|
Abiological Nitrogen Fixation
Abiological nitrogen fixation describes chemical processes that fix (react with) N2, usually with the goal of generating ammonia. The dominant technology for abiological nitrogen fixation is the Haber process, which uses an iron-based heterogeneous catalysts and H2 to convert N2 to NH3. This article focuses on homogeneous (soluble) catalysts for the same or similar conversions. Transition metals Vol'pin and Shur An early influential discovery of abiological nitrogen fixation was made by Vol'pin and co-workers in Russia in 1970. Aspects are described in an early review: "using a non-protic Lewis acid, aluminium tribromide, were able to demonstrate the truly catalytic effect of titanium by treating dinitrogen with a mixture of titanium tetrachloride, metallic aluminium, and aluminium tribromide at 50 °C, either in the absence or in the presence of a solvent, e.g. benzene. As much as 200 mol of ammonia per mol of was obtained after hydrolysis.…" These results led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photochemistry
Photochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the chemical effects of light. Generally, this term is used to describe a chemical reaction caused by absorption of ultraviolet (wavelength from 100 to 400 nm), visible light (400–750 nm) or infrared radiation (750–2500 nm). In nature, photochemistry is of immense importance as it is the basis of photosynthesis, vision, and the formation of vitamin D with sunlight. Photochemical reactions proceed differently than temperature-driven reactions. Photochemical paths access high energy intermediates that cannot be generated thermally, thereby overcoming large activation barriers in a short period of time, and allowing reactions otherwise inaccessible by thermal processes. Photochemistry can also be destructive, as illustrated by the photodegradation of plastics. Concept Grotthuss–Draper law and Stark-Einstein law Photoexcitation is the first step in a photochemical process where the reactant is elevated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Dinitrogen Complex
Transition metal dinitrogen complexes are coordination compounds that contain transition metals as ion centers the dinitrogen molecules (N2) as ligands. Historical background Transition metal complexes of N2 have been studied since 1965 when the first complex was reported by Allen and Senoff. This diamagnetic complex, 2+.html" ;"title="u(NH3)5(N2)sup>2+">u(NH3)5(N2)sup>2+, was synthesized from hydrazine hydrate and ruthenium trichloride and consists of a u(NH3)5sup>2+ centre attached to one end of N2. The existence of N2 as a ligand in this compound was identified by IR spectrum with a strong band around 2170–2100 cm−1. In 1966, the molecular structure of u(NH3)5(N2)l2 was determined by Bottomly and Nyburg by X-ray crystallography. The dinitrogen complex ''trans''- rCl(N2)(PPh3)2is made by treating Vaska's complex with aromatic acyl azides. It has a planar geometry. The first preparation of a metal-dinitrogen complex using dinitrogen was reported in 1967 by Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
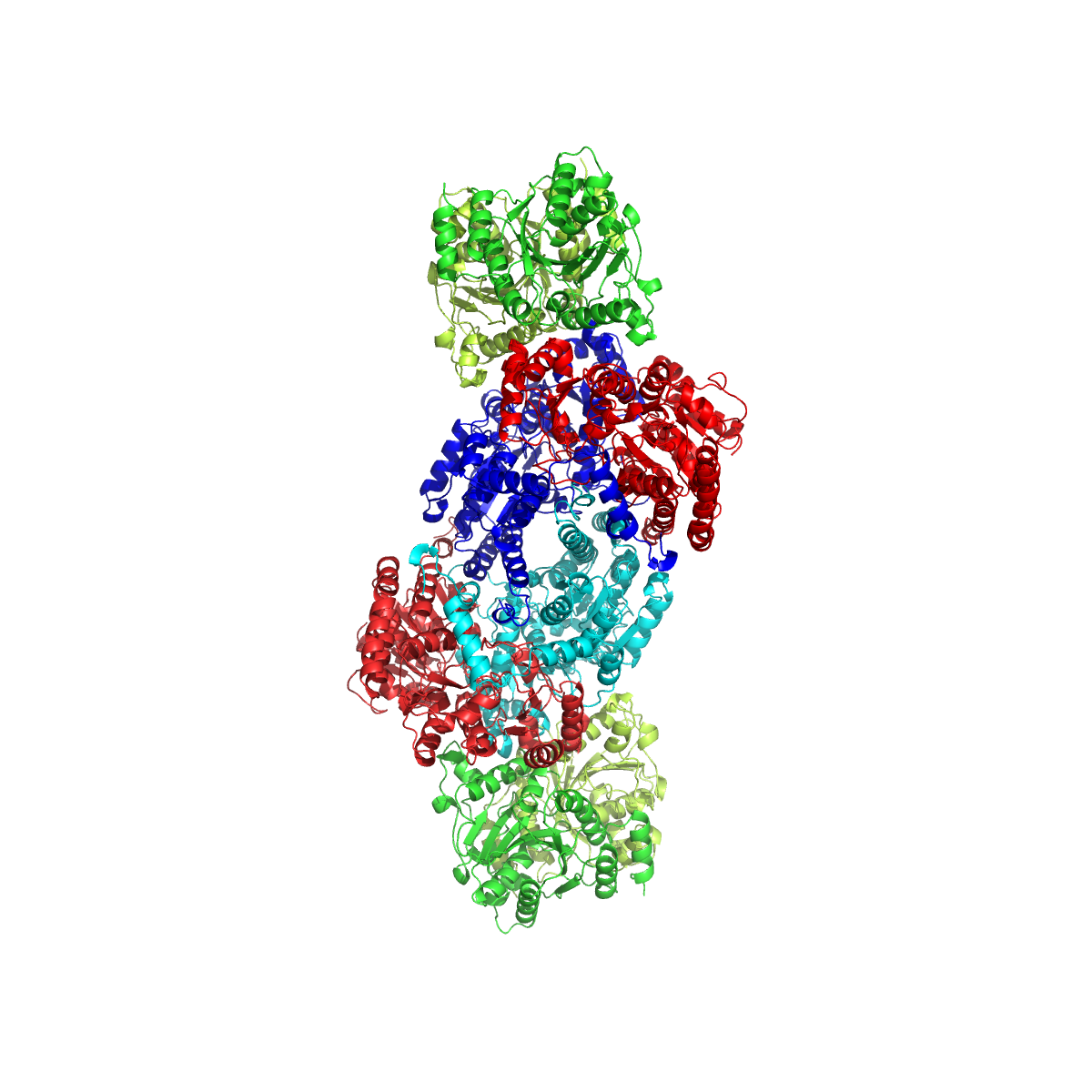
Nitrogenase
Nitrogenases are enzymes () that are produced by certain bacteria, such as cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria) and rhizobacteria. These enzymes are responsible for the Organic redox reaction, reduction of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3). Nitrogenases are the only family of enzymes known to catalyze this reaction, which is a key step in the process of nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation is required for all forms of life, with nitrogen being essential for the biosynthesis of molecules (nucleotides, amino acids) that create plants, animals and other organisms. They are encoded by the Nif genes or Homologous chromosome, homologs. They are related to protochlorophyllide reductase. Classification and structure Although the equilibrium formation of ammonia from molecular hydrogen and nitrogen has an overall negative enthalpy of reaction ( \Delta H^ = -45.2 \ \mathrm \, \mathrm \; \mathrm ), the activation energy is very high ( E_\mathrm = 230-420 \ \mathrm \, \mathrm ). Nitrogenase a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitriles
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a functional group. The prefix ''cyano-'' is used interchangeably with the term ''nitrile'' in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including methyl cyanoacrylate, used in super glue, and nitrile rubber, a nitrile-containing polymer used in latex-free laboratory and medical gloves. Nitrile rubber is also widely used as automotive and other seals since it is resistant to fuels and oils. Organic compounds containing multiple nitrile groups are known as cyanocarbons. Inorganic compounds containing the group are not called nitriles, but cyanides instead. Though both nitriles and cyanides can be derived from cyanide salts, most nitriles are not nearly as toxic. Structure and basic properties The N−C−C geometry is linear in nitriles, reflecting the sp hybridization of the triply bonded carbon. The C−N distance is short at 1.16 Å, consistent with a triple bond. Nitriles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tris(trimethylsilyl)amine
Tris(trimethylsilyl)amine is the simplest tris(trialkylsilyl)amine which are having the general formula (R3Si)3N, in which all three hydrogen atoms of the ammonia are replaced by trimethylsilyl groups (-Si(CH3)3). Tris(trimethylsilyl)amine has been for years in the center of scientific interest as a stable intermediate in chemical nitrogen fixation (i. e. the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen N2 into organic substrates under normal conditions). Production Early attempts to prepare tris(trimethylsilyl)amine from ammonia and trimethylchlorosilane (TMS-Cl) were unsuccessful even at temperatures of 500 °C and in the presence of the base pyridine. The reaction of ammonia and trimethylchlorosilane stops at the stage of the doubly silylated product bis(trimethylsilyl)amine (usually referred to as hexamethyldisilazane, HMDS). Tris(trimethylsilyl)amine is obtained by reaction of the sodium salt of hexamethyldisilazane - from hexamethyldisilazane and sodium amide or from hexamet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylsilyl Chloride
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound ( silyl halide), with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry. Preparation TMSCl is prepared on a large scale by the '' direct process'', the reaction of methyl chloride with a silicon-copper alloy. The principal target of this process is dimethyldichlorosilane, but substantial amounts of the trimethyl and monomethyl products are also obtained. The relevant reactions are (Me = CH3): : x MeCl + Si → Me3SiCl, Me2SiCl2, MeSiCl3, other products Typically about 2–4% of the product stream is the monochloride, which forms an azeotrope with MeSiCl3. Reactions and uses TMSCl is reactive toward nucleophiles, resulting in the replacement of the chloride. In a characteristic reaction of TMSCl, the nucleophile is water, resulting in hydrolysis to give the hexamethy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Nitride
Lithium nitride is a compound with the formula Li3N. It is the only stable alkali metal nitride. The solid has a reddish-pink color and high melting point. Preparation and handling Lithium nitride is prepared by direct combination of elemental lithium with nitrogen gas: :6 Li + N2 → 2 Li3N Instead of burning lithium metal in an atmosphere of nitrogen, a solution of lithium in liquid sodium metal can be treated with N2. Lithium nitride reacts violently with water to produce ammonia: :Li3N + 3 H2O → 3 LiOH + NH3 Structure and properties ''alpha''-Li3N (stable at room temperature and pressure) has an unusual crystal structure that consists of two types of layers, one sheet has the composition Li2N− contains 6-coordinate N centers and the other sheet consists only of lithium cations. Two other forms are known: ''beta''-Lithium nitride, formed from the alpha phase at has the sodium arsenide (Na3As) structure; ''gamma''-Lithium nitride (same structure as Li3Bi) forms fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil. When cut, it exhibits a metallic luster, but moist air corrodes it quickly to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish. It never occurs freely in nature, but only in (usually ionic) compounds, such as pegmatitic minerals, which were once the main source of lithium. Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brines. Lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride. The nucleus of the lithium atom verges on instability, since the two stable lithium isotopes foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borylene
A borylene is the boron analogue of a carbene. The general structure is R-B: with R an organic residue and B a boron atom with two unshared electrons. Borylenes are of academic interest in organoboron chemistry. A singlet ground state is predominant with boron having two vacant sp2 orbitals and one doubly occupied one. With just one additional substituent the boron is more electron deficient than the carbon atom in a carbene. For this reason stable borylenes are more uncommon than stable carbenes. Some borylenes such as boron monofluoride (BF) and boron monohydride (BH) the parent compound also known simply as borylene, have been detected in microwave spectroscopy and may exist in stars. Other borylenes exist as reactive intermediates and can only be inferred by chemical trapping. The first stable terminal borylene complex OC)5WBN(SiMe3)2was reported by Holger Braunschweig et al. in 1998. In this compound a borylene is coordinated to a transition metal. Borylenes are also s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Base
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons. Trimethylborane (Me3B) is a Lewis acid as it is capable of accepting a lone pair. In a Lewis adduct, the Lewis acid and base share an electron pair furnished by the Lewis base, forming a dative bond. In the context of a specific chemical reaction between NH3 and Me3B, a lone pair from NH3 will form a dative bond with the empty orbital of Me3B to form an adduct NH3•BMe3. The terminology refers to the contributions of Gilbert N. Lewis. From p. 142: "We are inclined to think of substances as pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |