|
AMY (scientific Instrument)
The AMY detector was used by particle physicists at the TRISTAN electron-positron collider at KEK in Japan between 1984 and 1995 to search for new particles and perform precision studies of the strong and electroweak forces. It was built and operated by physicists from many countries, including: the USA, Japan, South Korea, China, and the Philippines. For tracking charged particles, the detector contained an Inner Tracking Chamber and a Central Drift Chamber. A novel X-ray detector, sensitive to x-rays produced by electrons via synchrotron radiation in AMY's 3Tesla solenoidal magnet, was used for electron identification. The Barrel electromagnetic calorimeter was a sampling calorimeter using lead as its passive material and gas for sampling. AMY also had a muon detection system outside of the magnet return yoke. Its most highly cited paper is "Multi - hadron event properties in e+e− annihilation at s√=52 GeV to 57-GeV" While the names of most particle physics experiments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physicists
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three generations of fermions, but ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that contain an odd number of quarks are called baryons and those that contain an even number are called mesons. Two baryons, the proton and the neutron, make up most of the mass of ordinary matter. Mesons are unstable and the longest-lived last for only a few hundredths of a micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Detector
X-ray detectors are devices used to measure the flux, spatial distribution, spectrum, and/or other properties of X-rays. Detectors can be divided into two major categories: imaging detectors (such as photographic plates and X-ray film (photographic film), now mostly replaced by various digitizing devices like image plates or flat panel detectors) and dose measurement devices (such as ionization chambers, Geiger counters, and dosimeters used to measure the local radiation exposure, dose, and/or dose rate, for example, for verifying that radiation protection equipment and procedures are effective on an ongoing basis). X-ray imaging To obtain an image with any type of image detector the part of the patient to be X-rayed is placed between the X-ray source and the image receptor to produce a shadow of the internal structure of that particular part of the body. X-rays are partially blocked ("attenuated") by dense tissues such as bone, and pass more easily through soft tissues. Areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
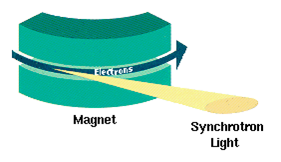
Synchrotron Radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INSPIRE-HEP
INSPIRE-HEP is an open access digital library for the field of high energy physics (HEP). It is the successor of the Stanford Physics Information Retrieval System (SPIRES) database, the main literature database for high energy physics since the 1970s. History SPIRES was (in addition to the CERN Document Server (CDS), arXiv and parts of Astrophysics Data System) one of the main Particle Information Resources. A survey conducted in 2007 found that SPIRES database users wanted the portal to provide more services than the, at that time, already 30-year-old system could provide. On the second annual Summit of Information Specialists in Particle Physics and Astrophysics in May 2008, the physics laboratories CERN, DESY, SLAC and Fermilab therefore announced that they would work together to create a new Scientific Information System for high energy physics called INSPIRE. It interacts with other HEP service providers like arXiv.org, Particle Data Group, NASA's Astrophysics Data System. and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics Facilities
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass. They vary greatly in size or quantity, from subatomic particles like the electron, to microscopic particles like atoms and molecules, to macroscopic particles like powders and other granular materials. Particles can also be used to create scientific models of even larger objects depending on their density, such as humans moving in a crowd or celestial bodies in motion. The term ''particle'' is rather general in meaning, and is refined as needed by various scientific fields. Anything that is composed of particles may be referred to as being particulate. However, the noun ''particulate'' is most frequently used to refer to pollutants in the Earth's atmosphere, which are a suspension of unconnected particles, rather than a connected particle aggregation. Conceptual properties The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |