|
AOGCM
A general circulation model (GCM) is a type of climate model. It employs a mathematical model of the general circulation of a planetary atmosphere or ocean. It uses the Navier–Stokes equations on a rotating sphere with thermodynamic terms for various energy sources (radiation, latent heat). These equations are the basis for computer programs used to simulate the Earth's atmosphere or oceans. Atmospheric and oceanic GCMs (AGCM and OGCM) are key components along with sea ice and land-surface components. GCMs and global climate models are used for weather forecasting, understanding the climate, and forecasting climate change. Versions designed for decade to century time scale climate applications were originally created by Syukuro Manabe and Kirk Bryan at the Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL) in Princeton, New Jersey. These models are based on the integration of a variety of fluid dynamical, chemical and sometimes biological equations. Terminology The acrony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Model
Numerical climate models use quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the important drivers of climate, including atmosphere, oceans, land surface and ice. They are used for a variety of purposes from study of the dynamics of the climate system to projections of future climate. Climate models may also be qualitative (i.e. not numerical) models and also narratives, largely descriptive, of possible futures. Quantitative climate models take account of incoming energy from the sun as short wave electromagnetic radiation, chiefly visible and short-wave (near) infrared, as well as outgoing long wave (far) infrared electromagnetic. An imbalance results in a change in temperature. Quantitative models vary in complexity. For example, a simple radiant heat transfer model treats the earth as a single point and averages outgoing energy. This can be expanded vertically (radiative-convective models) and/or horizontally. Coupled atmosphere–ocean–sea ice global climate models ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
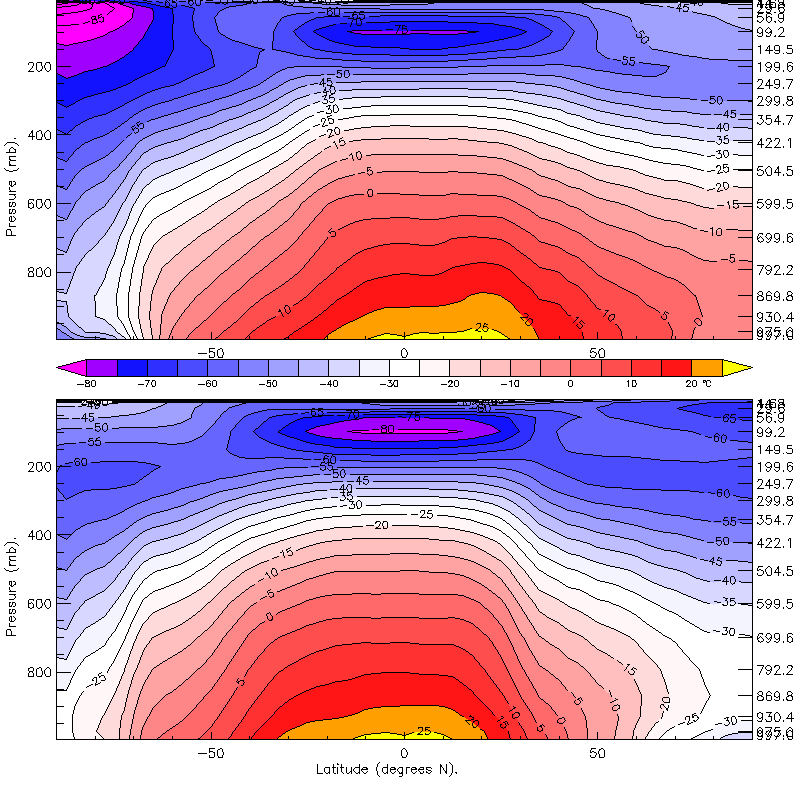
HadCM3
HadCM3 (abbreviation for ''Hadley Centre Coupled Model, version 3'') is a coupled atmosphere-ocean general circulation model (AOGCM) developed at the Hadley Centre in the United Kingdom. It was one of the major models used in the IPCC Third Assessment Report in 2001. Unlike earlier AOGCMs at the Hadley Centre and elsewhere (including its predecessor HadCM2), HadCM3 does not need flux adjustment (additional "artificial" heat and freshwater fluxes at the ocean surface) to produce a good simulation. The higher ocean resolution of HadCM3 is a major factor in this; other factors include a good match between the atmospheric and oceanic components; and an improved ocean mixing scheme (Gent and McWilliams). HadCM3 has been run to produce simulations for periods of over a thousand years, showing little drift in its surface climate. HadCM3 is composed of two components: the atmospheric model HadAM3 and the ocean model HadOM3 (which includes a sea ice model). Simulations use a 360-day cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirk Bryan (oceanographer)
Kirk Bryan Jr. (born July 21, 1929), son of Kirk Bryan, Sr.(geologist, 1888–1950) is an American oceanographer who is considered to be the founder of numerical ocean modeling. Starting in the 1960s at the Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, then located in Washington, D.C., Bryan worked with a series of colleagues to develop numerical schemes for solving the equations of motion describing flow on a sphere. His work on these schemes led to the so-called "Bryan-Cox code" with which many early simulations were made, and which led to the Modular Ocean Model currently used by many numerical oceanographers and climate scientists. In addition to his important contributions in developing numerical codes, Bryan was also involved in early efforts to apply them to understanding the global climate system. In 1967, he published, with Michael Cox, the first model of the 3-dimensional circulation of the ocean, forced by both winds and thermodynamic forcing. In 1969, a paper with Syukuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Wave
In fluid dynamics, gravity waves are waves generated in a fluid medium or at the interface between two media when the force of gravity or buoyancy tries to restore equilibrium. An example of such an interface is that between the atmosphere and the ocean, which gives rise to wind waves. A gravity wave results when fluid is displaced from a position of equilibrium. The restoration of the fluid to equilibrium will produce a movement of the fluid back and forth, called a ''wave orbit''. Gravity waves on an air–sea interface of the ocean are called surface gravity waves (a type of surface wave), while gravity waves that are the body of the water (such as between parts of different densities) are called ''internal waves''. Wind-generated waves on the water surface are examples of gravity waves, as are tsunamis and ocean tides. The period of wind-generated gravity waves on the free surface of the Earth's ponds, lakes, seas and oceans are predominantly between 0.3 and 30 secon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadley Centre For Climate Prediction And Research
The Met Office Hadley Centre — named in honour of George Hadley — is one of the United Kingdom's leading centres for the study of scientific issues associated with climate change. It is part of, and based at the headquarters of the Met Office in Exeter. Foundation The Hadley Centre was founded in 1990, having been approved by the then British Prime Minister Mrs Margaret Thatcher and was first named the ''Hadley Centre for Climate Research and Prediction'' but subsequently renamed on various occasions. Major aims The centre has several major aims: *To understand physical, chemical and biological processes within the climate system and develop state-of-the-art climate models *To use climate models to simulate global and regional climate variability and change *To predict inter-annual to decadal variability of climate *To predict long term climate change *To monitor global and national climate variability and change *To attribute recent changes in climate to speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Geophysical Union
The American Geophysical Union (AGU) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization of Earth, atmospheric, ocean, hydrologic, space, and planetary scientists and enthusiasts that according to their website includes 130,000 people (not members). AGU's activities are focused on the organization and dissemination of scientific information in the interdisciplinary and international fields within the Earth and space sciences. The geophysical sciences involve four fundamental areas: atmospheric and ocean sciences; solid-Earth sciences; hydrologic sciences; and space sciences. The organization's headquarters is located on Florida Avenue in Washington, D.C. History The AGU was established in December 1919 by the National Research Council (NRC) to represent the United States in the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics (IUGG), and its first chairman was William Bowie of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey (USCGS). For more than 50 years, it operated as an unincorporated affili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Geophysical Research
The ''Journal of Geophysical Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal. It is the flagship journal of the American Geophysical Union. It contains original research on the physical, chemical, and biological processes that contribute to the understanding of the Earth, Sun, and Solar System. It has seven sections: A (Space Physics), B (Solid Earth), C (Oceans), D (Atmospheres), E (Planets), F (Earth Surface), and G (Biogeosciences). All current and back issues are available online for subscribers. History The journal was originally founded under the name ''Terrestrial Magnetism'' by the American Geophysical Union's president Louis Agricola Bauer in 1896. It was renamed to ''Terrestrial Magnetism and Atmospheric Electricity'' in 1899 and in 1948 it acquired its current name. In 1980, three specialized sections were established: ''A: Space Physics'', ''B: Solid Earth'', and ''C: Oceans''. Subsequently, further sections have been added: ''D: Atmospheres'' in 1984, ''E: Planets'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Corporation For Atmospheric Research
The University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) is a US nonprofit consortium of more than 100 colleges and universities providing research and training in the atmospheric and related sciences. UCAR manages the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) and provides additional services to strengthen and support research and education through its community programs. Its headquarters, in Boulder, Colorado, include NCAR's Mesa Laboratory, designed by I.M. Pei. UCAR was established in 1959 by faculty from 14 leading universities to support and nourish the atmospheric sciences. They were motivated by a newly recognized need for pooled observational and computational facilities and a strong research staff, which together would allow the academic community to carry out complex, long-term scientific programs beyond the reach of individual universities. This group’s first major action, in partnership with the National Science Foundation, was to establish NCAR. Since then, U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Center For Atmospheric Research
The US National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR ) is a US federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) managed by the nonprofit University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) and funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF). NCAR has multiple facilities, including the I. M. Pei-designed Mesa Laboratory headquarters in Boulder, Colorado. Studies include meteorology, climate science, atmospheric chemistry, solar-terrestrial interactions, environmental and societal impacts. Tools and technologies NCAR was instrumental in developing lidar, light radar, now a key archaeological tool, as well as providing a broad array of tools and technologies to the scientific community for studying Earth’s atmosphere, including, * Specialized instruments to measure atmospheric processes * Research aircraft * High-performance computing and cyberinfrastructure, including supercomputers * Mauna Loa Solar Observatory * Cooperative field campaigns * Atmospheric models o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charts the seas, conducts deep sea exploration, and manages fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the U.S. exclusive economic zone. Purpose and function NOAA's specific roles include: * ''Supplying Environmental Information Products''. NOAA supplies to its customers and partners information pertaining to the state of the oceans and the atmosphere, such as weather warnings and forecasts via the National Weather Service. NOAA's information services extend as well to climate, ecosystems, and commerce. * ''Providing Environmental Stewardship Services''. NOAA is a steward of U.S. coastal and marine environments. In coordination with federal, state, local, tribal and international authorities, NOAA manages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



