Spirulidae, and the order Spirulida. Because of the shape of its internal shell, it is commonly known as the ram's horn squid or the little post horn squid. Because the live animal has a light-emitting organ, it is also sometimes known as the tail-light squid. Live specimens of this cephalopod are very rarely seen because it is a deep-ocean dweller. The small internal shell of the species is, however, quite a familiar object to many beachcombers. The shell of ''Spirula'' is extremely light in weight, very buoyant, and surprisingly durable; it very commonly floats ashore onto tropical beaches (and sometimes even temperate beaches) all over the world. This seashell is known to shell collectors as the ram's horn shell or simply as ''Spirula''. Description ''S. spirula'' has a squid-like body between 35 mm and 45 mm long. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic Cephalopods
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and is the only boundary between geological periods to remain formally undefined. By the beginning of the Jurassic, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belemnites
Belemnites may refer to: *Belemnitida Belemnitida (or the belemnite) is an extinct order of squid-like cephalopods that existed from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous. Unlike squid, belemnites had an internal skeleton that made up the cone. The parts are, from the arms-most to ..., an extinct order of cephalopods commonly known as "belemnites" * ''Belemnites'' (genus), a belemnite genus from the Early Jurassic {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopelagic Zone
The mesopelagic zone (Greek μέσον, middle), also known as the middle pelagic or twilight zone, is the part of the pelagic zone that lies between the photic epipelagic and the aphotic bathypelagic zones. It is defined by light, and begins at the depth where only 1% of incident light reaches and ends where there is no light; the depths of this zone are between approximately 200 to 1,000 meters (~656 to 3,280 feet) below the ocean surface. The mesopelagic zone occupies about 60% of the planet's surface and about 20% of the ocean's volume, amounting to a large part of the total biosphere. It hosts a diverse biological community that includes bristlemouths, blobfish, bioluminescent jellyfish, giant squid, and a myriad of other unique organisms adapted to live in a low-light environment. It has long captivated the imagination of scientists, artists and writers; deep sea creatures are prominent in popular culture. Physical conditions The mesopelagic zone includes the regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epipelagic
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes that supply nutrients into the upper water column. The photic zone is home to the majority of aquatic life due to the activity (primary production) of the phytoplankton. Photosynthesis in photic zone In the photic zone, the photosynthesis rate exceeds the respiration rate. This is due to the abundant solar energy which is used as an energy source for photosynthesis by primary producers such as phytoplankton. These phytoplankton grow extremely quickly because of sunlight's heavy influence, enabling it to be produced at a fast rate. In fact, ninety five percent of photosynthesis in the ocean occurs in the photic zone. Therefore, if we go deeper, beyond the photic zone, such as into the compensation point, there is little to no p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
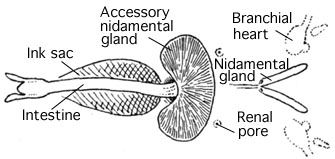
Ink Sac
An ink sac is an anatomical feature that is found in many cephalopod mollusks used to produce the defensive cephalopod ink. With the exception of nocturnal and very deep water cephalopods, all Coleoidea (squid, octopus and cuttlefish) which dwell in light conditions have an ink sac, which can be used to expel a cloud of dark ink in order to confuse predators. The ink sac is a muscular bag which originated as an extension of the hind gut; it is a modified hypobranchial gland.Nair, J.R., D. Pillai, S.M. Joseph, P. Gomathi, P.V. Senan & P.M. Sherief (2011). ''Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences'' 40(1): 13–27. It lies beneath the gut and opens into the anus, into which its contents – almost pure melanin – can be squirted; its proximity to the base of the funnel means that the ink can be distributed by ejected water as the cephalopod uses its jet propulsion. The ejected cloud of melanin is bound by mucus Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigoteuthis
''Mastigoteuthis'' is a genus of whip-lash squid containing at least seven valid species. Some teuthologists consider ''Idioteuthis'' synonymous with this taxon. The genus contains bioluminescent species. Species *Genus ''Mastigoteuthis'' **''Mastigoteuthis agassizii'' Verrill, 1881 **''Mastigoteuthis dentata'' Hoyle, 1904 **''Mastigoteuthis flammea'' Chun, 1908 **'' Mastigoteuthis glaukopis'' Chun, 1908 **''Mastigoteuthis grimaldii'' (Joubin, 1895) **''Mastigoteuthis psychrophila'' Nesis, 1977 **''Mastigoteuthis schmidti'' Degner, 1925 **''Mastigoteuthis hastula'' * (Berry, 1920) **'' Mastigoteuthis inermis'' * Rancurel, 1972 **''Mastigoteuthis iselini'' * MacDonald & Clench, 1934 **''Mastigoteuthis okutanii'' * Salcedo-Vargas, 1997 **''Mastigoteuthis tyroi'' * Salcedo-Vargas, 1997 ''Magnapinna talismani'' was previously placed in this genus, but is now considered a species of bigfin squid. The taxa listed above with an asterisk (*) are ''taxon inquirendum In biological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |