|
Abstract Painter
Abstract art uses visual language of shape, form, color and line to create a composition which may exist with a degree of independence from visual references in the world. Western art had been, from the Renaissance up to the middle of the 19th century, underpinned by the logic of perspective and an attempt to reproduce an illusion of visible reality. By the end of the 19th century many artists felt a need to create a new kind of art which would encompass the fundamental changes taking place in technology, science and philosophy. The sources from which individual artists drew their theoretical arguments were diverse, and reflected the social and intellectual preoccupations in all areas of Western culture at that time. Abstract art, non-figurative art, non-objective art, and non-representational art are all closely related terms. They have similar, but perhaps not identical, meanings. Abstraction indicates a departure from reality in depiction of imagery in art. This departure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Delaunay, 1913, Premier Disque, 134 Cm, 52
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauvism
Fauvism /ˈfoʊvɪzm̩/ is the style of ''les Fauves'' (French language, French for "the wild beasts"), a group of early 20th-century modern artists whose works emphasized painterly qualities and strong colour over the Representation (arts), representational or Realism (visual arts), realistic values retained by Impressionism. While Fauvism as a style began around 1904 and continued beyond 1910, the movement as such lasted only a few years, 1905–1908, and had three exhibitions.John Elderfield, The ''"Wild Beasts" Fauvism and Its Affinities,'' 1976, Museum of Modern Art, p.13, The leaders of the movement were André Derain, Maurice de Vlaminck, and Henri Matisse. Artists and style Besides Matisse and Derain, other artists included Robert Deborne, Albert Marquet, Charles Camoin, Louis Valtat, Jean Puy, Maurice de Vlaminck, Henri Manguin, Raoul Dufy, Othon Friesz, Georges Rouault, Jean Metzinger, Kees van Dongen and Georges Braque (subsequently Picasso's partner in Cubism). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Pottery
Medieval Islamic pottery occupied a geographical position between Chinese ceramics, the unchallenged leaders of Eurasian production, and the pottery of the Byzantine Empire and Europe. For most of the period it can fairly be said to have been between the two in terms of aesthetic achievement and influence as well, borrowing from China and exporting to and influencing Byzantium and Europe. The use of drinking and eating vessels in gold and silver, the ideal in ancient Rome and Persia as well as medieval Christian societies, is prohibited by the Hadiths, with the result that pottery and glass were used for tableware by Muslim elites, as pottery (but less often glass) also was in China but was much rarer in Europe and Byzantium. In the same way, Islamic restrictions greatly discouraged figurative wall-painting, encouraging the architectural use of schemes of decorative and often geometrically-patterned titles, which are the most distinctive and original specialty of Islamic ceram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriental Rug
An oriental rug is a heavy textile made for a wide variety of utilitarian and symbolic purposes and produced in " Oriental countries" for home use, local sale, and export. Oriental carpets can be pile woven or flat woven without pile, using various materials such as silk, wool, and cotton. Examples range in size from pillows to large, room-sized carpets, and include carrier bags, floor coverings, decorations for animals, Islamic prayer rugs ('Jai'namaz'), Jewish Torah ark covers ('' parochet''), and Christian altar covers. Since the High Middle Ages, oriental rugs have been an integral part of their cultures of origin, as well as of the European and, later on, the North American culture. Geographically, oriental rugs are made in an area referred to as the “Rug Belt”, which stretches from Morocco across North Africa, the Middle East, and into Central Asia and northern India. It includes countries such as northern China, Tibet, Turkey, Iran, the Maghreb in the west, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Architecture
Islamic architecture comprises the architectural styles of buildings associated with Islam. It encompasses both secular and religious styles from the early history of Islam to the present day. The Islamic world encompasses a wide geographic area historically ranging from western Africa and Europe to eastern Asia. Certain commonalities are shared by Islamic architectural styles across all these regions, but over time different regions developed their own styles according to local materials and techniques, local dynasties and patrons, different regional centers of artistic production, and sometimes different religious affiliations. Early Islamic architecture was influenced by Roman, Byzantine, Iranian, and Mesopotamian architecture and all other lands which the Early Muslim conquests conquered in the seventh and eighth centuries.: "As the Arabs did not have an architectural tradition suited to the needs of a great empire, they adopted the building methods of the defeated S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabesque
The arabesque is a form of artistic decoration consisting of "surface decorations based on rhythmic linear patterns of scrolling and interlacing foliage, tendrils" or plain lines, often combined with other elements. Another definition is "Foliate ornament, used in the Islamic world, typically using leaves, derived from stylised half-palmettes, which were combined with spiralling stems". It usually consists of a single design which can be 'tessellation, tiled' or seamlessly repeated as many times as desired. Within the very wide range of Eurasian decorative art that includes Motif (visual arts), motifs matching this basic definition, the term "arabesque" is used consistently as a technical term by history of art, art historians to describe only elements of the decoration found in two phases: Islamic art from about the 9th century onwards, and European decorative art from the Renaissance onwards. Interlace (art), Interlace and Scroll (art), scroll decoration are terms used for mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Geometric Patterns
Islamic geometric patterns are one of the major forms of Islamic ornament, which tends to avoid using figurative images, as it is forbidden to create a representation of an important Islamic figure according to many holy scriptures. The geometric designs in Islamic art are often built on combinations of repeated squares and circles, which may be overlapped and interlaced, as can arabesques (with which they are often combined), to form intricate and complex patterns, including a wide variety of tessellations. These may constitute the entire decoration, may form a framework for floral or calligraphic embellishments, or may retreat into the background around other motifs. The complexity and variety of patterns used evolved from simple stars and lozenges in the ninth century, through a variety of 6- to 13-point patterns by the 13th century, and finally to include also 14- and 16-point stars in the sixteenth century. Geometric patterns occur in a variety of forms in Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
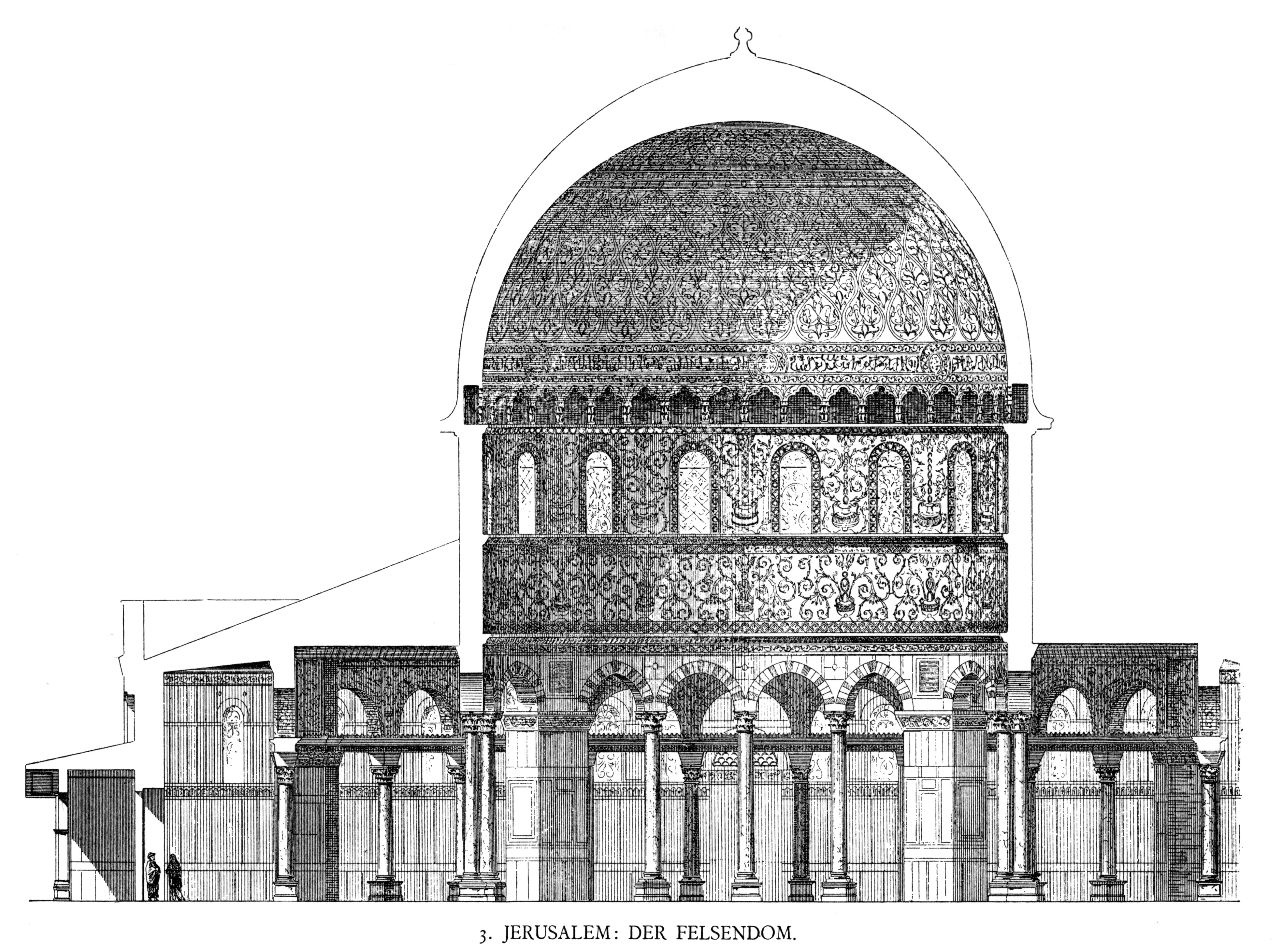
Dome Of The Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial construction was undertaken by the Umayyad Caliphate on the orders of Abd al-Malik during the Second Fitna in 691–692 CE, and it has since been situated on top of the site of the Second Jewish Temple (built in to replace the destroyed Solomon's Temple), which was destroyed by the Romans in 70 CE. The original dome collapsed in 1015 and was rebuilt in 1022–23. The Dome of the Rock is the world's oldest surviving work of Islamic architecture. Its architecture and mosaics were patterned after nearby Byzantine churches and palaces, although its outside appearance was significantly changed during the Ottoman period and again in the modern period, notably with the addition of the gold-plated roof, in 1959–61 and again in 1993. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniconism In Islam
Aniconism in Islam is the avoidance of images ( aniconism) of sentient beings in some forms of Islamic art. Islamic aniconism stems in part from the prohibition of idolatry and in part from the belief that the creation of living forms is God's prerogative. The Quran does not explicitly prohibit visual representation of any living being. The corpus of ''hadith'' (sayings attributed to the Islamic prophet Muhammad) contains more explicit prohibitions of images of living beings, challenging painters to "breathe life" into their images and threatening them with punishment on the Day of Judgment. Muslims have interpreted these prohibitions in different ways in different times and places. Religious Islamic art has been typically characterized by the absence of figures and extensive use of calligraphic, geometric and abstract floral patterns. However, representations of Muhammad (in some cases, with his face concealed) and other religious figures are found in some manuscripts from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signed Abdülkadir Şükri Efendi - Hilye-i Şerif (written Portrait Of The Prophet) - Google Art Project
Signing may refer to: * Using sign language * Signature, placing one's name on a document * Signature (other) * Manual communication, signing as a form of communication using the hands in place of the voice * Digital signature A digital signature is a mathematical scheme for verifying the authenticity of digital messages or documents. A valid digital signature, where the prerequisites are satisfied, gives a recipient very high confidence that the message was created b ..., signing as a method of authenticating digital information See also * Wikipedia:Sign your posts on talk pages, the Wikipedia policy of signing Talk pages {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Calligraphy
Islamic calligraphy is the artistic practice of handwriting and calligraphy, in the languages which use Arabic alphabet or the alphabets derived from it. It includes Arabic, Persian, Ottoman, and Urdu calligraphy.Chapman, Caroline (2012). ''Encyclopedia of Islamic Art and Architecture'', It is known in Arabic as ''khatt Arabi'' (), which translates into Arabic line, design, or construction. The development of Islamic calligraphy is strongly tied to the Qur'an; chapters and excerpts from the Qur'an are a common and almost universal text upon which Islamic calligraphy is based. Although artistic depictions of people and animals are not explicitly forbidden by the Qur'an, pictures have traditionally been limited in Islamic books in order to avoid idolatry. Although some scholars dispute this, Kufic script was supposedly developed around the end of the 7th century in Kufa, Iraq, from which it takes its name. The style later developed into several varieties, including floral, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Calligraphy
Chinese calligraphy is the writing of Chinese characters as an art form, combining purely visual art and interpretation of the literary meaning. This type of expression has been widely practiced in China and has been generally held in high esteem across East Asia. Calligraphy is considered one of the four most-sought skills and hobbies of ancient Chinese literati, along with playing stringed musical instruments, the board game "Go", and painting. There are some general standardizations of the various styles of calligraphy in this tradition. Chinese calligraphy and ink and wash painting are closely related: they are accomplished using similar tools and techniques, and have a long history of shared artistry. Distinguishing features of Chinese painting and calligraphy include an emphasis on motion charged with dynamic life. According to Stanley-Baker, "Calligraphy is sheer life experienced through energy in motion that is registered as traces on silk or paper, with time and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)