|
Abhika
Abihka was one of the four mother towns of the Muscogee Creek confederacy. ''Abihka'' is also sometimes used to refer to all Upper Creek (or ''Muscogee'') people. History Origins The Abihka were the remnants of the 16th century "Chiefdom of Coosa." The bulk of the Natchez people settled with the Abihka after being dispersed by the French in the 18th century. Etymology The name "Abihka" (meaning unknown), is sometimes used to refer to all the Upper Creek peoples. Territory The members of the Abihka were Upper Creek Indians. Their main place of residence was along the banks of the Coosa and Alabama rivers, in what is now Talladega County, Alabama. Besides the town of Abihka, the Creek had established other important towns in their territory: ''Abihkutchi'', ''Tuckabutche'', ''Talladega'', ''Coweta'', and ''Kan-tcati''. Ceremonial grounds After the removal to the Indian Territory, refugees from the Abihka mother-town established a ceremonial stomp dance ground which they call Abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscogee Creek Confederacy
The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy ( in the Muscogee language), are a group of related indigenous (Native American) peoples of the Southeastern WoodlandsTranscribed documents Sequoyah Research Center and the American Native Press Archives in the . Their original homelands are in what now comprises southern , much of , western |
Muscogee Tribal Towns
The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy ( in the Muscogee language), are a group of related indigenous (Native American) peoples of the Southeastern WoodlandsTranscribed documents Sequoyah Research Center and the American Native Press Archives in the . Their original homelands are in what now comprises southern , much of , western |
Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans who held aboriginal title to their land as a sovereign independent state. In general, the tribes ceded land they occupied in exchange for Land grant#United States, land grants in 1803. The concept of an Indian Territory was an outcome of the US federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the Indian Territory in the American Civil War, American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the US government was one of Cultural assimilation of Native Americans#Americanization and assimilation (1857–1920), assimilation. The term ''Indian Reserve (1763), Indian Reserve'' describes lands the Kingdom of Great Britain, British set aside for Indigenous tribes between the Appalachian Mountains and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native American Tribes In Alabama
Native may refer to: People * Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth * Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory ** Native Americans (other) In arts and entertainment * Native (band), a French R&B band * Native (comics), a character in the X-Men comics universe * ''Native'' (album), a 2013 album by OneRepublic * ''Native'' (2016 film), a British science fiction film * ''The Native'', a Nigerian music magazine In science * Native (computing), software or data formats supported by a certain system * Native language, the language(s) a person has learned from birth * Native metal, any metal that is found in its metallic form, either pure or as an alloy, in nature * Native species In biogeography, a native species is indigenous to a given region or ecosystem if its presence in that region is the result of only local natural evolution (though often popularised as "with no human intervention") d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Appalachian Mississippian Culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building large, earthen platform mounds, and often other shaped mounds as well. It was composed of a series of urban settlements and satellite villages linked together by loose trading networks. The largest city was Cahokia, believed to be a major religious center located in what is present-day southern Illinois. The Mississippian way of life began to develop in the Mississippi River Valley (for which it is named). Cultures in the tributary Tennessee River Valley may have also begun to develop Mississippian characteristics at this point. Almost all dated Mississippian sites predate 1539–1540 (when Hernando de Soto explored the area), with notable exceptions being Natchez communities. These maintained Mississippian cultural practices into the 18th century. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trading Post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded. Typically the location of the trading post would allow people from one geographic area to trade in goods produced in another area. In some examples, local inhabitants could use a trading post to exchange local products for goods they wished to acquire. Examples Major towns in the Hanseatic League were known as ''kontors'', a form of trading posts. Charax Spasinu was a trading post between the Roman and Parthian Empires. Manhattan and Singapore were both established as trading posts, by Dutchman Peter Minuit and Englishman Stamford Raffles respectively, and later developed into major settlements. Other uses * In the context of scouting, trading post usually refers to a camp store in which snacks, craft materials, and general merchandise are sold. "Trading posts" also refers to a cub scout actitivty in which cub teams (or indivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alice Brown Davis
Alice Brown Davis (September 10, 1852 – June 21, 1935) was the first female Principal Chief of the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, and served from 1922–1935, appointed by President Warren G. Harding.Waldowski, Paula"Alice Brown Davis: A Leader Of Her People."''Seminole Nation, Indian Territory History and Genealogy.'' 4 Aug 2009 (retrieved 25 Nov 2009) She was of Seminole (Tiger Clan) and Scots descent. Her older brother John Frippo Brown had served as chief of the tribe and their brother Andrew Jackson Brown as treasurer. Early life and education Alice Brown was born on September 10, 1852, in the Cherokee town of Park Hill, Indian Territory and grew up near Fort Gibson. Her father, Dr. John Frippo Brown, was from Scotland and a graduate of the University of Edinburgh. He accompanied the Seminole as a military surgeon during their forced removal from Florida. During this journey, he married Lucy Redbeard, a Seminole from ''Katcvlke'' or the Tiger Clan. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henryetta, Oklahoma
Henryetta is a city in Okmulgee County, Oklahoma, United States. The population was 5,927 at the 2010 census, down 9.6 percent from the figure of 6,096 recorded in 2000. History Hugh Henry established a ranch on Creek Nation land in 1885. He soon found a deposit of coal, which he began using to fuel the forge at his ranch. Discovery of more coal deposits in the large Henryetta Coal Formation attracted several railroads to develop these mines. A settlement named Furrs grew up around the mines. The name changed to Henryetta when a post office opened on August 28, 1900.Bamburg, Maxine"Henryetta,"''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture'', Oklahoma Historical Society, Accessed July 22, 2015. At statehood in 1907, Henryetta had 1,051 residents. The economy was based on agriculture, coal, natural gas and oil. In 1909, the area had fourteen coal mines, producing 65,000 tons per month. By 1910, the population had grown to 1,671. The town added a broom factory, several brick factori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomp Dance
The stomp dance is performed by various Eastern Woodland tribes and Native American communities in the United States, including the Muscogee, Yuchi, Cherokee, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Delaware, Miami, Caddo, Tuscarora, Ottawa, Quapaw, Peoria, Shawnee, Seminole,Conlon, PaulaDance, American Indian. ''Oklahoma Historical Society's Encyclopedia of 612-3 History and Culture.'' (retrieved 6 July 2009) Natchez,Sturtevant and Fogelson, 367 and Seneca-Cayuga tribes. Stomp dance communities are active in North Carolina, Oklahoma, Alabama, Mississippi, and Florida. Names and etymology The English term ''stomp dance'' refers to the "shuffle and stomp" movements of the dance. In the Muskogee language the dance is called ''opvnkv haco'', which can mean "drunken", "crazy" or "inspirited" dance. This usually refers to the exciting, yet meditative effect the dance and the medicine have on the participants. In the Shawnee language, the dance is called ''nikanikawe'' which refers to a dance involvi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Removal
Indian removal was the United States government policy of forced displacement of self-governing tribes of Native Americans from their ancestral homelands in the eastern United States to lands west of the Mississippi Riverspecifically, to a designated Indian Territory (roughly, present-day Oklahoma). The Indian Removal Act, the key law which authorized the removal of Native tribes, was signed by Andrew Jackson in 1830. Although Jackson took a hard line on Indian removal, the law was enforced primarily during the Martin Van Buren administration. After the passage of the Indian Removal Act in 1830, approximately 60,000 members of the Cherokee, Muscogee (Creek), Seminole, Chickasaw, and Choctaw nations (including thousands of their black slaves) were forcibly removed from their ancestral homelands, with thousands dying during the Trail of Tears. Indian removal, a popular policy among incoming settlers, was a consequence of actions by European settlers in North America during th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
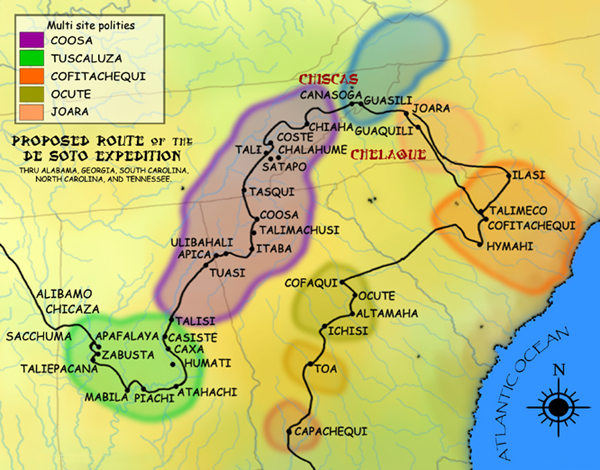
Chiefdom Of Coosa
The Coosa chiefdom was a powerful Native American paramount chiefdom in what are now Gordon and Murray counties in Georgia, in the United States."Late Prehistoric/Early Historic Chiefdoms (ca. A.D. 1300-1850)" ''''. Retrieved July 22, 2010. It was inhabited from about 1400 until about 1600, and dominated several smaller chiefdoms. The total population of Coosa's area of influence, reaching into present-day Tennessee and Alabama, has been estimated at 50,000. Hernando de Soto and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_1900.jpg)