|
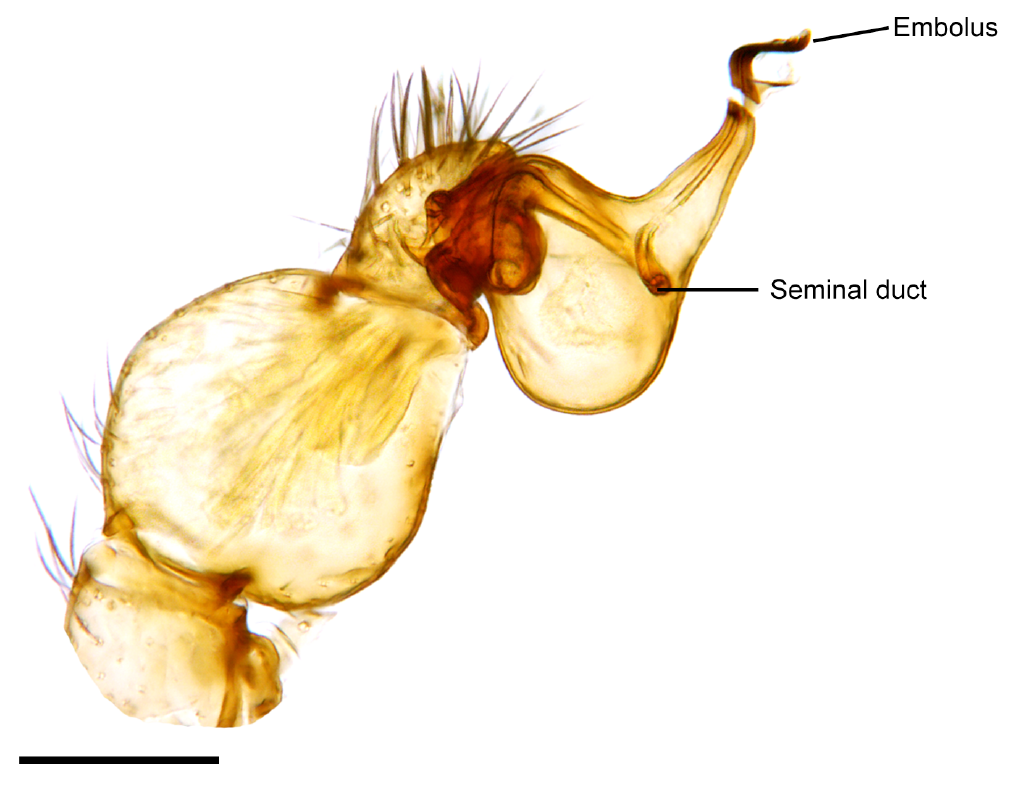
Acanthogonatus Peniasco
''Acanthogonatus peniasco'' is a mygalomorph spider of Chile, its name arising from its type locality: El Peñasco, Linares, VII Region (del Maule), Chile.Goloboff, Pablo A. "A revision of the South American spiders of the family Nemesiidae (Araneae, Mygalomorphae). Part 1, Species from Peru, Chile, Argentina, and Uruguay. Bulletin of the AMNH; no. 224." (1995). Females differ from those of '' A. franki'' and '' A. recinto'' in the shorter, wider, and more sclerotized spermathecal ducts, and from those of other species in the genus by having 1-1-1 P spines in the patella IV. Description *Female: total length ; cephalothorax length ; cephalic region length , width ; fovea width ; medial ocular quadrangle , width ; labium length , width ; sternum length , width . Its cephalic region is moderately convex, with a deep fovea with a posterior notch. Its labium possesses 2 cuspules. A serrula is present. Its posterior sternal sigilla is oval and submarginal, with its sternum being re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mygalomorphae
The Mygalomorphae, or mygalomorphs, are an infraorder of spiders, and comprise one of three major groups of living spiders with over 3000 species, found on all continents except Antarctica. Many members are known as trapdoor spiders due to them forming trapdoors over their burrows. Other prominent groups include Australian funnel web spiders and tarantulas, with the latter accounting for around one third of all mygalomorphs. Description This group of spiders comprises mostly heavy-bodied, stout-legged spiders including tarantulas, Australian funnel-web spiders, mouse spiders, and various families of spiders commonly called trapdoor spiders. Like the " primitive" suborder of spiders Mesothelae, they have two pairs of book lungs, and downward-pointing chelicerae. Because of this, the two groups were once believed to be closely related. Later it was realized that the common ancestors of all spiders had these features (a state known as symplesiomorphy). Following the branching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setae
In biology, setae (singular seta ; from the Latin word for "bristle") are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms. Animal setae Protostomes Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. They help, for example, earthworms to attach to the surface and prevent backsliding during peristaltic motion. These hairs make it difficult to pull a worm straight from the ground. Setae in oligochaetes (a group including earthworms) are largely composed of chitin. They are classified according to the limb to which they are attached; for instance, notosetae are attached to notopodia; neurosetae to neuropodia. Crustaceans have mechano- and chemosensory setae. Setae are especially present on the mouthparts of crustaceans and can also be found on grooming limbs. In some cases, setae are modified into scale like structures. Setae on the legs of krill and other small crustaceans help them to gather phytoplankton. It captures them and allows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiders Of South America
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel, however, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had a separate t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pycnothelidae
''Pycnothelidae'' is a family of mygalomorph spiders first described in 1917. It was downgraded to a subfamily of the funnel-web trapdoor spiders in 1985, but returned to family status in 2020. Genera , the World Spider Catalog accepted the following genera: *'' Acanthogonatus'' Karsch, 1880 – South America *''Bayana'' Pérez-Miles, Costa & Montes de Oca, 2014 *''Pionothele ''Pionothele'' is a genus of African mygalomorph spiders in the family Pycnothelidae. It was first described by William Frederick Purcell in 1902. it contains 2 species, found in Namibia and South Africa: '' P. gobabeb'', and '' P. straminea''. ...'' Purcell, 1902 – South Africa, Namibia *'' Pycnothele'' Chamberlin, 1917 – Uruguay, Brazil, Argentina *'' Stanwellia'' Rainbow & Pulleine, 1918 – Australia, New Zealand *'' Stenoterommata'' Holmberg, 1881 – Brazil, Uruguay, Argentina References Mygalomorphae families {{Mygalomorphae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotinoecus
''Scotinoecus'' is a genus of South America South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...n funnel-web spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1892. Originally placed with the curtain web spiders, it was moved to the Hexathelidae in 1980. Species it contains four species: *'' Scotinoecus cinereopilosus'' (Simon, 1889) ( type) – Chile *'' Scotinoecus fasciatus'' Tullgren, 1901 – Chile, Argentina *'' Scotinoecus major'' Ríos-Tamayo & Goloboff, 2012 – Chile *'' Scotinoecus ruiles'' Ríos-Tamayo & Goloboff, 2012 – Chile References Hexathelidae Mygalomorphae genera Spiders of South America {{Mygalomorphae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calathotarsus
''Calathotarsus'' is a genus of spiders in the family Migidae Migidae, also known as tree trapdoor spiders, is a family of spiders with about 100 species in eleven genera. They are small to large spiders with little to no hair and build burrows with a trapdoor. Some species live in tree fern stems. They hav .... It was first described in 1903 by Eugène Simon. , it contains 4 species, occurring in Chile and Argentina. Species References Migidae Mygalomorphae genera Spiders of South America {{Mygalomorphae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm ''Bombyx mori'' reared in captivity (sericulture). The shimmering appearance of silk is due to the triangular prism-like structure of the silk fibre, which allows silk cloth to refract incoming light at different angles, thus producing different colors. Silk is produced by several insects; but, generally, only the silk of moth caterpillars has been used for textile manufacturing. There has been some research into other types of silk, which differ at the molecular level. Silk is mainly produced by the larvae of insects undergoing complete metamorphosis, but some insects, such as webspinners and raspy crickets, produce silk throughout their lives. Silk production also occurs in hymenoptera ( bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mottling
Mottle is a pattern of irregular marks, spots, streaks, blotches or patches of different shades or colours. It is commonly used to describe the surface of plants or the skin of animals. In plants, mottling usually consists of yellowish spots on plants, and is usually a sign of disease or malnutrition. Many plant viruses cause mottling, some examples being: * Tobacco vein mottling virus * Bean pod mottle virus Mottling is sometimes used to describe uneven discolored patches on the skin of humans as a result of cutaneous ischemia (lowered blood flow to the surfaces of the skin) or Herpes zoster infections. The medical term for mottled skin is dyschromia. Although this is not always the case, mottling can occur in the dying patient and commonly indicates that the end of life is near. Mottling usually occurs in the extremities (lower first) and progresses up as cardiac function declines and circulation throughout the body is poor. In animals, mottling may be a sign of disease, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palpus
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles: the coxa, the trochanter, the femur, the short patella, the tibia, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spiders, or chelate weapons ( pincers) of great size, as in scorpions. The pedipalps of Solifugae are covered in setae, but have not been studied in detail. Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicerae
The chelicerae () are the mouthparts of the subphylum Chelicerata, an arthropod group that includes arachnids, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. Commonly referred to as "jaws", chelicerae may be shaped as either articulated fangs, or similarly to pincers. Some chelicerae, such as those found on nearly all spiders, are hollow and contain (or are connected to) venom glands, and are used to inject venom into prey or a perceived threat. In ''Pisaurina mira'', also known as the nursery web spider, the chelicerae are utilized to snatch the prey once it becomes within reach, facilitating the "sit-and-wait ambush predator" behavior. Both pseudoscorpions and harvestmen have structures on their chelicerae that are used for grooming (papillae in pseudoscorpions, cheliceral teeth in Opiliones). Types Chelicerae can be divided into three kinds: jackknife chelicerae, scissor chelicerae, and 3-segmented chelate chelicerae. Jackknife chelicerae The jackknife chelicera is subchelate (with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after declaring in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon), meaning "chest". Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body (gladiolus) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |