|
Abbaye De Valmont
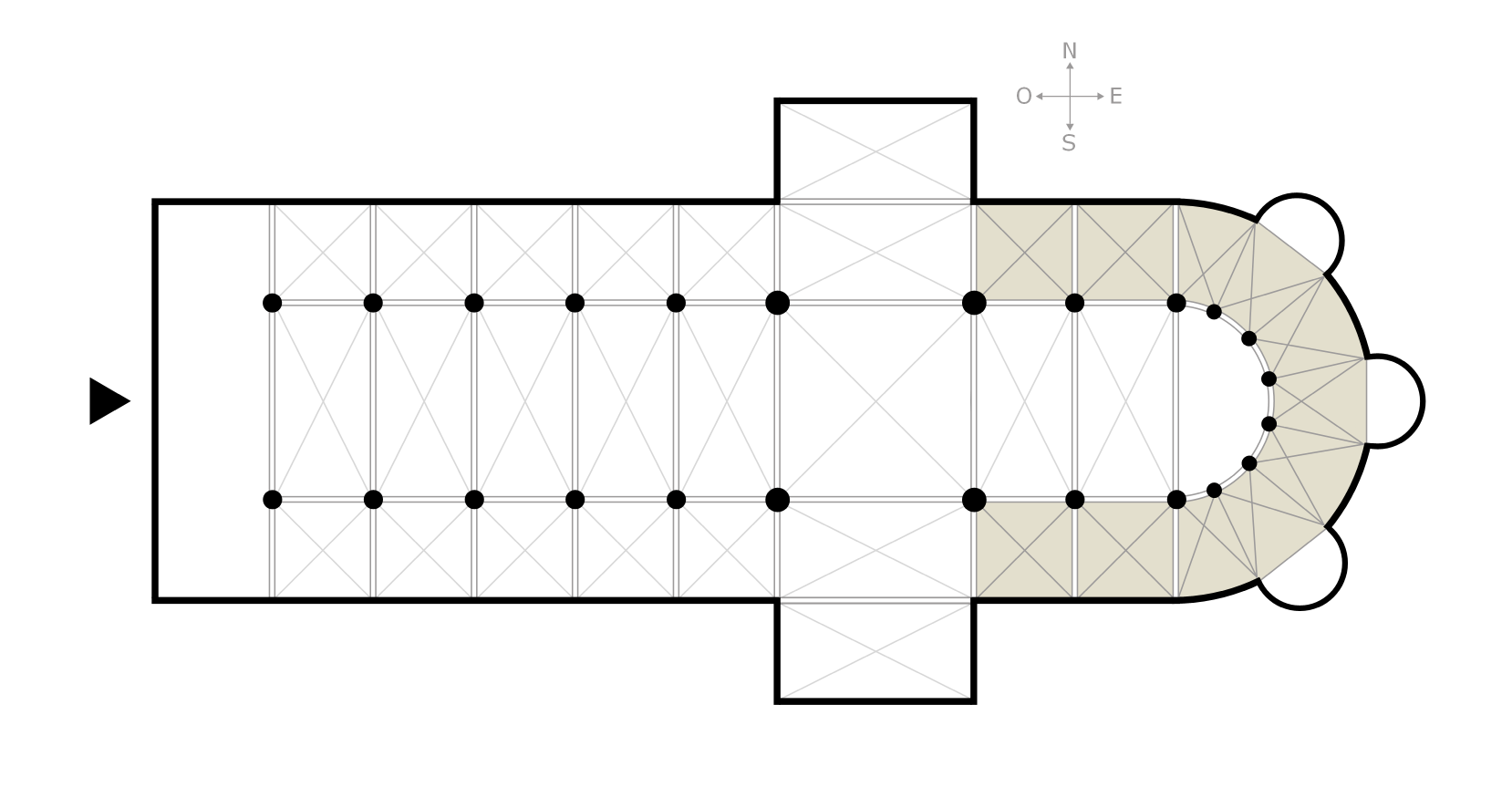
Valmont Abbey (''Abbaye de Valmont'', ''Sainte-Marie de Valmont'' or ''abbaye Sainte-Marie'') is a Benedictine abbey in Valmont, Seine-Maritime, France. Its chapel and surviving ruins of other parts of the abbey were classed as historical monuments in 1951 and the facades and roofs of all the abbey buildings were made historic monuments in 1965. History The Abbey was founded in 1169 by Nicolas d'Estouteville with Benedictines monks, from Hambye Abbey. It never had more than 25 monks and was destroyed and rebuilt several times with the abbey church only truly completed in the 16th century – Countess Marie II of Saint-Pol is buried in it. The abbey buildings were built from 1678 to 1782 under Louis de La Fayette (1634–1729), commendatory abbot, who tried to introduce the Saint Maur reforms to the abbey in 1680. It was finally reformed in 1754 by the Maurists and was rebuilt during the second half of the 18th century, until the French Revolution when it was dissolved – its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valmont, Seine-Maritime
Valmont () is a commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region in northern France. Geography A farming village in the Pays de Caux, situated some northeast of Le Havre, at the junction of the D10, D17, D28 and D69 roads. The village is surrounded by woodland. Just outside the village, at ''Le Vivier'', is the source of the river Valmont. History The commune was created in 1822 and 1825 by the merger of four former parishes of Valmont, Saint-Ouen-au-Bosc, Rouxmesnil and Le Bec-au-Cauchois. In 1169, the abbey of Notre-Dame-du-Pre was founded here by Nicolas of Estouteville. It was devastated during the Hundred Years' War but was repaired and became a nunnery. In 1416 the Battle of Valmont took place near the town, as part of the Hundred Years' War. Population Places of interest * The ruins of Notre-Dame abbey, dating from the twelfth century. * The church of St. Nicolas. * The chateau of Estouteville, dating from the eleventh century with a donjon and a lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Style
Renaissance architecture is the European architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 16th centuries in different regions, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of Ancient Greece, ancient Greek and Ancient Rome, Roman thought and material culture. Stylistically, Renaissance architecture followed Gothic architecture and was succeeded by Baroque architecture. Developed first in Florence, with Filippo Brunelleschi as one of its innovators, the Renaissance style quickly spread to other Italian cities. The style was carried to Spain, France, Germany, England, Russia and other parts of Europe at different dates and with varying degrees of impact. Renaissance style places emphasis on symmetry, proportion (architecture), proportion, geometry and the regularity of parts, as demonstrated in the architecture of classical antiquity and in particular ancient Roman architecture, of which many examples remained. Orderly arrangements of columns, pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of Middle Ages, medieval Europe, the population of the metropolitan area (french: functional area (France), aire d'attraction) is 702,945 (2018). People from Rouen are known as ''Rouennais''. Rouen was the seat of the Exchequer of Normandy during the Middle Ages. It was one of the capitals of the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman dynasties, which ruled both England and large parts of modern France from the 11th to the 15th centuries. From the 13th century onwards, the city experienced a remarkable economic boom, thanks in particular to the development of textile factories and river trade. Claimed by both the French and the English during the Hundred Years' War, it was on its soil that Joan of Arc was tried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fécamp Abbey
The Abbey of the Holy Trinity at Fécamp, commonly known as Fécamp Abbey (french: Abbaye de la Trinité de Fécamp), is a Benedictine abbey in Fécamp, Seine-Maritime, Upper Normandy, France. The abbey is known as the first producer of bénédictine, a herbal liqueur based on brandy. First foundation Around 658, Waningus, a Merovingian count, founded a nunnery here, which was destroyed by the Vikings in 841. Another convent he founded in 660, near the site of the Precious Relic, was destroyed by the Vikings in 842. Around the ducal palace, the foundations of two chapels have been found. Second foundation In the 990s Richard I of Normandy, who was born in Fécamp, began the rebuilding of the church. It was Richard II who invited the zealous Saint William of Volpiano in 1001 to rekindle the life of the abbey under the Cluniac Benedictine rules. These two Norman rulers, who were originally buried outside, were later interred in 1162 by Henry II of England within the southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaillon
Gaillon () is a commune in the Eure department in northern France. History The origins of Gaillon are not really known. In 892, Rollo, a Viking chief, might have ravaged Gaillon and the region, before he became the first prince of the Normans and count of Rouen in 911. The Gaillon history did begin, when the first dukes of Normandy built a keep to defend the border of Normandy against their enemies : the kings of France. The first castle of Gaillon belonged to a whole system of defence along the Norman border such as Evreux, Pacy-sur-Eure, Vernon, Malassis, Gasny, Baudemont, etc. In 1192 King Philip II Augustus of France seized the castle in his battle with Richard the Lion Heart to conquer Normandy. Richard decided to build a new one a few kilometers away in Les Andelys on the other bank of the Seine River : Château Gaillard. In 1262 the castle was exchanged between King Louis IX and Eudes Rigaud (Archbishop of Rouen) and it became the residence of the Rouen archbishops unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bec Abbey
Bec Abbey, formally the Abbey of Our Lady of Bec (french: Abbaye Notre-Dame du Bec), is a Benedictine monastic foundation in the Eure ''département'', in the Bec valley midway between the cities of Rouen and Bernay. It is located in Le Bec Hellouin, Normandy, France, and was the most influential abbey of the 12th-century Anglo- Norman kingdom. Like all abbeys, Bec maintained annals of the house but uniquely its first abbots also received individual biographies, brought together by the monk of Bec, Milo Crispin. Because of the abbey's cross-Channel influence, these hagiographic lives sometimes disclose historical information of more than local importance. Name The name of the abbey derives from the bec, or stream, that runs nearby. The word derives from the Scandinavian root, ''bekkr''. First foundation The abbey was founded in 1034 by Saint Herluin, whose life was written by Gilbert Crispin, Abbot of Westminster, formerly of Bec, and collated with three other lives by Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triforium
A triforium is an interior gallery, opening onto the tall central space of a building at an upper level. In a church, it opens onto the nave from above the side aisles; it may occur at the level of the clerestory windows, or it may be located as a separate level below the clerestory. Masonry triforia are generally vaulted and separated from the central space by arcades. Early triforia were often wide and spacious, but later ones tend to be shallow, within the thickness of an inner wall, and may be blind arcades not wide enough to walk along. The outer wall of the triforium may itself have windows (glazed or unglazed openings), or it may be solid stone. A narrow triforium may also be called a "blind-storey", and looks like a row of window frames. History ''Triforium'' is derived from the Latin ''tres'', ''tria'' "three", and ''foris'', "door, entrance"; its Greek equivalent is τρίθυρον, which originally referred to a building with three doors. The earliest examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
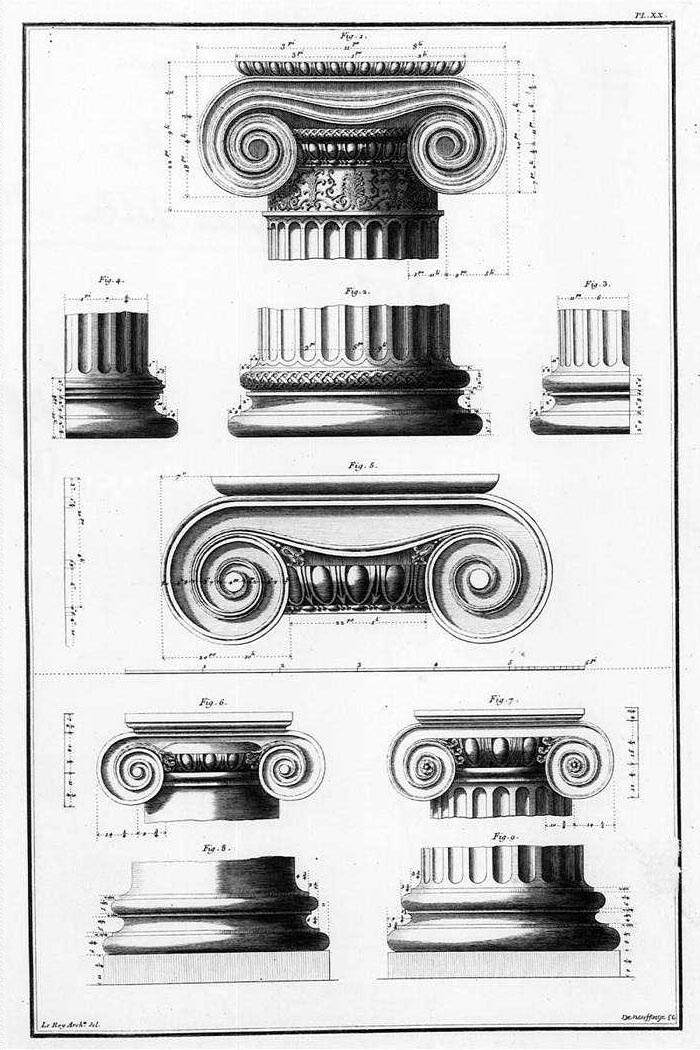
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulatory
The ambulatory ( la, ambulatorium, ‘walking place’) is the covered passage around a cloister or the processional way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar. The first ambulatory was in France in the 11th century but by the 13th century ambulatories had been introduced in England and many English cathedrals were extended to provide an ambulatory. The same feature is often found in Indian architecture and Buddhist architecture generally, especially in older periods. Ritual circumambulation or parikrama around a stupa or cult image is important in Buddhism and Hinduism. Often the whole building was circumambulated, often many times. The Buddhist chaitya hall always allowed a path for this, and the Durga temple, Aihole (7th or 8th century) is a famous Hindu example. The term is also used to describe a garden feature in the grounds of a country house. A typical example is the one shown, which stands in the grounds of Horton Court in Gloucest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choir
A choir ( ; also known as a chorale or chorus) is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform. Choirs may perform music from the classical music repertoire, which spans from the medieval era to the present, or popular music repertoire. Most choirs are led by a conductor, who leads the performances with arm, hand, and facial gestures. The term ''choir'' is very often applied to groups affiliated with a church (whether or not they actually occupy the quire), whereas a ''chorus'' performs in theatres or concert halls, but this distinction is not rigid. Choirs may sing without instruments, or accompanied by a piano, pipe organ, a small ensemble, or an orchestra. A choir can be a subset of an ensemble; thus one speaks of the "woodwind choir" of an orchestra, or different "choirs" of voices or instruments in a polychoral composition. In typical 18th century to 21st century oratorios and masses, 'choru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germain Pilon
Germain Pilon (c. 1525 – 3 February 1590)Connat & Colombier 1951; Thirion 1996. was a French Renaissance sculptor. Biography He was born in Paris and trained with his father, Andre Pilon. Documents show that he and his father executed several religious statues and tomb effigies in collaboration. Since Connat & Colombier established that Germain was born c. 1525 (rather than about ten years later, as previously believed), several early works have been reattributed to him, including the marble grouping ''Diana with a Stag'' (originally at the Château d'Anet, Eure-et-Loir; now at the Louvre).''Diana with a Stag'' was formerly attributed to Jean Goujon, but Anthony Blunt conclusively rejected that attribution in 1953 and argued the statue is very likely an early work of Germain Pilon (see Blunt & Beresford 1999, pp. 80–81). Thirion considers Blunt's reattribution to be relatively convincing (Thirion 1996, p. 812). Later he worked with Pierre Bontemps. Pilon became expert with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annunciation
The Annunciation (from Latin '), also referred to as the Annunciation to the Blessed Virgin Mary, the Annunciation of Our Lady, or the Annunciation of the Lord, is the Christian celebration of the biblical tale of the announcement by the angel Gabriel to Mary that she would conceive and bear a son through a virgin birth and become the mother of Jesus Christ, the Christian Messiah and Son of God, marking the Incarnation. Gabriel told Mary to name her son Jesus, meaning "YHWH is salvation". According to , the Annunciation occurred "in the sixth month" of Elizabeth's pregnancy with John the Baptist. Many Christians observe this event with the Feast of the Annunciation on 25 March, an approximation of the northern vernal equinox nine full months before Christmas, the ceremonial birthday of Jesus. The Annunciation is a key topic in Christian art in general, as well as in Marian art in the Catholic Church, having been especially prominent during the Middle Ages and Renaissance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |