|
AK Model
The AK model of economic growth is an endogenous growth model used in the theory of economic growth, a subfield of modern macroeconomics. In the 1980s it became progressively clearer that the standard neoclassical exogenous growth models were theoretically unsatisfactory as tools to explore long run growth, as these models predicted economies without technological change and thus they would eventually converge to a steady state, with zero per capita growth. A fundamental reason for this is the diminishing return of capital; the key property of AK endogenous-growth model is the absence of diminishing returns to capital. In lieu of the diminishing returns of capital implied by the usual parameterizations of a Cobb–Douglas production function, the AK model uses a linear model where output is a linear function of capital. Its appearance in most textbooks is to introduce endogenous growth theory. Origin of the concept In neoclassical growth models the economy is assumed to reach a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endogenous Growth Model
Endogenous growth theory holds that economic growth is primarily the result of endogenous and not external forces. Endogenous growth theory holds that investment in human capital, innovation, and knowledge are significant contributors to economic growth. The theory also focuses on positive externalities and spillover effects of a knowledge-based economy which will lead to economic development. The endogenous growth theory primarily holds that the long run growth rate of an economy depends on policy measures. For example, subsidies for research and development or education increase the growth rate in some endogenous growth models by increasing the incentive for innovation. Models In the mid-1980s, a group of growth theorists became increasingly dissatisfied with common accounts of exogenous factors determining long-run growth. They favored a model that replaced the exogenous growth variable (unexplained technical progress) with a model in which the key determinants of growth wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Political Economy
The ''Journal of Political Economy'' is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal published by the University of Chicago Press. Established by James Laurence Laughlin in 1892, it covers both theoretical and empirical economics. In the past, the journal published quarterly from its introduction through 1905, ten issues per volume from 1906 through 1921, and bimonthly from 1922 through 2019. The editor-in-chief is Magne Mogstad (University of Chicago). It is considered one of the top five journals in economics. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in EBSCO, ProQuest, EconLit , Research Papers in Economics, Current Contents/Social & Behavioral Sciences, and the Social Sciences Citation Index. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 9.103, ranking it 4/376 journals in the category "Economics". The journal is department-owned University of Chicago journal. Notable papers Among the most influential papers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
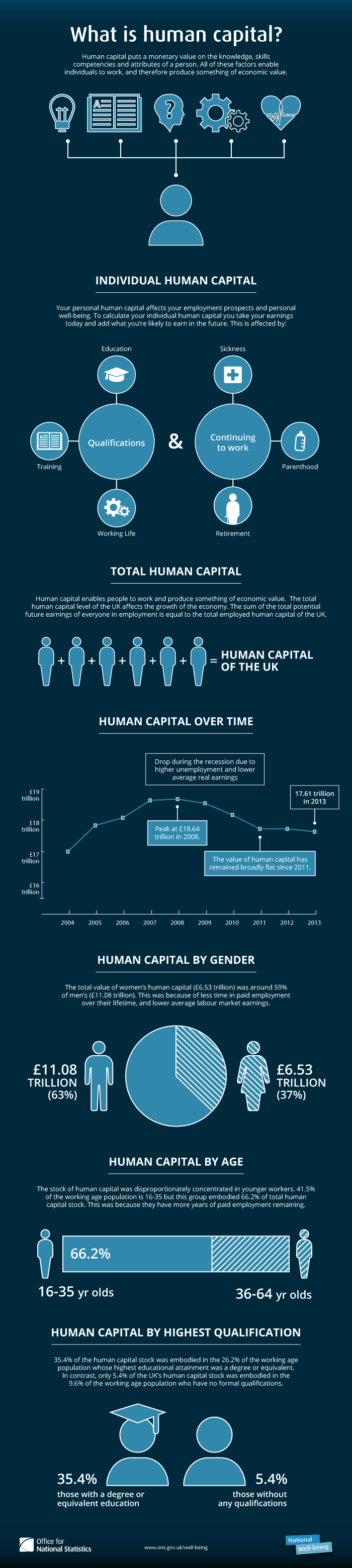
Human Capital
Human capital is a concept used by social scientists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial impact on individual earnings. Research indicates that human capital investments have high economic returns throughout childhood and young adulthood. Companies can invest in human capital, for example, through education and training, enabling improved levels of quality and production. As a result of his conceptualization and modeling work using Human Capital as a key factor, the 2018 Nobel Prize for Economics was jointly awarded to Paul Romer, who founded the modern innovation-driven approach to understanding economic growth. In the recent literature, the new concept of task-specific human capital was coined in 2004 by Robert Gibbons, an economist at MIT, and Michael Waldman, an economist at Cornell University. The concept emphasizes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Growth
Economic growth can be defined as the increase or improvement in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services produced by an economy in a financial year. Statisticians conventionally measure such growth as the percent rate of increase in the real gross domestic product, or real GDP. Growth is usually calculated in real terms – i.e., inflation-adjusted terms – to eliminate the distorting effect of inflation on the prices of goods produced. Measurement of economic growth uses national income accounting. Since economic growth is measured as the annual percent change of gross domestic product (GDP), it has all the advantages and drawbacks of that measure. The economic growth-rates of countries are commonly compared using the ratio of the GDP to population (per-capita income). The "rate of economic growth" refers to the geometric annual rate of growth in GDP between the first and the last year over a period of time. This growth rate represents the trend in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Pokrovskii
Vladimir Nikolajevich Pokrovskii (russian: Влад’имир Никол’аевич Покр’овский; born 11 May 1934) is a Russian scientist known for his original contributions to polymer physics and economic theory. He was the founder of the Altai (Russia, Barnaul) school of dynamics of nonlinear fluids (Yurii Altukhov, Grigorii Pyshnograi and others). Biography Pokrovskii was born May 11, 1934 into a Russian family in the rural locality Altayskoye, Altaysky District, Altai Krai (Russian: Алтайское, Алтайского края), Russia. He graduated from Tomsk State University in Siberia as a physicist (Department of Theoretical Physics) in 1958 and in the same year was employed as a teacher of physics at Tomsk Polytechnic University. In 1964 he moved to the Branch of Institute of Chemical Physics of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR (Chernogolovka, Moscow region) where in positions of Senior Research Fellow was engaged in studying of suspensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depreciation
In accountancy, depreciation is a term that refers to two aspects of the same concept: first, the actual decrease of fair value of an asset, such as the decrease in value of factory equipment each year as it is used and wear, and second, the allocation in accounting statements of the original cost of the assets to periods in which the assets are used (depreciation with the matching principle). Depreciation is thus the decrease in the value of assets and the method used to reallocate, or "write down" the cost of a tangible asset (such as equipment) over its useful life span. Businesses depreciate long-term assets for both accounting and tax purposes. The decrease in value of the asset affects the balance sheet of a business or entity, and the method of depreciating the asset, accounting-wise, affects the net income, and thus the income statement that they report. Generally, the cost is allocated as depreciation expense among the periods in which the asset is expected to be used. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Growth Rate
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 7.9 billion in 2020. The UN projected population to keep growing, and estimates have put the total population at 8.6 billion by mid-2030, 9.8 billion by mid-2050 and 11.2 billion by 2100. However, some academics outside the UN have increasingly developed human population models that account for additional downward pressures on population growth; in such a scenario population would peak before 2100. World human population has been growing since the end of the Black Death, around the year 1350. A mix of technological advancement that improved agricultural productivity and sanitation and medical advancement that reduced mortality increased population growth. In some geographies, this has slowed through the process called the demographic tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Output Elasticity
In economics, output elasticity is the percentage change of output (GDP Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ... or production of a single firm) divided by the percentage change of an input. It is sometimes called ''partial output elasticity'' to clarify that it refers to the change of only one input. As with every elasticity, this measure is defined locally, i.e. defined at a point. If the production function contains only one input, then the output elasticity is also an indicator of the degree of returns to scale. If the coefficient of output elasticity is greater than 1, then production is experiencing increasing returns to scale. If the coefficient is less than 1, then production is experiencing decreasing returns to scale. If the coefficient is 1, then production is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Factor Productivity
In economics, total-factor productivity (TFP), also called multi-factor productivity, is usually measured as the ratio of aggregate output (e.g., GDP) to aggregate inputs. Under some simplifying assumptions about the production technology, growth in TFP becomes the portion of growth in output not explained by growth in traditionally measured inputs of labour and capital used in production. TFP is calculated by dividing output by the weighted geometric average of labour and capital input, with the standard weighting of 0.7 for labour and 0.3 for capital. Total factor productivity is a measure of productive efficiency in that it measures how much output can be produced from a certain amount of inputs. It accounts for part of the differences in cross-country per-capita income. For relatively small percentage changes, the rate of ''TFP'' growth can be estimated by subtracting growth rates of labor and capital inputs from the growth rate of output. Background Technology growth and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
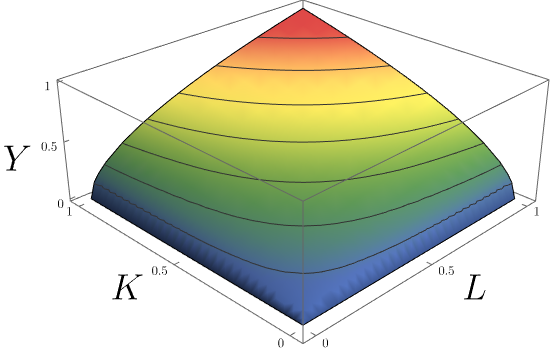
Cobb–Douglas Production Function
In economics and econometrics, the Cobb–Douglas production function is a particular functional form of the production function, widely used to represent the technological relationship between the amounts of two or more inputs (particularly physical capital and labor) and the amount of output that can be produced by those inputs. The Cobb–Douglas form was developed and tested against statistical evidence by Charles Cobb and Paul Douglas between 1927 and 1947; according to Douglas, the functional form itself was developed earlier by Philip Wicksteed. Formulation In its most standard form for production of a single good with two factors, the function is : Y=AL^\beta K^\alpha where: * ''Y'' = total production (the real value of all goods produced in a year or 365.25 days) * ''L'' = labour input (person-hours worked in a year or 365.25 days) * ''K'' = capital input (a measure of all machinery, equipment, and buildings; the value of capital input divided by the price of capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant Returns To Scale
In economics, returns to scale describe what happens to long-run returns as the scale of production increases, when all input levels including physical capital usage are variable (able to be set by the firm). The concept of returns to scale arises in the context of a firm's production function. It explains the long-run linkage of the rate of increase in output (production) relative to associated increases in the inputs (factors of production). In the long run, all factors of production are variable and subject to change in response to a given increase in production scale. While economies of scale show the effect of an increased output level on unit costs, returns to scale focus only on the relation between input and output quantities. There are three possible types of returns to scale: increasing returns to scale, constant returns to scale, and diminishing (or decreasing) returns to scale. If output increases by the same proportional change as all inputs change then there are cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Capital
Social capital is "the networks of relationships among people who live and work in a particular society, enabling that society to function effectively". It involves the effective functioning of social groups through interpersonal relationships, a shared sense of Identity (social science), identity, a shared understanding, shared Social norm, norms, shared Value (ethics), values, Trust (social sciences), trust, cooperation, and Reciprocity (social psychology), reciprocity. Social capital is a measure of the value of resources, both Tangibility, tangible (e.g., public spaces, private property) and intangible (e.g., Social actor, actors, human capital, people), and the impact that ideal creators have on the resources involved in each relationship, and on larger groups. Some have described it as a form of capital that produces Public good (economics), public goods for a common purpose, although this does not align with how it has been measured. Social capital has been used to expla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |