|
Abel (hominid)
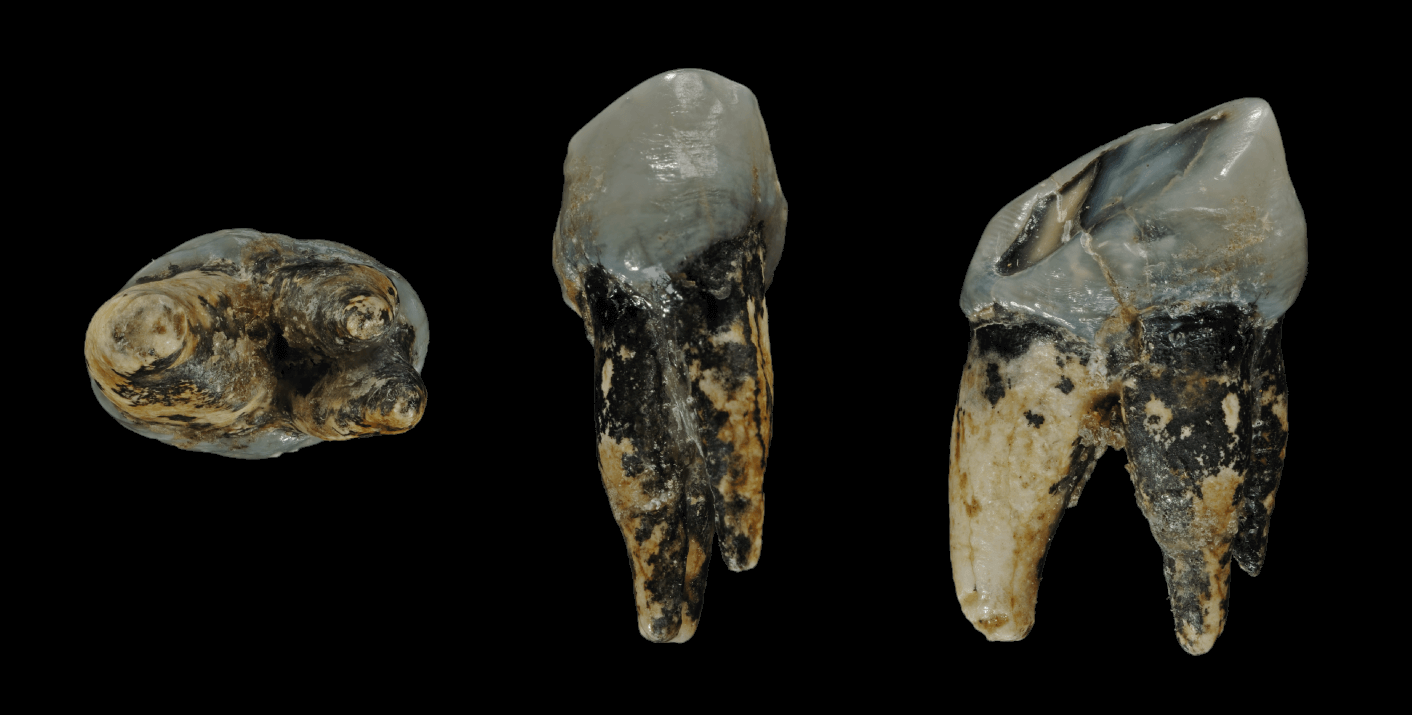
Abel (KT-12/H1) is the name given to the only specimen ever discovered of ''Australopithecus bahrelghazali''. Abel was found in January 1995 in Chad in the Kanem Region by the paleontologist Michel Brunet,Brunet, M., Beauvilain, A., Coppens, Y., Heintz, É., Moutaye, A.H.E et Pilbeam, D. (1995) - "The first australopithecine 2,500 kilometres west of the Rift Valley (Chad)", ''Nature'', 378, pp. 273-275. who named the fossil "Abel" in memory of his close friend Abel Brillanceau, who had died of malaria in 1989. Of Abel remains only part of a jaw, which explains the little information discernable concerning its way of life. The few teeth confirm it to be of the genus ''Australopithecus'': it has a second premolar with a broad and molarized crown, not dissimilar to the Lucy fossil, and as such to the ''Australopithecus afarensis''. See also *List of human evolution fossils The following tables give an overview of notable finds of hominin fossils and remains relating to human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australopithecus Bahrelghazali
''Australopithecus bahrelghazali'' is an extinct species of australopithecine discovered in 1995 at Koro Toro, Bahr el Gazel, Chad, existing around 3.5 million years ago in the Pliocene. It is the first and only australopithecine known from Central Africa, and demonstrates that this group was widely distributed across Africa as opposed to being restricted to East and southern Africa as previously thought. The validity of ''A. bahrelghazali'' has not been widely accepted, in favour of classifying the specimens as ''A. afarensis'', a better known Pliocene australopithecine from East Africa, because of the anatomical similarity and the fact that ''A. bahrelghazali'' is known only from 3 partial jawbones and an isolated premolar. The specimens inhabited a lakeside grassland environment with sparse tree cover, possibly similar to the modern Okavango Delta, and similarly predominantly ate C4 savanna foods—such as grasses, sedges, storage organs, or rhizomes—and to a lesser degree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon to the southwest, Nigeria to the southwest (at Lake Chad), and Niger to the west. Chad has a population of 16 million, of which 1.6 million live in the capital and largest city of N'Djamena. Chad has several regions: a desert zone in the north, an arid Sahelian belt in the centre and a more fertile Sudanian Savanna zone in the south. Lake Chad, after which the country is named, is the second-largest wetland in Africa. Chad's official languages are Arabic and French. It is home to over 200 different ethnic and linguistic groups. Islam (55.1%) and Christianity (41.1%) are the main religions practiced in Chad. Beginning in the 7th millennium BC, human populations moved into the Chadian basin in great numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanem Region
Kanem ( ar, كانم) is one of the 23 regions of Chad. It is named after the famous Kanem Empire, which was centred in this vicinity. The region's capital is Mao. It was created in 2002 from the former Prefecture of Kanem. In 2008, a portion of the Kanem region (the Bahr el Gazel Department) was split off to become the new Bahr el Gazel Region. Geography The region borders Borkou Region to the north, Bahr el Gazel Region to the east, Hadjer-Lamis Region and Lac Region to the south, and Niger to the west. Settlements Mao is the regional capital; other major settlements include Am Doback, Kekedina, Nokou, Ntiona, Rig Rig, Wadjigui and Ziguey. Demographics As [er the census of 2009, the population in the region was 354,603, 51.4% female. The average size of household was 4.50: 4.50 in rural households and 4.90 in urban areas. The number of households was 78,145: 70,779 in rural areas and 7,366 in urban areas. The number of nomads in the region was 10,056, 2.6% of the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, ( gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and engineering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michel Brunet (paleontologist)
Michel Brunet (born April 6, 1940) is a French paleontologist and a professor at the Collège de France. In 2001 Brunet announced the discovery in Central Africa of the skull and jaw remains of a late Miocene hominid nicknamed Toumaï. These remains may predate the earliest previously known hominid remains, Lucy, by over three million years; however, this conclusion is the subject of a significant controversy. Biography Brunet was born in 1940 in Vienne, in the region of Poitou. After having passed his first years in the countryside, at 8 he moved with his family to Versailles. He took a Ph.D. in paleontology at the Sorbonne and then became Professor of Vertebrate paleontology at the University of Poitiers, specializing in hoofed mammals. A turning point in Brunet's career was when he heard that paleoanthropologist David Pilbeam was searching for fossil apes in Pakistan and the ancestors of the hominids. This spurred Brunet to form with his colleague Emile Heintz a team with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the ''Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spread by h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australopithecus
''Australopithecus'' (, ; ) is a genus of early hominins that existed in Africa during the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. The genus ''Homo'' (which includes modern humans) emerged within ''Australopithecus'', as sister to e.g. ''Australopithecus sediba''. Also the genera ''Paranthropus'' and ''Kenyanthropus'' emerged within ''Australopithecus''. ''Australopithecus'' is a member of the subtribe Australopithecina, which sometimes also includes ''Ardipithecus'', though the term "australopithecine" is sometimes used to refer only to members of ''Australopithecus''. Species include ''Australopithecus garhi, A. garhi'', ''Australopithecus africanus, A. africanus'', ''Australopithecus sediba, A. sediba'', ''Australopithecus afarensis, A. afarensis, Australopithecus anamensis, A. anamensis, Australopithecus bahrelghazali, A. bahrelghazali'' and ''Australopithecus deyiremeda, A. deyiremeda''. Debate exists as to whether some ''Australopithecus'' species should be reclassified into ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premolar
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth. They have at least two cusps. Premolars can be considered transitional teeth during chewing, or mastication. They have properties of both the canines, that lie anterior and molars that lie posterior, and so food can be transferred from the canines to the premolars and finally to the molars for grinding, instead of directly from the canines to the molars. Human anatomy The premolars in humans are the maxillary first premolar, maxillary second premolar, mandibular first premolar, and the mandibular second premolar. Premolar teeth by definition are permanent teeth distal to the canines, preceded by deciduous molars. Morphology There is always one large buccal cusp, especially so in the mandibular first premolar. The lower second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucy (Australopithecus)
AL 288-1, commonly known as Lucy, is a collection of several hundred pieces of fossilized bone representing 40 percent of a female of the hominin species ''Australopithecus afarensis''. In Ethiopia, the assembly is also known as (ድንቅ ነሽ), which means "you are marvelous" in Amharic. Lucy was discovered in 1974 in Africa, at Hadar, a site in the Awash Valley of the Afar Triangle in Ethiopia, by paleoanthropologist Donald Johanson of the Cleveland Museum of Natural History. The Lucy specimen is an early australopithecine and is dated to about 3.2 million years ago. The skeleton presents a small skull akin to that of non-hominin apes, plus evidence of a walking-gait that was bipedal and upright, akin to that of humans (and other hominins); this combination supports the view of human evolution that bipedalism preceded increase in brain size. A 2016 study proposes that ''Australopithecus afarensis'' was also to a large extent tree-dwelling, though the extent of this is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australopithecus Afarensis
''Australopithecus afarensis'' is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived from about 3.9–2.9 million years ago (mya) in the Pliocene of East Africa. The first fossils were discovered in the 1930s, but major fossil finds would not take place until the 1970s. From 1972 to 1977, the International Afar Research Expedition—led by anthropologists Maurice Taieb, Donald Johanson and Yves Coppens—unearthed several hundreds of hominin specimens in Hadar, Ethiopia, the most significant being the exceedingly well-preserved skeleton AL 288-1 ("Lucy") and the site AL 333 ("the First Family"). Beginning in 1974, Mary Leakey led an expedition into Laetoli, Tanzania, and notably recovered fossil trackways. In 1978, the species was first described, but this was followed by arguments for splitting the wealth of specimens into different species given the wide range of variation which had been attributed to sexual dimorphism (normal differences between males and females). ''A. afa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Human Evolution Fossils
The following tables give an overview of notable finds of Hominini, hominin fossils and Skeleton, remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the Chimpanzee–human last common ancestor, human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roughly 7 to 8 million years ago. As there are thousands of fossils, mostly fragmentary, often consisting of single bones or isolated teeth with complete skulls and skeletons rare, this overview is not complete, but show some of the most important findings. The fossils are arranged by approximate age as determined by radiometric dating and/or incremental dating and the species name represents current consensus; if there is no clear scientific consensus the other possible classifications are indicated. The early fossils shown are not considered ancestors to ''Homo sapiens'' but are closely related to ancestors and are therefore important to the study of the lineage. After 1.5 million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australopithecus Fossils
''Australopithecus'' (, ; ) is a genus of early hominins that existed in Africa during the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. The genus ''Homo'' (which includes modern humans) emerged within ''Australopithecus'', as sister to e.g. ''Australopithecus sediba''. Also the genera ''Paranthropus'' and ''Kenyanthropus'' emerged within ''Australopithecus''. ''Australopithecus'' is a member of the subtribe Australopithecina, which sometimes also includes ''Ardipithecus'', though the term "australopithecine" is sometimes used to refer only to members of ''Australopithecus''. Species include ''A. garhi'', '' A. africanus'', ''A. sediba'', ''A. afarensis, A. anamensis, A. bahrelghazali'' and '' A. deyiremeda''. Debate exists as to whether some ''Australopithecus'' species should be reclassified into new genera, or if ''Paranthropus'' and ''Kenyanthropus'' are synonymous with ''Australopithecus'', in part because of the taxonomic inconsistency. The earliest known member of the genus, ''A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)