|
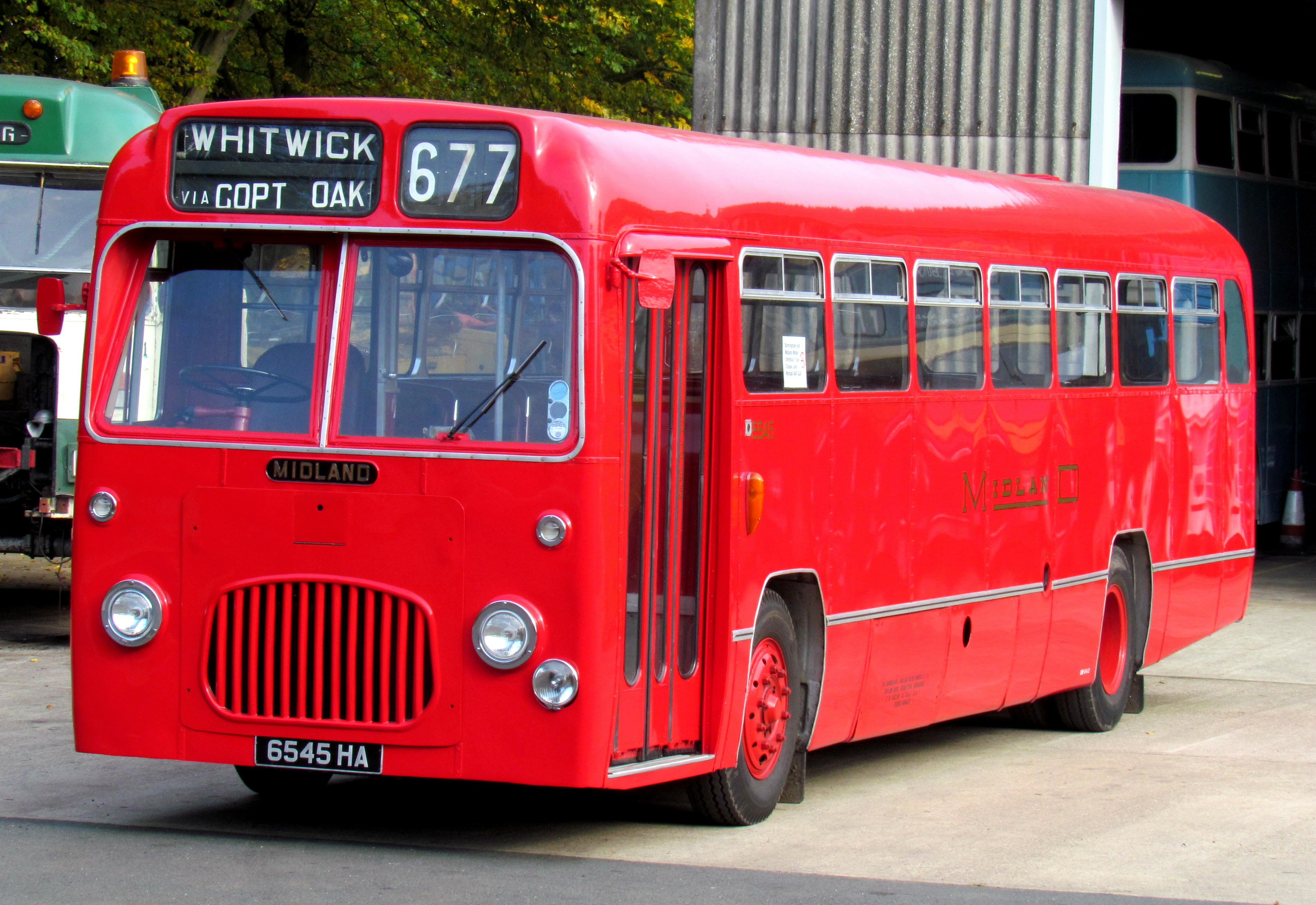
AEC Regent II
The AEC Regent II was a front-engined double-decker bus built by AEC from 1945 to 1947. Despite officially being a new type it was very similar to the 1929 Regent. The Regent IIs were all documented as being new with the A173 (also known as the 7.7-litre) engine and a four speed sliding mesh gearbox. The only vehicles that were not standard were the 100 purchased by B.M.M.O. (Birmingham & Midland Motor Omnibus Company), which were classified as O661/20 as the front had to be re-designed so they could carry similar bonnets and radiator grilles that B.M.M.O. had designed for the double deckers they built themselves. Operators The only other Regent IIs to differ from standard were Dundee Corporation's fleet of ex- London Transport STLs, all of which carried flared-bottomed Weymann bodies. Dundee changed the sliding mesh gearbox for the pre-selective version - a move which may have been expected from a concern like London Transport (who favoured pre-select vehicles) but not of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Associated Equipment Company
Associated Equipment Company (AEC) was a British vehicle manufacturer that built buses, motorcoaches and trucks from 1912 until 1979. The name Associated Equipment Company was hardly ever used; instead it traded under the AEC and ACLO brands. During World War One, AEC was the most prolific British lorry manufacturer; after building London's buses before the great war. History Inception The London General Omnibus Company (LGOC) was founded in 1855 to amalgamate and regulate the horse-drawn omnibus services then operating in London. The company began producing motor omnibuses for its own use in 1909 with the X-type designed by its chief motor engineer, Frank Searle, at works in Blackhorse Lane, Walthamstow. The X-type was followed by Searle's B-type design, considered to be one of the first mass-produced commercial vehicles. In 1912, LGOC was taken over by the Underground Group of companies, which at that time owned most of the London Underground, and extensive tram oper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southall
Southall () is a large suburban county of West London, England, part of the London Borough of Ealing and is one of its seven major towns. It is situated west of Charing Cross and had a population of 69,857 as of 2011. It is generally divided in three parts: the mostly residential area around Lady Margaret Road (Dormers Wells); the main commercial centre at High Street and Southall Broadway (part of the greater Uxbridge Road); and Old Southall/Southall Green to the south consisting of Southall railway station, industries and Norwood Green bounded by the M4. It was historically a municipal borough of Middlesex administered from Southall Town Hall until 1965. Southall is located on the Grand Union Canal (formerly the Grand Junction Canal) which first linked London with the rest of the growing canal system. It was one of the last canals to carry significant commercial traffic (through the 1950s) and is still open to traffic and is used by pleasure craft. The canal separates it f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AEC Regent I
The AEC Regent I was a bus chassis manufactured by AEC. History The AEC Regent I was a bus chassis introduced by AEC in 1929. Twelve pre-production examples had been completed by July 1929, with mainstream production commencing in October 1929. It was succeeded by the AEC Regent II in 1942. Survivors *Birmingham City Transport 486 at the Transport Museum Wythall *Thomas Tilling The Tilling Group was one of two conglomerates that controlled almost all of the major bus operators in the United Kingdom between World Wars I and II and until nationalisation in 1948. Tilling, together with the other conglomerate, British El ... 922 at the London Bus Museum London Bus Museum [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AEC Regent III
The AEC Regent III (also known as Regent 3 or Regent Mark III) was a type of double-decker bus chassis manufactured by AEC. It was mainly built for operation outside London and overseas. It could be fitted with AEC's 9.6-litre diesel engine (except a minority with 7.7-litre ones), 'Wilson' preselective epicyclic gearbox (except for a minority with crash gearboxes; a synchromesh option also became available in the early 1950s) and air-pressure operated brakes (except a minority with vacuum brakes). The Regent III was available with bodies from a number of manufacturers including Park Royal, Metro Cammell Weymann and Charles H. Roe. AEC Regent III was superseded by the AEC Regent V, not the AEC Regent IV underfloor-engined double decker which existed as a one-off prototype only. The last Regent IIIs were supplied to Reading Corporation in 1956. Regent III in London London Transport acquired 76 AEC Regent III buses with Weymann lowbridge A lowbridge double-deck bus is a do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front-engine, Rear-wheel-drive Layout
In automotive design, a FR, or front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout is one where the engine is located at the front of the vehicle and driven wheels are located at the rear via a drive shaft. This was the traditional automobile layout for most of the 20th century. Modern designs commonly use the front-engine, front-wheel-drive layout (FF). It is also used in high-floor buses and school buses. Front mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout In automotive design, a front mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout (FMR) is one that places the engine in the front, with the rear wheels of vehicle being driven. In contrast to the front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout (FR), the engine is pushed back far enough that its center of mass is to the rear of the front axle. This aids in weight distribution and reduces the moment of inertia, improving the vehicle's handling. The mechanical layout of an FMR is substantially the same as an FR car. Some models of the same vehicle can be classified as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-decker Bus
A double-decker bus or double-deck bus is a bus that has two storeys or decks. They are used for mass transport in the United Kingdom, the United States, New Zealand, Europe, Asia and also in cities such as Sydney; the best-known example is the red London bus, namely the AEC Routemaster. Early double-deckers put the driver in a separate cab. Passenger access was via an open platform at the rear and a bus conductor collected fares. Modern double-deckers have a main entrance door at the front and the driver takes fares, thus halving the number of workers aboard, but slowing the boarding process. The rear open platform, popular with passengers, was abandoned for safety reasons, as there was a risk of passengers falling when running and jumping onto the bus. Double-deckers are primarily for commuter transport, but open-top models are used as sight-seeing buses for tourists. William Gladstone, speaking of London's double-deck horse-drawn omnibuses, once observed that "...the best w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midland Red
Midland RedCompanies House extract company no 82681 Midland Red Omnibus Company Limited formerly Birmingham & Midland Motor Omnibus Company Limited was a bus company that operated in from 1905 until 1981. It was one of the largest English bus companies, operating over a large area between in the south and in the north, and from |
Hood (vehicle)
The hood (American English) or bonnet (Commonwealth English) is the hinged cover over the engine of motor vehicles. Hoods can open to allow access to the engine compartment, or trunk (boot in Commonwealth English) on rear-engine and some mid-engine vehicles) for maintenance and repair. Terminology In British terminology, ''hood'' refers to a fabric cover over the passenger compartment of the car (known as the 'roof' or 'top' in the US). In many motor vehicles built in the 1930s and 1940s, the resemblance to an actual hood or bonnet is clear when open and viewed head-on; in modern vehicles it continues to serve the same purpose but no longer resembles a head covering. Styles and materials On front-engined cars, the hood may be hinged at either the front or the rear edge, or in earlier models (e.g. the Ford Model T) it may be split into two sections, one each side, each hinged along the centre line. A further variant combines the bonnet and wheelarches into one section and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grille (motor Vehicle)
In automotive engineering, a grille covers an opening in the body of a vehicle to allow air to enter or exit. Most vehicles feature a grille at the front of the vehicle to protect the radiator and engine. Merriam-Webster describes grilles as "a grating forming a barrier or screen; especially: an ornamental one at the front end of an automobile." The word 'grille' is commonly misspelled as 'grill' which instead refers to the cooking method. Other common grille locations include below the front bumper, in front of the wheels (to cool the brakes), in the cowl for cabin ventilation, or on the rear deck lid (in rear engine vehicles). Grilles evolved from previously installed gravel shields that were designed to protect exposed radiators typically used on cars until the early 1930s. Design The front fascia of a motor vehicle has an important role in attracting buyers. The principal function of the grille is to admit cooling air to the car's radiator. However, the look of the vehicl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Passenger Transport Board
The London Passenger Transport Board was the organisation responsible for local public transport in London and its environs from 1933 to 1948. In common with all London transport authorities from 1933 to 2000, the public name and brand was London Transport. History The London Passenger Transport Board (LPTB) was established pursuant to the London Passenger Transport Act 1933 enacted on 13 April 1933. The bill had been introduced by Herbert Morrison, who was Transport Minister in the Labour Government until 1931. Because the legislation was a hybrid bill it had been possible to allow it to 'roll over' into the new parliament under the incoming National Government. The new government, although dominated by Conservatives, decided to continue with the bill, with no serious changes, despite its extensive transfer of private undertakings into the public sector. On 1 July 1933, the LPTB came into being, covering the "London Passenger Transport Area". The LPTB's financial structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as '' Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Anglia Transport Museum
The East Anglia Transport Museum is an open-air transport museum, with numerous historic public transport vehicles (including many in full working order). It is located in Carlton Colville a suburb of Lowestoft, Suffolk. It is the only museum in the country where visitors can ride on buses, trams and trolleybuses, as well as a narrow-gauge railway. What the Museum offers The museum has many exhibits ranging from a 1904 Lowestoft Corporation tram to a 1985 Sinclair C5. Tram rides are available on a route passing the museum's trolleybus depot and up to a terminus at Woodside. Originally, the trolleybus route extended as far as the trolleybus depot where passengers could change for a ride on the museum's 2 ft gauge railway to Chapel Road (the other end of the tram route), or they could stay on the trolleybus whilst it performed a 3-point turn and returned to the museum entrance via the same route. 12 July 2008 marked Britain's first trolleybus extension for many decades thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Portrait_of_Robert_Cheseman_(1485-1547)_Mauritshuis_276.jpg)