|
Abu Al-Futuh Al-Razi
Abu al-Futuh al-Razi ( ar, žŻž©┘ł ž¦┘ä┘üž¬┘łžŁ ž¦┘äž▒ž¦ž▓┘Ŗ), full name Ab┼½ al-Fut┼½ßĖź al-ßĖżusayn ibn ╩┐Al─½ ibn MußĖźammad ibn AßĖźmad al-Khuz─ü╩┐─½ al-R─üz─½ al-N─½s─üb┼½r─½ () or Abu al-Futuh Jamal al-Din al-Razi al-Nisaburi (), also known as Khaza'i Nishaburi ( fl. 6th A.H./12th century), was a Shi╩┐ite theologian and author. He came from an Arab family originally from Nishapur and supposedly from the Khuza'a tribe, which settled in Nishapur. His grandfather had moved to Rayy, where he taught and later died in or after 1131 CE. His most famous work, '' Rawz al-jinan wa Ruh al-Janan'', is considered the first Persian-language exegesis on the Quran. The book, consisting of twenty volumes, is the earliest surviving Persian tafs─½r Tafsir ( ar, ž¬┘üž│┘Ŗž▒, tafs─½r ) refers to exegesis, usually of the Quran. An author of a ''tafsir'' is a ' ( ar, ┘ģ┘Å┘üž│┘æž▒; plural: ar, ┘ģ┘üž│┘æž▒┘ł┘å, mufassir┼½n). A Quranic ''tafsir'' attempts to provide elucidation, explanation, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floruit
''Floruit'' (; abbreviated fl. or occasionally flor.; from Latin for "they flourished") denotes a date or period during which a person was known to have been alive or active. In English, the unabbreviated word may also be used as a noun indicating the time when someone flourished. Etymology and use la, fl┼Źruit is the third-person singular perfect active indicative of the Latin verb ', ' "to bloom, flower, or flourish", from the noun ', ', "flower". Broadly, the term is employed in reference to the peak of activity for a person or movement. More specifically, it often is used in genealogy and historical writing when a person's birth or death dates are unknown, but some other evidence exists that indicates when they were alive. For example, if there are wills attested by John Jones in 1204, and 1229, and a record of his marriage in 1197, a record concerning him might be written as "John Jones (fl. 1197ŌĆō1229)". The term is often used in art history when dating the career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ShiŌĆÖite
Sh─½╩┐a Islam or Sh─½╩┐─½sm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ╩┐Al─½ ibn Ab─½ ß╣¼─ülib as his successor (''khal─½fa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, most notably at the event of Ghadir Khumm, but was prevented from succeeding Muhammad as the leader of the Muslims as a result of the choice made by some of Muhammad's other companions (''ß╣ŻaßĖź─üba'') at Saqifah. This view primarily contrasts with that of Sunn─½ Islam, whose adherents believe that Muhammad did not appoint a successor before his death and consider Ab┼½ Bakr, who was appointed caliph by a group of senior Muslims at Saqifah, to be the first rightful (''r─üshid┼½n'') caliph after Muhammad. Adherents of Sh─½╩┐a Islam are called Sh─½╩┐a Muslims, Sh─½╩┐─½tes, or simply Sh─½╩┐a or Shia. Sh─½╩┐a Islam is based on a ''ßĖźad─½th'' report concerning Muhammad's pronouncement at Ghadir Khumm.Esposito, John. "What Everyone Needs to K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
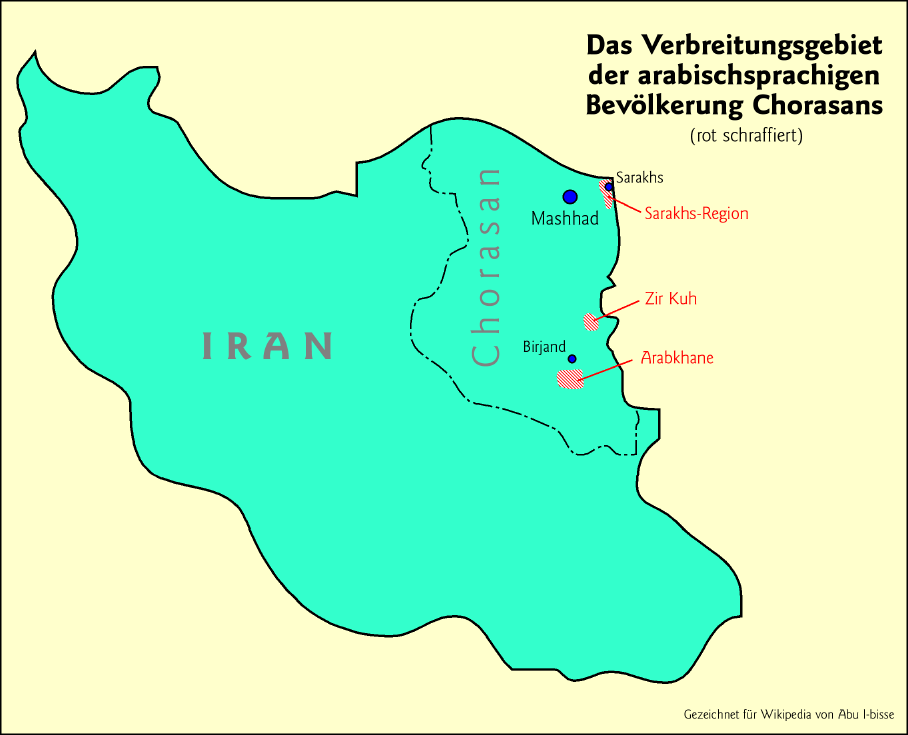
Arabs In Khorasan
Khorasani Arabs are Iranian Arabs who are descended from the Arabs who immigrated to the Khorasan area of Iran during the Abbasid Caliphate (750ŌłÆ1258). Unlike the Arabs of Iran's Khuzestan Province in the southwestern part of the country, who are direct descendants of the ancient population of the area, the Khorasani Arabs are descended from actual Arab migrants. According to a 2013 article in peer-reviewed journal ''Iran and the Caucasus'', the Khorasani Arabs, numbering , are "already almost totally Persianised". Most Khorasani Arabs belong to the tribes of Shaybani, Zangooyi, Mishmast, Khozaima, and Azdi. Khorasan Arabs are Persian speakers, and only a few speak Khorasani Arabic as their native language. The cities of Birjand, Mashhad, and Nishapur are home to large groups of Khorasani Arabs. According to ─░bn Al-Athir, the Arabic conquerors settled about 50,000 Arabic families in to Iranian Khorasan, modern day Northern Afghanistan and southern Turkmenistan, but the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nishapur
Nishapur or officially Romanized as Neyshabur ( fa, ;Or also "┘å█īž┤ž¦┘Š┘łž▒" which is closer to its original and historic meaning though it is less commonly used by modern native Persian speakers. In Persian poetry, the name of this city is written and pronounced as "┘å┘Éž┤ž¦ž©┘łž▒" (without the usage of "┘Š" or "ž©"). In modern times and among the general public and the Persian mass media, "┘å█īž┤ž¦ž©┘łž▒" is the most commonly used style of pronunciation and spelling of this city though "┘å█īž┤ž¦┘Š┘łž▒" is also correct. Ni┼Ī├ópur, Ni┼¤apur, N─½sh─üb┼½r, or Neyshapur are also the other Romanizations of this city. from Middle Persian ''"New-Shapuhr"'', meaning: "The New City of Shapur", "The Fair Shapur", or "The Perfect built of Shapur") is the second-largest city of Razavi Khorasan Province in the Northeast of Iran. Nishapur is situated in a fertile plain at the foot of Binalud Mountain Range and has been the historic capital of the Western Quarter of Greater Khorasan, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Khuza'ah
The Ban┼½ Khuz─ü╩┐ah ( ar, ž©┘å┘ł ž«ž▓ž¦ž╣ž® singular ''Khuz─ü╩┐─½'') is the name of an Azdite, QaßĖźß╣Ł─ünite tribe, which is one of the main ancestral tribes of the Arabian Peninsula. They ruled Mecca for a long period, prior to the Islamic prophet Muhammad's rule, and many members of the tribe now live in and around that city, but are also present in significant numbers in other countries, mainly Iraq, Palestine, and Jordan but also numbers can be found in Lebanon, Egypt, Libya, Syria, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait and UAE. The tribe acted as the custodians of Mecca before the Quraysh. They were the ruling kings of the Emirate of what is now modern-day Iraq, until the invasion of the Ottoman Empire in the late 1800s and were the rulers of the kingdom of the Middle Euphrates until the early-mid 20th century. During Muhammad's era They participated in the Battle of the Trench. The Banu Nadir began rousing the nomads of Najd. The Nadir enlisted the Banu Ghatafan by paying them half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayy
Shahr-e Ray ( fa, ž┤┘ćž▒ ž▒█ī, ) or simply Ray (Shar e Ray; ) is the capital of Ray County in Tehran Province, Iran. Formerly a distinct city, it has now been absorbed into the metropolitan area of Greater Tehran as the 20th district of municipal Tehran, the capital city of the country. Historically known as Rhages (), Rhagae and Arsacia, Ray is the oldest existing city in Tehran Province. In the classical era, it was a prominent city belonging to Media, the political and cultural base of the Medes. Ancient Persian inscriptions and the Avesta (Zoroastrian scriptures), among other sources, attest to the importance of ancient Ray. Ray is mentioned several times in the Apocrypha. It is also shown on the fourth-century Peutinger Map. The city was subject to severe destruction during the medieval invasions by the Arabs, Turks, and Mongols. Its position as a capital city was revived during the reigns of the Buyid Daylamites and the Seljuk Turks. Ray is richer than many other ancient c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rawd Al-Jinan
''Rawd al-Jinan wa Ruh al-Janan'' (''The Cool Breeze of Paradise and od'sBreath for the Soul'') also known as ''Tafs─½r Ab┼½ al- Fut┼½ßĖź'' is an exegesis on the Quran written by Abu l-Futuh al-Razi in the 6th A.H./12th century. The book, consisting of twenty volumes, is the earliest surviving Persian tafs─½r with an Im─üm─½ Im─ümah ( ar, žź┘É┘ģ┘Äž¦┘ģ┘Äž®) means "leadership" and is a concept in Twelver theology. The Twelve Imams are the spiritual and political successors to Muhammad, the Prophet of Islam, in the Twelver branch of Shia Islam. According to Twelver ... Sh─½╩┐─½ emphasis. It delves into mystical themes regularly.Abu l-Futuh al-Razi's entry in Brill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Classical Arabic, Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation in Islam, revelation from God in Islam, God. It is organized in 114 surah, chapters (pl.: , sing.: ), which consist of ─üyah, verses (pl.: , sing.: , construct case, cons.: ). In addition to its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic language. Muslims believe that the Quran was orally revealed by God to the Khatam an-Nabiyyin, final prophet, Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad, through the archangel Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning in the month of Ramadan, when Muhammad was 40; and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important miracle; a proof of his prophethood; and the culmination of a series of divine message ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tafs─½r
Tafsir ( ar, ž¬┘üž│┘Ŗž▒, tafs─½r ) refers to exegesis, usually of the Quran. An author of a ''tafsir'' is a ' ( ar, ┘ģ┘Å┘üž│┘æž▒; plural: ar, ┘ģ┘üž│┘æž▒┘ł┘å, mufassir┼½n). A Quranic ''tafsir'' attempts to provide elucidation, explanation, interpretation, context or commentary for clear understanding and conviction of God's will. Principally, a ''tafsir'' deals with the issues of linguistics, jurisprudence, and theology. In terms of perspective and approach, ''tafsir'' can be broadly divided into two main categories, namely ''tafsir bi-al-ma'thur'' (lit. received tafsir), which is transmitted from the early days of Islam through the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his companions, and ''tafsir bi-al-ra'y'' (lit. ''tafsir'' by opinion), which is arrived through personal reflection or independent rational thinking. There are different characteristics and traditions for each of the ''tafsirs'' representing respective schools and doctrines, such as Sunni Islam, Shia Islam, and Suf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Im─üm─½
Im─ümah ( ar, žź┘É┘ģ┘Äž¦┘ģ┘Äž®) means "leadership" and is a concept in Twelver theology. The Twelve Imams are the spiritual and political successors to Muhammad, the Prophet of Islam, in the Twelver branch of Shia Islam. According to Twelver theology, the successors to Muhammad are infallible human beings, who rule justly over the community and maintain and interpret sharia and undertake the esoteric interpretation of the Quran. The words and deeds of Muhammad and the Imams guide the community. For this, the Imams must be free from error and sin and chosen by divine decreeŌĆö ''nass''ŌĆöthrough the Prophet. Shi'a believe that divine wisdomŌĆö'AqlŌĆöis the source of the souls of the Prophets and Imams and gives them esoteric knowledgeŌĆö''hikmah''ŌĆöand that their suffering is a means by which their devotees may acquire divine grace. The Imam is not the recipient of divine revelation, but has a close relationship with God, who guides him, allowing the Imam in turn to guide oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quranic Exegesis Scholars
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ), which consist of verses (pl.: , sing.: , cons.: ). In addition to its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic language. Muslims believe that the Quran was orally revealed by God to the final prophet, Muhammad, through the archangel Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning in the month of Ramadan, when Muhammad was 40; and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important miracle; a proof of his prophethood; and the culmination of a series of divine messages starting with those revealed to Adam, including the Torah, the Psalms and the Gospel. The word ''Quran'' occurs some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1131 Deaths
Year 1131 ( MCXXXI) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events By place Levant * August 21 – King Baldwin II falls seriously ill, after his return from Antioch. He is moved to the patriarch's residence near the Holy Sepulchre, where he bequeaths the kingdom to his daughter Melisende, her husband Fulk and their infant son, Baldwin. He takes monastic vows, and dies soon after. Baldwin is buried in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, at Jerusalem.Steven Runciman (1952). ''A History of The Crusades. Vol II: The Kingdom of Jerusalem'', pp. 148ŌĆō149. . * September 14 – Melisende succeeds her father Baldwin II to the throne, and reigns jointly with Fulk, as King and Queen of Jerusalem. Their coronation, in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, is celebrated with festivities. Europe * Ramon Berenguer III (the Great), count of Barcelona, dies after a 34-year reign. He leaves most of his Catalonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |