|
ANKRD11
Ankyrin repeat domain 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANKRD11 gene. Function This locus encodes an ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein. The encoded protein inhibits ligand-dependent activation of transcription. Mutations in this gene have been associated with KBG syndrome, which is characterized by macrodontia, distinctive craniofacial features, short stature, skeletal anomalies, global developmental delay, seizures and intellectual disability. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. Related pseudogenes exist on chromosomes 2 and X. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * {{gene-16-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrodontia (tooth)
Macrodontia is a type of localized gigantism in which teeth are larger than normal. Macrodontia seen in permanent teeth is thought to affect around 0.03 to 1.9 percent of the worldwide population. Generally, patients with macrodontia have one or two teeth in their mouth that is abnormally large; however, single tooth growth is seen in a number of cases as well. The three types of macrodontia are true generalized macrodontia, relative generalized macrodontia, and macrodontia of a single tooth. True generalized macrodontia is very rare while Macrodontia of a single tooth is much more commonly seen. Macrodontia should not be confused with other oral conditions such as taurodontism (bull teeth), fusion (double tooth), or the jaws being relatively small, giving the appearance of macrodontia. Patients sometimes also exhibit other co-morbidities associated with macrodontia such as enlarged pituitary glands and abnormal growth on one side of the face. Signs & Symptoms As is customary wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KBG Syndrome
KBG syndrome is a rare genetic disease that is the result of a mutation in the ANKRD11 gene at location 16q24.3. Only about a hundred known cases have been reported, although it is expected to be under-reported. The syndrome was first described by Herrmann in 1975 in three distinct families. Herrmann proposed the name KBG syndrome after the initials of affected families' last names, which aren't known to the general public. Characteristics Features of individuals with KBG may include: * Distinctive facial features ** Unusually large upper front teeth ( macrodontia) ** A short, wide skull ( brachycephaly) ** Wide eyebrows that may grow together (synophrys) ** Prominent nasal bridge ** Thin upper lip ** Widely spaced eyebrows (hypertelorism) ** A longer space between the bridge of the nose and upper lip (long philtrum) * Skeletal abnormalities ** Cervical ribs ** Delayed bone age ** Curved Pinky Fingers ** Flat Feet ** Short Stature * Emotional or behavioral changes ** Autism ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
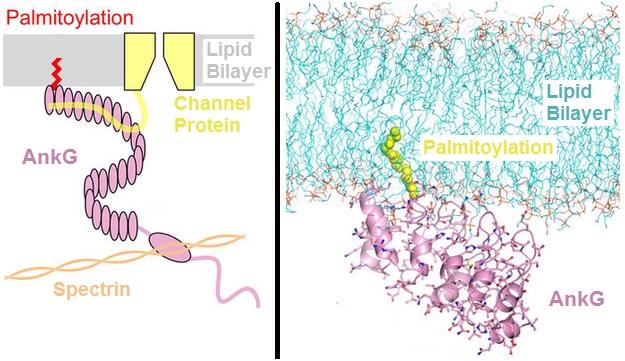
Ankyrin
Ankyrins are a family of proteins that mediate the attachment of integral membrane proteins to the spectrin-actin based membrane cytoskeleton. Ankyrins have binding sites for the beta subunit of spectrin and at least 12 families of integral membrane proteins. This linkage is required to maintain the integrity of the plasma membranes and to anchor specific ion channels, ion exchangers and ion transporters in the plasma membrane. The name is derived from the Greek word ἄγκυρα (''ankyra'') for "anchor". Structure Ankyrins contain four functional domains: an N-terminal domain that contains 24 tandem ankyrin repeats, a central domain that binds to spectrin, a death domain that binds to proteins involved in apoptosis, and a C-terminal regulatory domain that is highly variable between different ankyrin proteins. Membrane protein recognition The 24 tandem ankyrin repeats are responsible for the recognition of a wide range of membrane proteins. These 24 repeats contain 3 struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |