|
AI-complete
In the field of artificial intelligence (AI), tasks that are hypothesized to require artificial general intelligence to solve are informally known as AI-complete or AI-hard.Shapiro, Stuart C. (1992)Artificial Intelligence In Stuart C. Shapiro (Ed.), ''Encyclopedia of Artificial Intelligence'' (Second Edition, pp. 54–57). New York: John Wiley. (Section 4 is on "AI-Complete Tasks".) Calling a problem AI-complete reflects the belief that it cannot be solved by a simple specific algorithm. In the past, problems supposed to be AI-complete included computer vision, natural language understanding, and dealing with unexpected circumstances while solving any real-world problem. AI-complete tasks were notably considered useful for testing the presence of humans, as CAPTCHAs aim to do, and in computer security to circumvent brute-force attacks. History The term was coined by Fanya Montalvo by analogy with NP-complete and NP-hard in complexity theory, which formally describes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial General Intelligence
Artificial general intelligence (AGI)—sometimes called human‑level intelligence AI—is a type of artificial intelligence that would match or surpass human capabilities across virtually all cognitive tasks. Some researchers argue that state‑of‑the‑art large language models already exhibit early signs of AGI‑level capability, while others maintain that genuine AGI has not yet been achieved. AGI is conceptually distinct from artificial superintelligence (ASI), which would outperform the best human abilities across every domain by a wide margin. AGI is considered one of the definitions of Chinese room#Strong AI vs. AI research, strong AI. Unlike artificial narrow intelligence (ANI), whose competence is confined to well‑defined tasks, an AGI system can generalise knowledge, transfer skills between domains, and solve novel problems without task‑specific reprogramming. The concept does not, in principle, require the system to be an autonomous agent; a static model— ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAPTCHA
Completely Automated Public Turing Test to tell Computers and Humans Apart (CAPTCHA) ( ) is a type of challenge–response authentication, challenge–response turing test used in computing to determine whether the user is human in order to deter bot attacks and spam. The term was coined in 2003 by Luis von Ahn, Manuel Blum, Nicholas J. Hopper, and John Langford (computer scientist), John Langford. It is a contrived acronym for "Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart." A historically common type of CAPTCHA (displayed as reCAPTCHA v1) was first invented in 1997 by two groups working in parallel. This form of CAPTCHA requires entering a sequence of letters or numbers from a distorted image. Because the test is administered by a computer, in contrast to the standard Turing test that is administered by a human, CAPTCHAs are sometimes described as reverse Turing tests. Two widely used CAPTCHA services are Google's reCAPTCHA and the independent hC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fanya Montalvo
Fanya S. Montalvo (born in Monterey, Mexico) is a Mexican computer scientist. Education and career She received a Ph.D. in computer and information science from the University of Massachusetts Amherst in 1976. Her dissertation was titled ''Aftereffects, Adaptation, and Plasticity: A Neural Model for Tunable Feature Space.'' She was advised by Michael Anthony Arbib. Montalvo has been a research scientist at Lawrence Berkeley Labs, HP, MIT, and Digital Equipment Corporation. Montalvo works in the field of inconsistency robustness. She is on the governing board of the International Society for Inconsistency Robustness. According to Rosalind Picard, she is involved in considerations within emotional computing. She is known for having coined the term "AI-complete"John C. Mallery. "Thinking About Foreign Policy: Finding an Appropriate Role for Artificially Intelligent Computers" Master's thesis, M.I.T. Political Science Department. 1988 to denote an artificial intelligence task th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Translation
Machine translation is use of computational techniques to translate text or speech from one language to another, including the contextual, idiomatic and pragmatic nuances of both languages. Early approaches were mostly rule-based or statistical. These methods have since been superseded by neural machine translation and large language models. History Origins The origins of machine translation can be traced back to the work of Al-Kindi, a ninth-century Arabic cryptographer who developed techniques for systemic language translation, including cryptanalysis, frequency analysis, and probability and statistics, which are used in modern machine translation. The idea of machine translation later appeared in the 17th century. In 1629, René Descartes proposed a universal language, with equivalent ideas in different tongues sharing one symbol. The idea of using digital computers for translation of natural languages was proposed as early as 1947 by England's A. D. Booth and Warr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formalism (philosophy Of Mathematics)
In the philosophy of mathematics, formalism is the view that holds that statements of mathematics and logic can be considered to be statements about the consequences of the manipulation of strings (alphanumeric sequences of symbols, usually as equations) using established manipulation rules. A central idea of formalism "is that mathematics is not a body of propositions representing an abstract sector of reality, but is much more akin to a game, bringing with it no more commitment to an ontology of objects or properties than ludo or chess." According to formalism, mathematical statements are not "about" numbers, sets, triangles, or any other mathematical objects in the way that physical statements are about material objects. Instead, they are purely syntactic expressions—formal strings of symbols manipulated according to explicit rules without inherent meaning. These symbolic expressions only acquire interpretation (or semantics) when we choose to assign it, similar to how che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
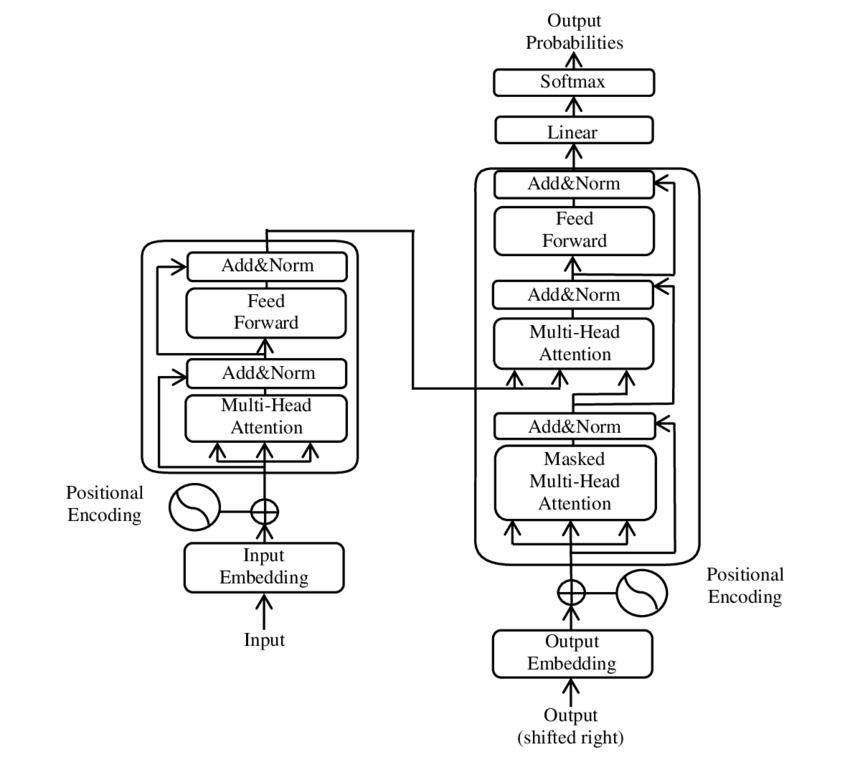
Large Language Model
A large language model (LLM) is a language model trained with self-supervised machine learning on a vast amount of text, designed for natural language processing tasks, especially language generation. The largest and most capable LLMs are generative pretrained transformers (GPTs), which are largely used in generative chatbots such as ChatGPT or Gemini. LLMs can be fine-tuned for specific tasks or guided by prompt engineering. These models acquire predictive power regarding syntax, semantics, and ontologies inherent in human language corpora, but they also inherit inaccuracies and biases present in the data they are trained in. History Before the emergence of transformer-based models in 2017, some language models were considered large relative to the computational and data constraints of their time. In the early 1990s, IBM's statistical models pioneered word alignment techniques for machine translation, laying the groundwork for corpus-based language modeling. A sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peer Review
Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work (:wiktionary:peer#Etymology 2, peers). It functions as a form of self-regulation by qualified members of a profession within the relevant Field of study, field. Peer review methods are used to maintain quality standards, improve performance, and provide credibility. In academia, scholarly peer review is often used to determine an academic paper's suitability for publication. Peer review can be categorized by the type and by the field or profession in which the activity occurs, e.g., #Medical, medical peer review. It can also be used as a teaching tool to help students improve writing assignments. Henry Oldenburg (1619–1677) was a German-born British philosopher who is seen as the 'father' of modern scientific peer review. It developed over the following centuries with, for example, the journal ''Nature (journal), Nature'' making it standard practice in 1973. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automated Reasoning
In computer science, in particular in knowledge representation and reasoning and metalogic, the area of automated reasoning is dedicated to understanding different aspects of reasoning. The study of automated reasoning helps produce computer programs that allow computers to reason completely, or nearly completely, automatically. Although automated reasoning is considered a sub-field of artificial intelligence, it also has connections with theoretical computer science and philosophy. The most developed subareas of automated reasoning are automated theorem proving (and the less automated but more pragmatic subfield of interactive theorem proving) and automated proof checking (viewed as guaranteed correct reasoning under fixed assumptions). Extensive work has also been done in reasoning by analogy using induction and abduction. Other important topics include reasoning under uncertainty and non-monotonic reasoning. An important part of the uncertainty field is that of argumentat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automated Theorem Proving
Automated theorem proving (also known as ATP or automated deduction) is a subfield of automated reasoning and mathematical logic dealing with proving mathematical theorems by computer programs. Automated reasoning over mathematical proof was a major motivating factor for the development of computer science. Logical foundations While the roots of formalized Logicism, logic go back to Aristotelian logic, Aristotle, the end of the 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of modern logic and formalized mathematics. Gottlob Frege, Frege's ''Begriffsschrift'' (1879) introduced both a complete propositional logic, propositional calculus and what is essentially modern predicate logic. His ''The Foundations of Arithmetic, Foundations of Arithmetic'', published in 1884, expressed (parts of) mathematics in formal logic. This approach was continued by Bertrand Russell, Russell and Alfred North Whitehead, Whitehead in their influential ''Principia Mathematica'', first published 1910� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to machine perception, perceive their environment and use machine learning, learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Amazon Alexa, Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); Generative artificial intelligence, generative and Computational creativity, creative tools (e.g., ChatGPT and AI art); and Superintelligence, superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure of arguments alone, independent of their topic and content. Informal logic is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. Informal logic examines arguments expressed in natural language whereas formal logic uses formal language. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a specific logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Logic plays a central role in many fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics. Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises that leads to a conclusion. An example is the argument from the premises "it's Sunday" and "if it's Sunday then I don't have to work" leading to the conclusion "I don't have to wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expert System
In artificial intelligence (AI), an expert system is a computer system emulating the decision-making ability of a human expert. Expert systems are designed to solve complex problems by reasoning through bodies of knowledge, represented mainly as if–then rules rather than through conventional procedural programming code. Expert systems were among the first truly successful forms of AI software. They were created in the 1970s and then proliferated in the 1980s, being then widely regarded as the future of AI — before the advent of successful artificial neural networks. An expert system is divided into two subsystems: 1) a ''knowledge base'', which represents facts and rules; and 2) an '' inference engine'', which applies the rules to the known facts to deduce new facts, and can include explaining and debugging abilities. History Early development Soon after the dawn of modern computers in the late 1940s and early 1950s, researchers started realizing the immense potential th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |