|
ARKA Descriptors In QSAR
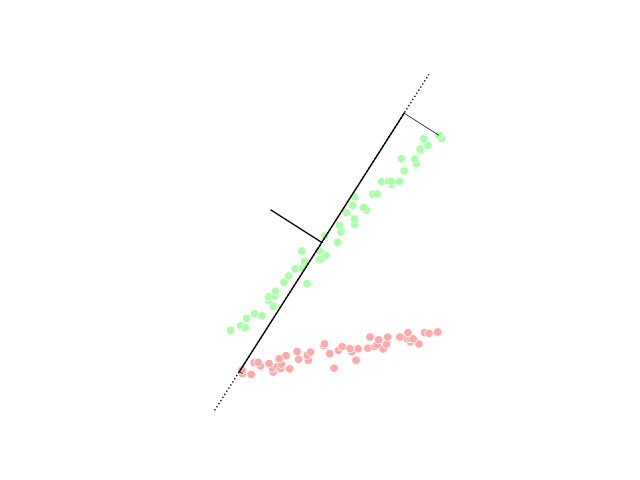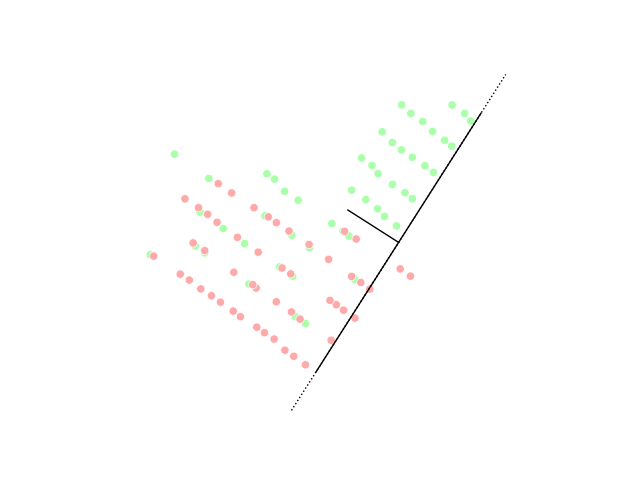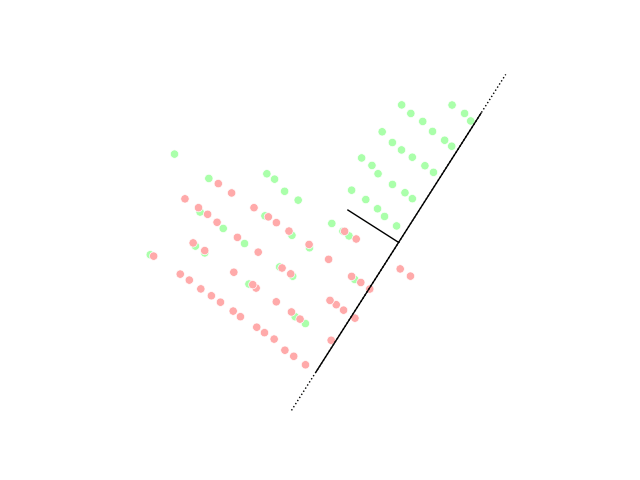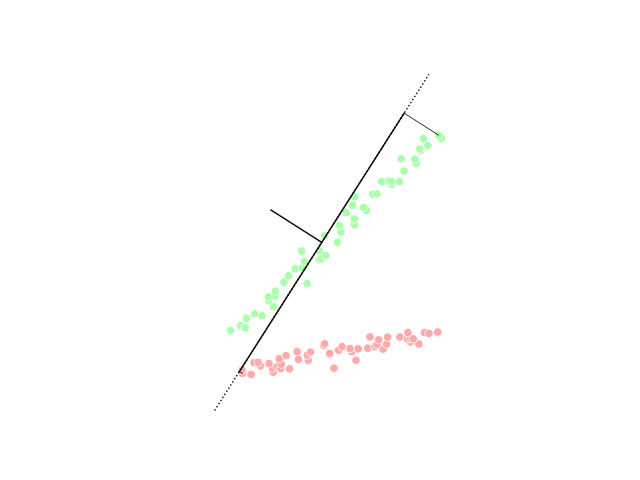
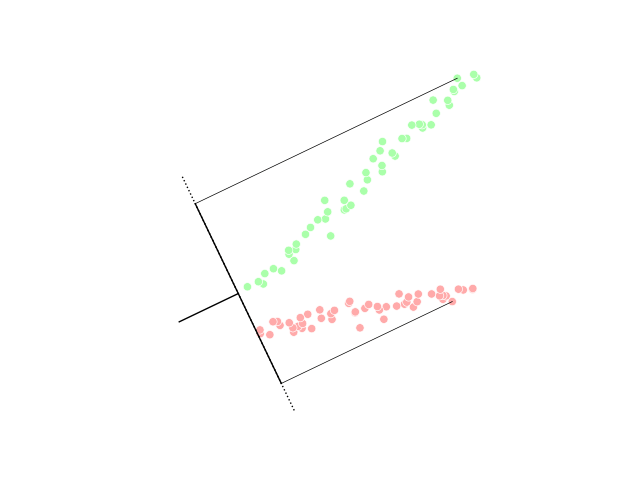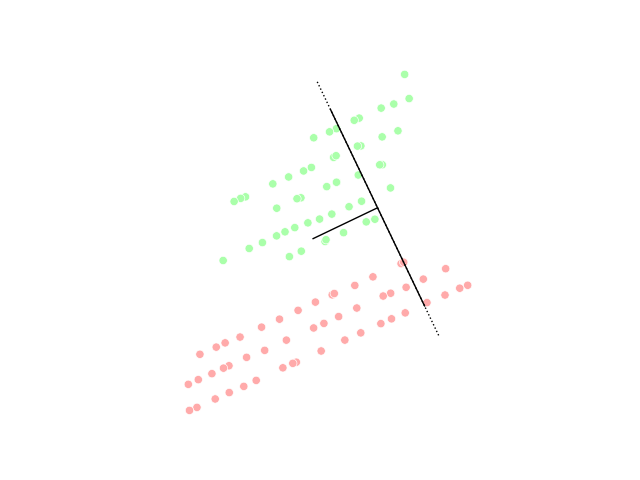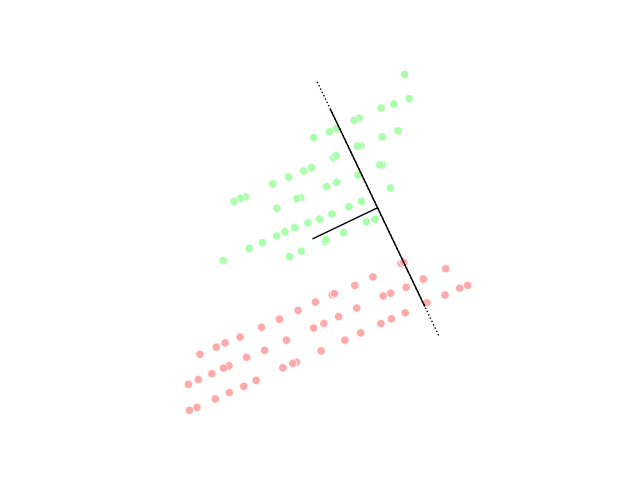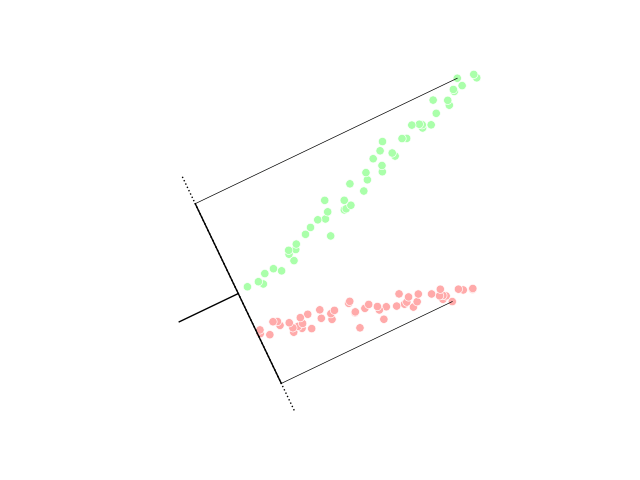
One of the most commonly used in silico approaches for assessing new molecules' activity/property/toxicity is the Quantitative Structure-Activity/Property/Toxicity Relationship ( QSAR/QSPR/QSTR), which generates predictive models for efficiently predicting query compounds . QSAR/QSPR/QSTR uses numerical chemical information in the form of molecular descriptors and correlates these to the response activity/property/toxicity using statistical techniques. While QSAR is essentially a similarity-based approach, the occurrence of activity/property cliffs may greatly reduce the predictive accuracy of the developed models. The novel Arithmetic Residuals in K-groups Analysis (ARKA) approach is a supervised dimensionality reduction technique developed by thDTC Laboratory Jadavpur University that can easily identify activity cliffs in a data set. Activity cliffs are similar in their structures but differ considerably in their activity. The basic idea othe ARKA descriptorsis to group the conven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Descriptor
Molecular descriptors play a fundamental role in chemistry, pharmaceutical sciences, environmental protection policy, and health researches, as well as in quality control, being the way molecules, thought of as real bodies, are transformed into numbers, allowing some mathematical treatment of the chemical information contained in the molecule. This was defined by Todeschini and Consonni as: "''The molecular descriptor is the final result of a logic and mathematical procedure which transforms chemical information encoded within a symbolic representation of a molecule into a useful number or the result of some standardized experiment.''" By this definition, the molecular descriptors are divided into two main categories: experimental measurements, such as log P, molar refractivity, dipole moment, polarizability, and, in general, additive physico-chemical properties, and theoretical molecular descriptors, which are derived from a symbolic representation of the molecule and can be fur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimensionality Reduction
Dimensionality reduction, or dimension reduction, is the transformation of data from a high-dimensional space into a low-dimensional space so that the low-dimensional representation retains some meaningful properties of the original data, ideally close to its intrinsic dimension. Working in high-dimensional spaces can be undesirable for many reasons; raw data are often sparse as a consequence of the curse of dimensionality, and analyzing the data is usually computationally intractable. Dimensionality reduction is common in fields that deal with large numbers of observations and/or large numbers of variables, such as signal processing, speech recognition, neuroinformatics, and bioinformatics. Methods are commonly divided into linear and nonlinear approaches. Linear approaches can be further divided into feature selection and feature extraction. Dimensionality reduction can be used for noise reduction, data visualization, cluster analysis, or as an intermediate step to facilitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification
Classification is the activity of assigning objects to some pre-existing classes or categories. This is distinct from the task of establishing the classes themselves (for example through cluster analysis). Examples include diagnostic tests, identifying spam emails and deciding whether to give someone a driving license. As well as 'category', synonyms or near-synonyms for 'class' include 'type', 'species', 'order', 'concept', 'taxon', 'group', 'identification' and 'division'. The meaning of the word 'classification' (and its synonyms) may take on one of several related meanings. It may encompass both classification and the creation of classes, as for example in 'the task of categorizing pages in Wikipedia'; this overall activity is listed under taxonomy. It may refer exclusively to the underlying scheme of classes (which otherwise may be called a taxonomy). Or it may refer to the label given to an object by the classifier. Classification is a part of many different kinds of activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q-RASAR
The quantitative Read-Across Structure-Activity Relationship (q-RASAR) concept has been developed by thDTC Laboratory, Jadavpur Universityby merging Read-Across and QSAR. It is a statistical modeling approach that uses the similarity and error-based measures as descriptors in addition to the usual structural and physicochemical descriptors, and it has been shown to enhance the external predictivity of QSAR/QSPR models. The novel quantitative read-across structure-activity relationship (q-RASAR) approach combines the advantages of both QSAR and read-across, thus resulting in enhanced predictivity for the same level of chemical information used. This approach utilizes similarity-based considerations yet can generate simple, interpretable, and transferable models. This approach may be used for any type of structural and physicochemical descriptors and with any modeling algorithms.The q-RASAR approachhas been used by different research groups for different endpoints. Among different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheminformatics
Cheminformatics (also known as chemoinformatics) refers to the use of physical chemistry theory with computer and information science techniques—so called "'' in silico''" techniques—in application to a range of descriptive and prescriptive problems in the field of chemistry, including in its applications to biology and related molecular fields. Such '' in silico'' techniques are used, for example, by pharmaceutical companies and in academic settings to aid and inform the process of drug discovery, for instance in the design of well-defined combinatorial libraries of synthetic compounds, or to assist in structure-based drug design. The methods can also be used in chemical and allied industries, and such fields as environmental science and pharmacology, where chemical processes are involved or studied. History Cheminformatics has been an active field in various guises since the 1970s and earlier, with activity in academic departments and commercial pharmaceutical rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimension Reduction
Dimensionality reduction, or dimension reduction, is the transformation of data from a high-dimensional space into a low-dimensional space so that the low-dimensional representation retains some meaningful properties of the original data, ideally close to its intrinsic dimension. Working in high-dimensional spaces can be undesirable for many reasons; raw data are often sparse as a consequence of the curse of dimensionality, and analyzing the data is usually computationally intractable. Dimensionality reduction is common in fields that deal with large numbers of observations and/or large numbers of variables, such as signal processing, speech recognition, neuroinformatics, and bioinformatics. Methods are commonly divided into linear and nonlinear approaches. Linear approaches can be further divided into feature selection and feature extraction. Dimensionality reduction can be used for noise reduction, data visualization, cluster analysis, or as an intermediate step to facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |