|
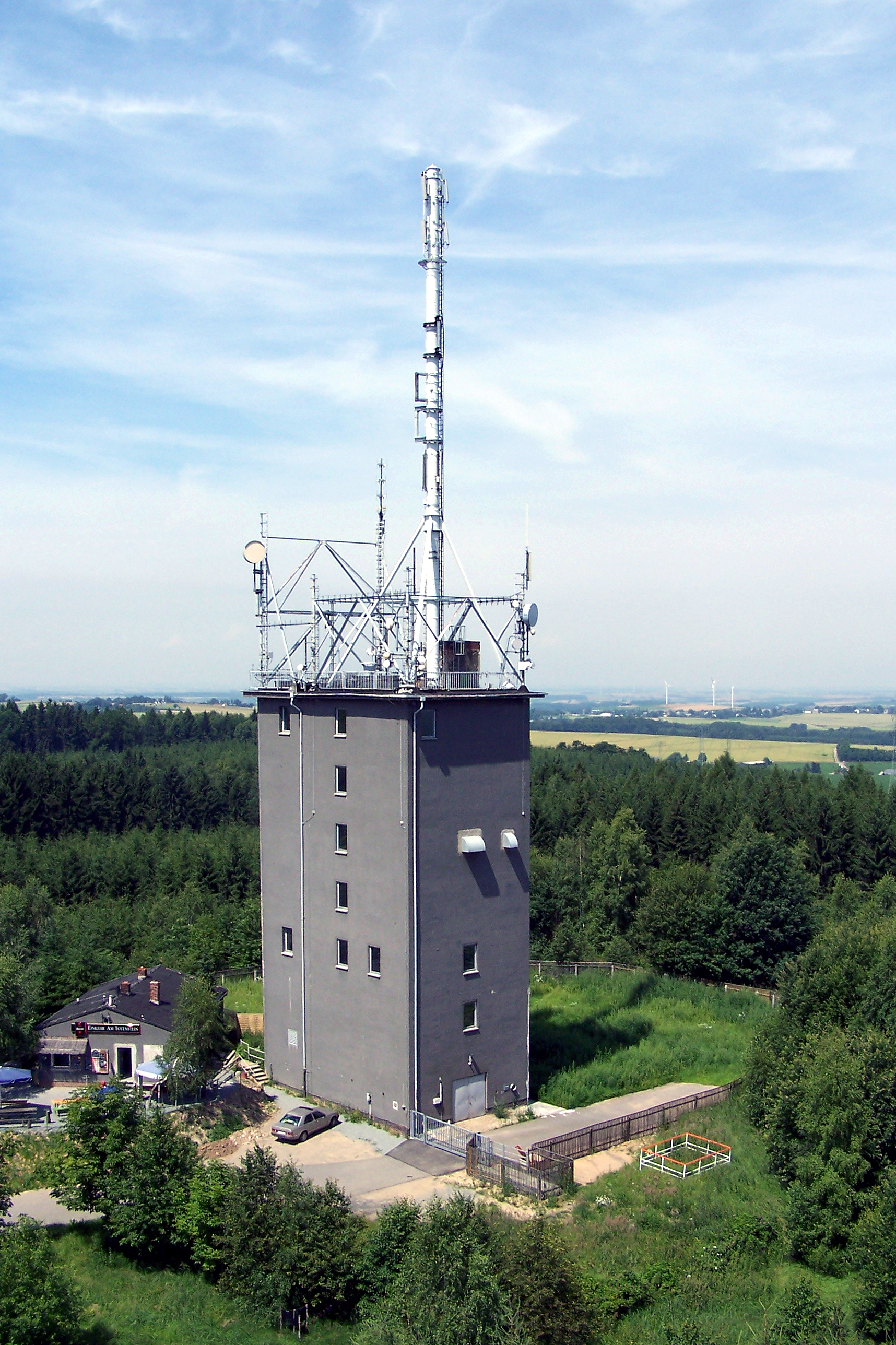
A Tower
{{short description, Type of communication tower in East Germany An A Tower (german: A-Turm) was a standard type of communication tower that was built in all provinces (''Bezirke'') of East Germany during the 1950s. These towers were 25 metres high, their roofs were equipped with a host of antennas and were painted green. Several had wooden cladding. In the second half of the 1950s, the Central Committee (ZK) of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) began building its own communications system, the ''Richtfunknetz der Partei'' (RFN) which was totally independent of all other communication networks. There were two levels of network: * Network Level 1: a network of microwave links from the ZK in Berlin to all SED provincial headquarters and * Network Level 2: from the provincial HQs to all county HQs. Their construction was prompted by the events of the popular uprising in East Germany on 17 June 1953. In all provinces of the GDR, apart from the urban conurbations, microwave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state was a part of the Eastern Bloc in the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state".Patrick Major, Jonathan Osmond, ''The Workers' and Peasants' State: Communism and Society in East Germany Under Ulbricht 1945–71'', Manchester University Press, 2002, Its territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II—the Soviet occupation zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR. Most scholars and academics describe the GDR as a totalitarian dictatorship. The GDR was establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petersberg Bei Halle
The Petersberg, at , is the highest point in the district of Saalekreis in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt. Its name is derived from St. Peter's Church, which is on the hill. Until the 14th century the Petersberg was known as the Lauterberg. Geography The Petersberg is located about 10 kilometres north of the German city of Halle on the River Saale not quite halfway between Halle and Köthen. The municipality of Petersberg with its hamlets of Drehlitz and Frößnitz lie on the hill. At the foot of the hill are the villages of Ostrau and Wallwitz as well as three small nature reserves. On the southern slopes of the hill is a small lake. A stretch of the A 14 motorway runs past the Petersberg to the west and south, and the B 6 federal highway runs by to the southwest. They form a junction at ''Halle-Trotha'', from where the Petersberg may easily be reached. Geology The Petersberg is the highest point of the Halle Porphyry complex. It was formed, like the other por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frauenstein (Ore Mountains)
Frauenstein () is a town in the district of Mittelsachsen, in Saxony, Germany. It is situated in the eastern Ore Mountains, southeast of Freiberg, and southwest of Dresden. Frauenstein Castle is located northeast of the town centre. Notable people * Andreas Silbermann (1678-1734), born in Kleinbobritzsch, organ builder * Gottfried Silbermann (1683-1753), organ builder, born in Kleinbobritzsch, spent his childhood years in Frauenstein from 1686 onwards * Thomas Schönlebe Thomas Schönlebe (born 6 August 1965) is a retired East German track and field athlete who competed in the 400 metres. He won the gold medal at the 1987 World Championships. In that race, he set a European record of 44.33 seconds which still ... (born 1965), athlete and Olympian References External links * http://www.frauenstein-erzgebirge.de Mittelsachsen {{Mittelsachsen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auersberg
Auersberg is a mountain in the Ore Mountains in Saxony, southeastern Germany. Auersberg is a 1018.2 m above sea level. It is located in the district of Wildenthal not far from the Czech border southeast of Eibenstock and northwest of Johanngeorgenstadt. Location and Geology Auersberg belongs to Wildenthal, which has been a district of Eibenstock since 1994. North of the Auersberg lies the Sosa dam. Below the summit there is a parking lot. When ascending to the Auersberg, you cross the Johanngeorgenstadt district of Sauschwemme. The main type of rock is medium-grained granite, which includes tourmaline. Also included in the granite are silver, tin and iron compounds, which were mined as early as the 16th century. At the peak of mining activity, there were up to 300 mines on the Auersberg. These included the Churhaus Saxony. In addition to the aforementioned rocks, quartz and slate have been proven to occur in veins on the summit. See also List of mountains in the Ore Mounta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichtentanne
Lichtentanne is a municipality in the district Zwickau, in Saxony, Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... References Zwickau (district) {{Zwickau-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bocka
Bocka is a municipality in the district of Greiz, in Thuringia, Germany. The town has a municipal association with Münchenbernsdorf Münchenbernsdorf is a town in the district of Greiz, in Thuringia, Germany. It is situated approximately 16 km southwest of Gera. The town is seat of a municipal association with eight members. Geography Münchenbernsdorf is located south .... References Municipalities in Thuringia Greiz (district) {{Greiz-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schneekopf
The Schneekopf near Gehlberg in the Thuringian county of Ilm-Kreis is and thus the second highest peak in the Thuringian Forest after its western neighbour, the Großer Beerberg (). The ''Adler'' Saddle between them is only about 59.4 metres lower than the two summits. To the east some distance away is its subpeak, the ''Sachsenstein'' (), to the south are the ''Teufelskreise'' () and ''Fichtenkopf'' (). The ''Goldlauterberg'' () further south marks the transition to the mountain of Großer Finsterberg (). Description The mountain is of volcanic origin and consists of porphyry. It is known for the Schneekopf balls (''Schneekopfkugel''), balls of porphyry ( druse) that occur here that form agate in the interior of crystals. They were formed during a volcanic eruption in the Permian. On the northern slopes of the mountain rises the Wilde Gera stream. From the summit plateau there is a good all round view of other summits in the Thuringian Forest and the Rhön mountains, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Großer Inselsberg
Großer Inselsberg is a mountain in the Thuringian Forest with a height of above sea level, located on Rennsteig in the districts of Gotha and Schmalkalden-Meiningen. It is the fourth-highest distinct mountain of Thuringia, after Großer Beerberg (), Schneekopf () and Großer Finsterberg () and forms a landmark that can be viewed in particular from northern and western directions. Geography The summit of Großer Inselsberg is located about NNE of Brotterode and southwest of Bad Tabarz. It forms a narrow, arched plateau of about length. The steep slopes are marked by deep dents and spurs formed by weathering. The summit has a dominance radius of extending to Sommerbachskopf ( a.s.l.) and a prominence of relative to the saddle at ''Heuberghaus''. With the exception of the buildings, the summit region of Großer Inselsberg has been a nature reserve since 30 March 1961. Geology Großer Inselsberg is a rhyolitic butte that has withstood the weathering of the surroundi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
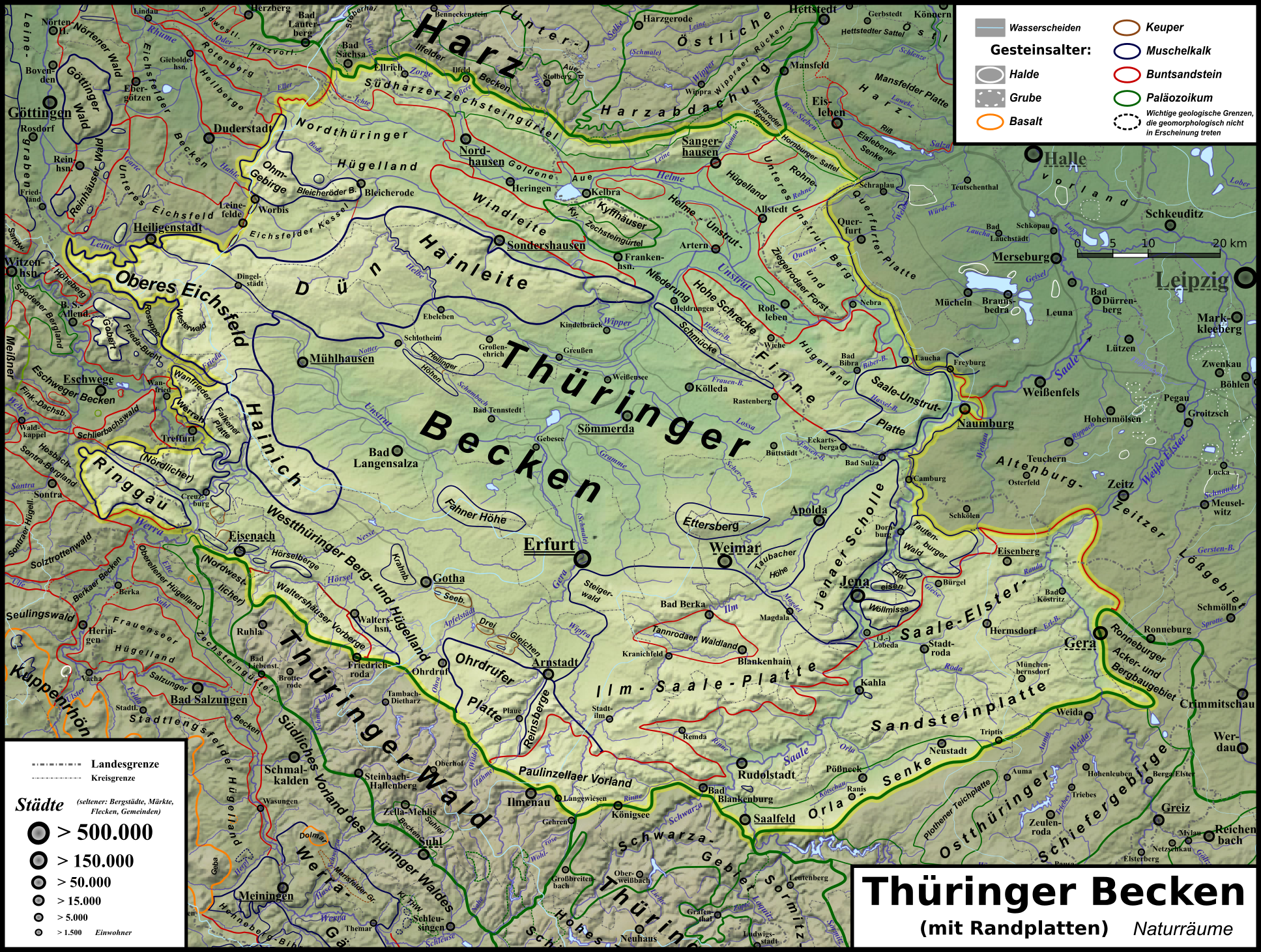
Ettersberg
The Thuringian Basin (german: Thüringer Becken) is a depression (geology), depression in the central and northwest part of Thuringia in Germany which is crossed by several rivers, the longest of which is the Unstrut. It stretches about from north to south and around from east to west. Its height varies from about 150 to . The Basin is surrounded by a wide outer girdle of limestone (Muschelkalk) ridges (including Hainich, Dün, Hainleite, Hohe Schrecke, Schmücke, Finne (hills), Finne), and to the southwest by the Thuringian Forest and to the southeast by sharply divided terraces (the Ilm-Saale and Ohrdruf Muschelkalk plateaus, and the Saale-Elster Bunter sandstone plateau). The Thuringian Basin belongs to the triassic period, during which horizontal beds of Bunter sandstone, Muschelkalk and Keuper were laid down. Below those lie the salt and gypsum layers of Magnesian Limestone (Zechstein). In the Cenozoic era the surrounding ridges were uplifted, whilst the Thuringian Basin sank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebra (Unstrut)
Nebra (official name: Nebra (Unstrut)) is a town in the district of Burgenlandkreis of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the river Unstrut. Nebra has become nationally and internationally known as the site where the Nebra sky disc, a notable Bronze Age artifact, was discovered. The town has a population of around 3,300. Geography Location Nebra lies between Querfurt and Naumburg on the Unstrut river in the west of Burgenlandkreis district. Subdivisions Neighboring communities Neighboring towns are Querfurt, Barnstädt and Steigra (all three in Saalekreis) to the north, Karsdorf to the east, Bad Bibra to the south and Kaiserpfalz to the west. History In 1962, four Magdalenian figurines were found near Nebra from the late Upper Paleolithic, which belong to the oldest known artwork in Saxony-Anhalt. The figures are 12,000 to 14,000 years old. The town is perhaps most famous due to the Nebra sky disk, which was found in Wangen near Nebra in 1999. It only be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |