|
ATM Kinase
ATM serine/threonine kinase or Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, symbol ATM, is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is recruited and activated by DNA double-strand breaks ( canonical pathway), oxidative stress, topoisomerase cleavage complexes, splicing intermediates, R-loops and in some cases by single-strand DNA breaks. It phosphorylates several key proteins that initiate activation of the DNA damage checkpoint, leading to cell cycle arrest, DNA repair or apoptosis. Several of these targets, including p53, CHK2, BRCA1, NBS1 and H2AX are tumor suppressors. In 1995, the gene was discovered by Yosef Shiloh who named its product ATM since he found that its mutations are responsible for the disorder ataxia–telangiectasia. In 1998, the Shiloh and Kastan laboratories independently showed that ATM is a protein kinase whose activity is enhanced by DNA damage. Throughout the cell cycle DNA is monitored for damage. Damages result from errors during replication, by-products of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L- stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, '' sericum''. Serine's structure was established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all life, living organisms, acting as the most essential part of heredity, biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a nucleic acid double helix, double helix of two Complementary DNA, complementary DNA strand, strands. DNA is often called double helix. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autophosphorylation
Autophosphorylation is a type of post-translational modification of proteins. It is generally defined as the phosphorylation of the kinase by itself. In eukaryotes, this process occurs by the addition of a phosphate group to serine, threonine or tyrosine residues within protein kinases, normally to regulate the catalytic activity.Petsko, GA and Ringe, D 2009, 'Protein Structure and Function', Oxford University Press Inc., New York, U.S.A Autophosphorylation may occur when a kinases' own active site catalyzes the phosphorylation reaction (cis autophosphorylation), or when another kinase of the same type provides the active site that carries out the chemistry (trans autophosphorylation). The latter often occurs when kinase molecules dimerize. In general, the phosphate groups introduced are gamma phosphates from nucleoside triphosphates, most commonly ATP. Function Protein kinases, many of which are regulated by autophosphorylation, are vital in controlling the cellular prolife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Dimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex or protein multimer, multimer formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually Non-covalent interaction, non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has roots meaning "two parts", ''wikt:di-#Prefix, di-'' + ''wikt:-mer#Suffix, -mer''. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure. A protein homodimer is formed by two identical proteins while a protein heterodimer is formed by two different proteins. Most protein dimers in biochemistry are not connected by covalent bonds. An example of a non-covalent heterodimer is the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is composed of two different amino acid chains. An exception is dimers that are linked by disulfide bridges such as the homodimeric protein IKBKG, NEMO. Some proteins contain specialized domains to ensure dimerization (dimerization domains) and specificity. The G protein- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic Electron Microscopy
Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is a transmission electron microscopy technique applied to samples cooled to cryogenic temperatures. For biological specimens, the structure is preserved by embedding in an environment of vitreous ice. An aqueous sample solution is applied to a grid-mesh and plunge-frozen in liquid ethane or a mixture of liquid ethane and propane. While development of the technique began in the 1970s, recent advances in detector technology and software algorithms have allowed for the determination of biomolecular structures at near-atomic resolution. This has attracted wide attention to the approach as an alternative to X-ray crystallography or NMR spectroscopy in the structural biology field. In 2017, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Jacques Dubochet, Joachim Frank, and Richard Henderson "for developing cryo-electron microscopy for the high-resolution structure determination of biomolecules in solution." '' Nature Methods'' also named cryo- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformation/transcription Domain-associated Protein
Transformation/transcription domain-associated protein, also known as TRRAP, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TRRAP'' gene. TRRAP belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase protein family. Function TRRAP is an adaptor protein, which is found in various multiprotein chromatin complexes with histone acetyltransferase activity (HAT), which in turn is responsible for epigenetic transcription activation. TRRAP has a central role in MYC (c-Myc) transcription activation, and also participates in cell transformation by MYC. It is required for p53/TP53-, E2F1-, and E2F4-mediated transcription activation. It is also involved in transcription activation mediated by the adenovirus E1A, a viral oncoprotein that deregulates transcription of key genes. TRRAP is also required for the mitotic checkpoint and normal cell cycle progression. The MRN complex (composed of MRE11, RAD50, and NBS1) is involved in the detection and repair of DNA double-strand breaks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HEAT Repeat Domain
A HEAT repeat is a protein tandem repeat structural motif composed of two alpha helices linked by a short loop. HEAT repeats can form alpha solenoids, a type of solenoid protein domain found in a number of cytoplasmic proteins. The name "HEAT" is an acronym for four proteins in which this repeat structure is found: Huntingtin, elongation factor 3 (EF3), protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), and the yeast kinase TOR1. HEAT repeats form extended superhelical structures which are often involved in intracellular transport; they are structurally related to armadillo repeats. The nuclear transport protein importin beta contains 19 HEAT repeats. Various HEAT repeat proteins and their structures Representative examples of HEAT repeat proteins include importin β (also known as karyopherin β) family, regulatory subunits of condensin and cohesin, separase, PIKKs (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related protein kinases) such as ATM (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated) and ATR (Ataxia telangiectasia an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MTOR
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), also referred to as the mechanistic target of rapamycin, and sometimes called FK506-binding protein 12-rapamycin-associated protein 1 (FRAP1), is a kinase that in humans is encoded by the ''MTOR'' gene. mTOR is a member of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase family of protein kinases. mTOR links with other proteins and serves as a core component of two distinct protein complexes, mTOR complex 1 and mTOR complex 2, which regulate different cellular processes. In particular, as a core component of both complexes, mTOR functions as a serine/threonine protein kinase that regulates cell growth, cell proliferation, cell motility, cell survival, protein synthesis, autophagy, and transcription. As a core component of mTORC2, mTOR also functions as a tyrosine protein kinase that promotes the activation of insulin receptors and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors. mTORC2 has also been implicated in the control and maintenanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA-PKcs
DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit, also known as DNA-PKcs, is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in repairing DNA double-strand breaks and has a number of other DNA housekeeping functions. In humans it is encoded by the gene designated as ''PRKDC'' or ''XRCC7''. DNA-PKcs belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase protein family. The DNA-Pkcs protein is a serine/threonine protein kinase consisting of a single polypeptide chain of 4,128 amino acids. Function DNA-PKcs is the catalytic subunit of a nuclear DNA-dependent serine/threonine protein kinase called DNA-PK. The second component is the autoimmune antigen Ku. On its own, DNA-PKcs is inactive and relies on Ku to direct it to DNA ends and trigger its kinase activity. DNA-PKcs is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair, which rejoins double-strand breaks. It is also required for V(D)J recombination, a process that utilizes NHEJ to promote immune system diversit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ataxia Telangiectasia And Rad3 Related
Serine/threonine-protein kinase ATR, also known as ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein (ATR) or FRAP-related protein 1 (FRP1), is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the ''ATR'' gene. It is a large kinase of about 301.66 kDa. ATR belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase protein family. ATR is activated in response to single strand breaks, and works with ATM to ensure genome integrity. Function ATR is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that is involved in sensing DNA damage and activating the DNA damage checkpoint, leading to cell cycle arrest in eukaryotes. ATR is activated in response to persistent single-stranded DNA, which is a common intermediate formed during DNA damage detection and repair. Single-stranded DNA occurs at stalled replication forks and as an intermediate in DNA repair pathways such as nucleotide excision repair and homologous recombination repair. ATR is activated during more persistent issues with DNA damage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which in turn are involved in cancer. PI3Ks are a family of related intracellular signal transducer enzymes capable of phosphorylating the 3 position hydroxyl group of the inositol ring of phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns). The pathway, with oncogene PIK3CA and tumor suppressor gene PTEN, is implicated in the sensitivity of cancer tumors to insulin and IGF1, and in calorie restriction. Discovery The discovery of PI3Ks by Lewis Cantley and colleagues began with their identification of a previously unknown phosphoinositide kinase associated with the polyoma middle T protein. They observed unique substrate specificity and chromatographic properties of the products of the lipid kinase, leading to the discovery that this phosphoinositide kinase had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
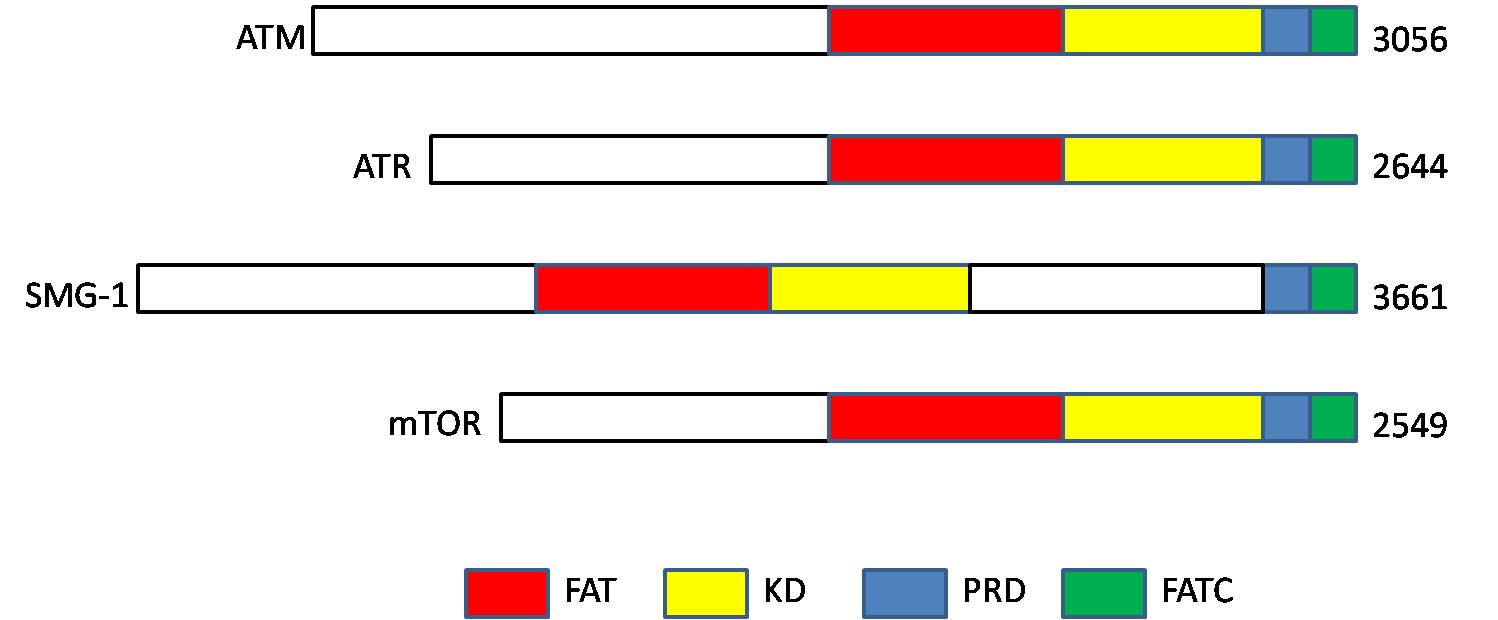
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related Kinase
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinases (PIKKs) are a family of Ser/Thr-protein kinases with sequence similarity to phosphatidylinositol-3 kinases ( PI3Ks). Members The human PIKK family includes six members: Structure PIKKs proteins contain the following four domains: # N-terminus FRAP-ATM- TRRAP (FAT) domain, # kinase domain (KD; PI3_PI4_kinase), # PIKK- regulatory domain (PRD), and # C-terminus The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, carboxy tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comp ... FAT-C-terminal (FATC) domain References External links Kinase Family PIKKaWikiKinome EC 2.7.11 Protein families {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |