|
APGAR
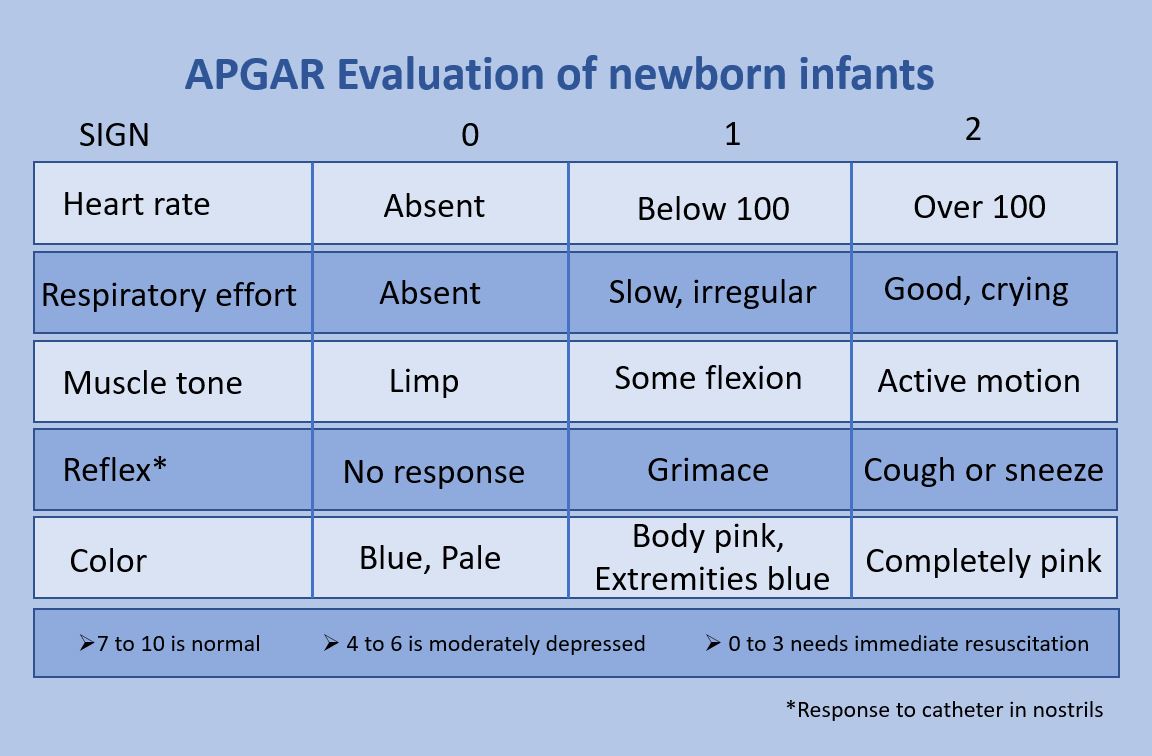
The Apgar score is a quick way for doctors to evaluate the health of all newborns at 1 and 5 minutes after birth and in response to resuscitation. It was originally developed in 1952 by an anesthesiologist at Columbia University, Virginia Apgar, as way to address the need for a standardized way to evaluate infants shortly after birth. Today, the categories developed by Apgar used to assess the health of a newborn remain largely the same as in 1952, though the way they are implemented and used has evolved over the years. The score is determined through the evaluation of the newborn in five criteria: activity (tone), pulse, grimace, appearance, and respiration. For each criterion, newborns can receive a score from 0 to 2. The list of criteria is a backronym of Apgar's surname. History and development of the Apgar score Apgar originally thought up the criteria as way to address the lack of a standardized way to assess the need for assistive breathing procedures for newborns. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apgar Score
The Apgar score is a quick way for doctors to evaluate the health of all newborns at 1 and 5 minutes after birth and in response to Neonatal resuscitation, resuscitation. It was originally developed in 1952 by an anesthesiologist at Columbia University, Virginia Apgar, as way to address the need for a standardized way to evaluate infants shortly after birth. Today, the categories developed by Apgar used to assess the health of a newborn remain largely the same as in 1952, though the way they are implemented and used has evolved over the years. The score is determined through the evaluation of the newborn in five criteria: activity (tone), pulse, grimace, appearance, and respiration. For each criterion, newborns can receive a score from 0 to 2. The list of criteria is a backronym of Apgar's surname. History and development of the Apgar score Apgar originally thought up the criteria as way to address the lack of a standardized way to assess the need for assistive breathing proced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midwifery
Midwifery is the health science and health profession that deals with pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period (including care of the newborn), in addition to the sexual and reproductive health of women throughout their lives. In many countries, midwifery is a medical profession (special for its independent and direct specialized education; should not be confused with the medical specialty, which depends on a previous general training). A professional in midwifery is known as a midwife. A 2013 Cochrane review concluded that "most women should be offered midwifery-led continuity models of care and women should be encouraged to ask for this option although caution should be exercised in applying this advice to women with substantial medical or obstetric complications." The review found that midwifery-led care was associated with a reduction in the use of epidurals, with fewer episiotomies or instrumental births, and a decreased risk of losing the baby before 24 weeks' gesta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backronym
A backronym is an acronym formed from an already existing word by expanding its letters into the words of a phrase. Backronyms may be invented with either serious or humorous intent, or they may be a type of false etymology or folk etymology. The word is a portmanteau of ''back'' and ''acronym''. An acronym is a word derived from the initial letters of the words of a phrase, such as ''radar'' from "''ra''dio ''d''etection ''a''nd ''r''anging". By contrast, a backronym is "an acronym deliberately formed from a phrase whose initial letters spell out a particular word or words, either to create a memorable name or as a fanciful explanation of a word's origin." Many fictional espionage organizations are backronyms, such as SPECTRE (''sp''ecial ''e''xecutive for ''c''ounterintelligence, ''t''errorism, ''r''evenge and ''e''xtortion) from the James Bond franchise. For example, the Amber Alert missing-child program was named after Amber Hagerman, a nine-year-old girl who was abducted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neonatal Resuscitation
Neonatal resuscitation, also known as newborn resuscitation, is an emergency procedure focused on supporting approximately 10% of newborn children who do not readily begin breathing, putting them at risk of irreversible organ injury and death. Through positive airway pressure, and in severe cases chest compressions, medical personnel certified in neonatal resuscitation can often stimulate neonates to begin breathing on their own, with attendant normalization of heart rate. Overview About a quarter of all neonatal deaths globally are caused by birth asphyxia. This dangerous condition of oxygen deprivation may begin before birth. For example, if the umbilical cord, which supplies oxygen throughout fetal development, is compressed or tears during delivery. Depending on how quickly and successfully the infant is resuscitated, hypoxic damage can occur to most of the infant's organs (heart, lungs, liver, gut, kidneys). One serious complication is a brain injury known as neonatal hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newborns
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to refer to Juvenile (organism), juveniles of other organisms. A newborn is, in colloquial use, an infant who is only hours, days, or up to one month old. In medical contexts, a newborn or neonate (from Latin, ''neonatus'', newborn) is an infant in the first 28 days after birth; the term applies to Preterm birth, premature, Pregnancy#Term, full term, and Postterm pregnancy, postmature infants. Before birth, the offspring is called a fetus. The term ''infant'' is typically applied to very young children under one year of age; however, definitions may vary and may include children up to two years of age. When a human child learns to walk, they are called a toddler instead. Other uses In British English, an ''infant school'' is for children ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mnemonic
A mnemonic ( ) device, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding. Mnemonics make use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues, and imagery as specific tools to encode information in a way that allows for efficient storage and retrieval. Mnemonics aid original information in becoming associated with something more accessible or meaningful—which, in turn, provides better retention of the information. Commonly encountered mnemonics are often used for lists and in auditory form, such as short poems, acronyms, initialisms, or memorable phrases, but mnemonics can also be used for other types of information and in visual or kinesthetic forms. Their use is based on the observation that the human mind more easily remembers spatial, personal, surprising, physical, sexual, humorous, or otherwise "relatable" information, rather than more abstract or impersonal forms of informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Scales
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infant Mortality
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five mortality rate, which is also referred to as the ''child mortality rate'', is also an important statistic, considering the infant mortality rate focuses only on children under one year of age. In 2013, the leading cause of infant mortality in the United States was birth defects. Other leading causes of infant mortality include birth asphyxia, pneumonia, congenital malformations, term birth complications such as abnormal presentation of the fetus umbilical cord prolapse, or prolonged labor, neonatal infection, diarrhea, malaria, measles, and malnutrition. One of the most common preventable causes of infant mortality is smoking during pregnancy. Lack of prenatal care, alcohol consumption during pregnancy, and drug use also cause complications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnostic Obstetrics And Gynaecology
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engineering and computer science, it is typically used to determine the causes of symptoms, mitigations, and solutions. Computer science and networking * Bayesian networks * Complex event processing * Diagnosis (artificial intelligence) * Event correlation * Fault management * Fault tree analysis * Grey problem * RPR Problem Diagnosis * Remote diagnostics * Root cause analysis * Troubleshooting * Unified Diagnostic Services Mathematics and logic * Bayesian probability * Block Hackam's dictum * Occam's razor * Regression diagnostics * Sutton's law copy right remover block Medicine * Medical diagnosis * Molecular diagnostics Methods * CDR Computerized Assessment System * Computer-assisted diagnosis * Differential diagnosis * Medical diagnos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Inventions ...
The following articles cover the timeline of United States inventions: *Timeline of United States inventions (before 1890), before the turn of the century * Timeline of United States inventions (1890–1945), before World War II *Timeline of United States inventions (1946–1991), for the post-war era *Timeline of United States inventions (after 1991), after the Fall of the Soviet Union {{DEFAULTSORT:Timeline of United States Inventions United States inventions United States The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paediatric Glasgow Coma Scale
The Paediatric Glasgow Coma Scale (British English) or the Pediatric Glasgow Coma Score (American English) or simply PGCS is the equivalent of the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) used to assess the level of consciousness of child patients. As many of the assessments for an adult patient would not be appropriate for infants, the Glasgow Coma Scale was modified slightly to form the PGCS. As with the GCS, the PGCS comprises three tests: eye, verbal and motor responses. The three values separately as well as their sum are considered. The lowest possible PGCS (the sum) is 3 (deep coma or death) whilst the highest is 15 (fully awake and aware person). The pediatric GCS is commonly used in emergency medical services. Coma scale Any combined score of less than eight represents a significant risk of mortality. See also *Apgar score The Apgar score is a quick way for doctors to evaluate the health of all newborns at 1 and 5 minutes after birth and in response to Neonatal resuscitation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow Coma Scale
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a clinical scale used to reliably measure a person's level of consciousness after a brain injury. The GCS assesses a person based on their ability to perform eye movements, speak, and move their body. These three behaviours make up the three elements of the scale: eye, verbal, and motor. A person's GCS score can range from 3 (completely unresponsive) to 15 (responsive). This score is used to guide immediate medical care after a brain injury (such as a car accident) and also to monitor hospitalised patients and track their level of consciousness. Lower GCS scores are correlated with higher risk of death. However, the GCS score alone should not be used on its own to predict the outcome for an individual person with brain injury. Scoring The Glasgow Coma Scale is used for people above the age of two and composed of three tests: eye, verbal, and motor responses. The scores for each of these tests are indicated in the table below. The Glasgow Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |