|
ACsEV
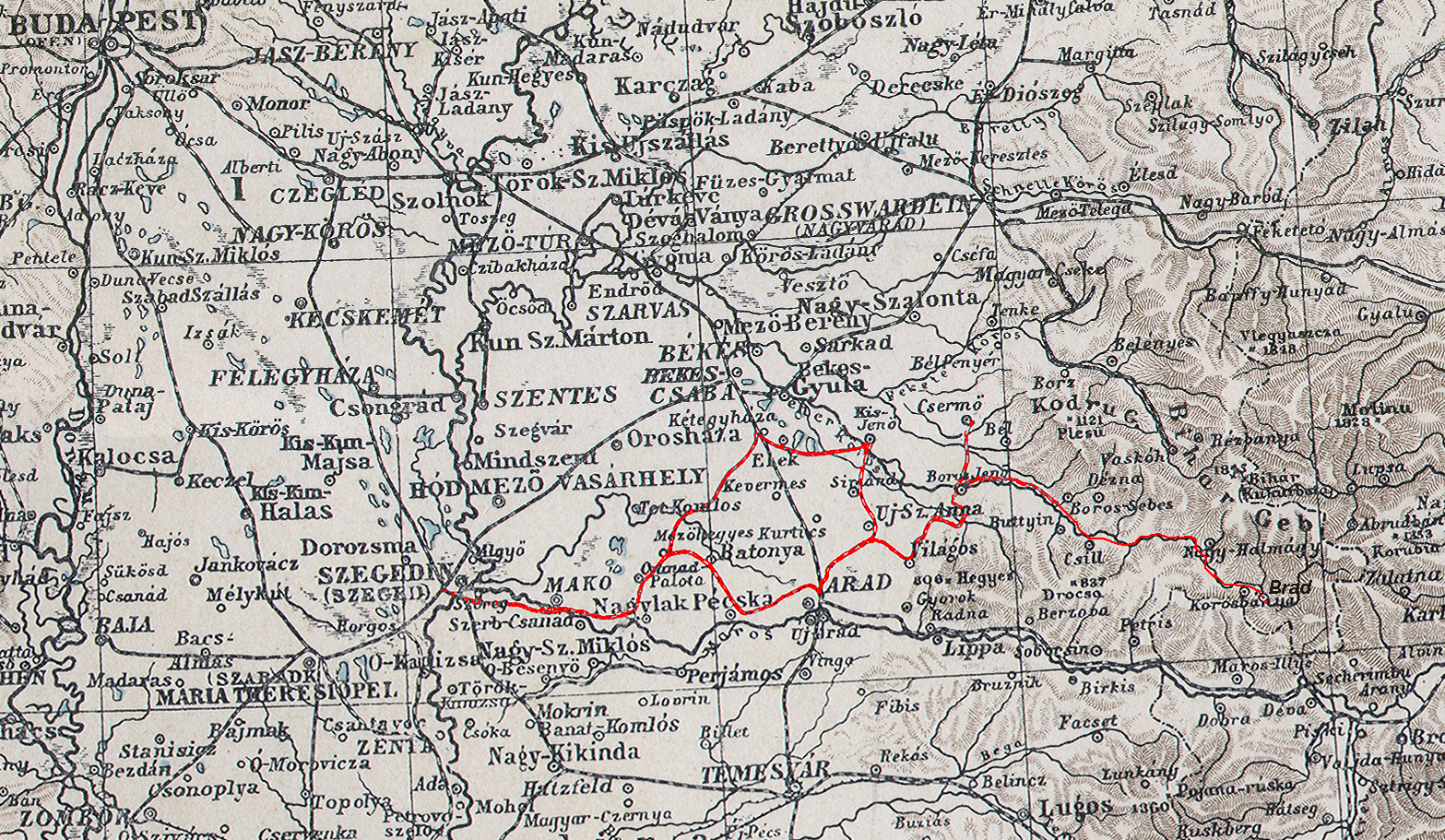
The ACsEV (Aradi és Csanádi Egyesült Vasutak, En.: Arad & Csanad United Railways) were a Hungarian joint-stock railway company. Till 1920, the network had a length of 391 km. Since 1903, the company bought more than forty petrol-electric self-propelled rail cars, and thus for some years performed one of the most advanced passenger transports in the world. Due to changes of the borders, in 1920 more than half of the company's network was taken over by the Romanian Railways (CFR). Predecessors The ''Arad–Körösvölgyi Vasút'' (Arad – Körös-Valley Railway was founded in 1873. From 1 February 1877 to 25 September 1881, it built its line from Arad northeastward to Boressebes ( Ro.: Sebiș) in the Fehér-Körös ( Crişul Alb) valley. The ''Arad–Csanádi Vasút'' (''Arad–Csanád Railway''), licensed in 1881, built its Y-shaped network between Arad and Szeged in the short space of time from 5 November 1882 to 20 May 1883. In 1886, both companies merged to for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACsEV Rot
The ACsEV (Aradi és Csanádi Egyesült Vasutak, En.: Arad & Csanad United Railways) were a Hungarian joint-stock railway company. Till 1920, the network had a length of 391 km. Since 1903, the company bought more than forty petrol-electric self-propelled rail cars, and thus for some years performed one of the most advanced passenger transports in the world. Due to changes of the borders, in 1920 more than half of the company's network was taken over by the Romanian Railways (CFR). Predecessors The ''Arad–Körösvölgyi Vasút'' (Arad – Körös-Valley Railway was founded in 1873. From 1 February 1877 to 25 September 1881, it built its line from Arad northeastward to Boressebes ( Ro.: Sebiș) in the Fehér-Körös ( Crişul Alb) valley. The ''Arad–Csanádi Vasút'' (''Arad–Csanád Railway''), licensed in 1881, built its Y-shaped network between Arad and Szeged in the short space of time from 5 November 1882 to 20 May 1883. In 1886, both companies merged to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weitzer Railmotor
The railmotors of J. Weitzer ''Engine- & Waggon-Building & Iron Casting Joint-stock Company'' ( Hu.: ''Weitzer János Gép,- Waggongyár és Vasöntöde Részvénytársaság'') were Europe's first self-propelled railcars with internal combustion engine built in considerable numbers. The principle of their petrol–electric transmission and the four-cylinder petrol engines came from De Dion-Bouton in France. The electric engines were produced Siemens-Schuckert in Germany. The first cars were constructed in 1903, the series since 1906. Reports of their use can be added to a total of 65 sold railmotors and 40 trailers. Most of these railmotors were built for , 11 for metre gauge and 11 for . The last ones ran on petrol-electric traction till 1960. History The Hungarian minister of trade, Lajos Láng, started a campaign for the development of self-propelled railcars in order to economize passenger transport on secondary railroads. The producers involved were Ganz & Cie., Weitze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrol–electric Transmission
Petrol–electric transmission (UK English) or gasoline–electric transmission or gas–electric transmission (US English) is a transmission system for vehicles powered by petrol engines. Petrol–electric transmission was used for a variety of applications in road, rail, and marine transport, in the early 20th century. After World War I, it was largely superseded by diesel-electric transmission, a similar transmission system used for diesel engines; but petrol-electric has become popular again in modern hybrid electric vehicles. Petrol–electric transmission was used in certain niche markets in the early 20th century, such as in the petrol–electric railway locomotives produced in Britain for use on the War Department Light Railways during World War I or for privately owned Arad & Csanad United Railways. In France, the Crochat petrol–electric transmission system was used for standard gauge locomotives (up to 240 kW of electrical power). Description Petrol-electric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chișineu-Criș
Chișineu-Criș ( Hungarian: ''Kisjenő'') is a town in Arad County, Crișana, Romania. Geography The town is situated on the north-western side of the county, at a distance from Arad, the county seat. The administrative territory stretches over on the Crișul Alb Plateau, on both sides of the river Crișul Alb. The town was formed by merging the villages of Chișineu Mic and Pădureni. The town administers one village, Nădab (''Nadab''). Demographics In 1910, the town had 2821 inhabitants: 1376 (48.8%) spoke Hungarian, 1355 (48%) spoke Romanian, 49 (1.7%) spoke German. In 2011, 73.5% of inhabitants were Romanians, 19.3% Hungarians and 6.3% Roma. Economy Although the town economy is predominant agricultural, during the last decade the second and third economic sectors had a growing evolution. For most of the tourists Chișineu-Criș is a transit town towards central and Western Europe. The most attractive sightseeing spot of the town is the Crișul Alb River and its banks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oradea
Oradea (, , ; german: Großwardein ; hu, Nagyvárad ) is a city in Romania, located in Crișana, a sub-region of Transylvania. The county seat, seat of Bihor County, Oradea is one of the most important economic, social and cultural centers in the western part of Romania. The city is located in the north-west of the country, nestled between hills on the Crișana plain, on the banks of the river Crișul Repede, that divides the city into almost equal halves. Located about from Borș, Bihor, Borș, one of the most important crossing points on Romania's border with Hungary, Oradea ranks List of cities and towns in Romania, tenth in size among Romanian cities. It covers an area of , in an area of contact between the extensions of the Apuseni Mountains and the Crișana-Banat extended plain. Oradea enjoys a high standard of living and ranks among the most livable cities in the country. The city is also a strong industrial center in the region, hosting some of Romania's largest companies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timișoara
), City of Roses ( ro, Orașul florilor), City of Parks ( ro, Orașul parcurilor) , image_map = Timisoara jud Timis.svg , map_caption = Location in Timiș County , pushpin_map = Romania#Europe , pushpin_relief = 1 , pushpin_label_position = bottom , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Counties of Romania, County , subdivision_name1 = Timiș County, Timiș , subdivision_type2 = Subdivisions of Romania, Status , subdivision_name2 = County seat , established_title = First official record , established_date = 1212 (as ''castrum regium Themes'') , leader_party = Save Romania Union, USR , leader_title = Mayor , leader_name = Dominic Fritz , leader_title1 = Deputy mayors , leader_name1 = Ruben Lațcău (Save Romania Union, USR)Cosmin Tab� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szolnok
Szolnok (; also known by other alternative names) is the county seat of Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county in central Hungary. A city with county rights, it is located on the banks of the Tisza river, in the heart of the Great Hungarian Plain, which has made it an important cultural and economic crossroads for centuries. Szolnok also has one of Hungary’s best waterpolo teams. Name and etymology Szolnok was named for the first steward of the city, Szaunik or Zounok. The town was first officially mentioned under the name Zounok in 1075. In the following centuries, it was recorded as Zounok, Saunic, Zounuc, and Zawnuch. The variety of spellings likely comes from phonetic discrepancies occurring when Hungarian sounds - originally written in runic Old Hungarian script - were recorded using the Latin alphabet. Another possibility revolves around speculation that the name Szaunik was not a personal name after all, but rather a title relating to the significant salt trade (salt, hu, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian State Railways
Hungarian State Railways ( hu, Magyar Államvasutak, MÁV) is the Hungarian national railway company, with divisions "MÁV START Zrt." (passenger transport), "MÁV-Gépészet Zrt." (maintenance), "MÁV-Trakció Zrt." and "MÁV Cargo Zrt" (freight transport). The head office is in Budapest. History 1846–1918 Construction of Hungary's first railway line began in the second half of 1844. The first steam locomotive railway line was opened on 15 July 1846 between Pest and Vác. This date is regarded as the birth date of the Hungarian railways. The Romantic poet Sándor Petőfi rode on the first train and wrote a poem predicting that rails would connect Hungary like blood vessels in the human body. After the failed revolution, the existing lines were nationalized by the Austrian State and new lines were built. As a result of the Austro-Sardinian War in the late 1850s, all these lines were sold to Austrian private companies. During this time the company of Ábrahám Gan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makó
Makó (, german: Makowa, yi, מאַקאָווע Makowe, ro, Macău or , sk, Makov) is a town in Csongrád County, in southeastern Hungary, from the Romanian border. It lies on the Maros River. Makó is home to 23,272 people and it has an area of , of which is arable land. Makó is the fourth-largest town in Csongrád County after Szeged, Hódmezővásárhely and Szentes. The town is from Hódmezővásárhely, from Szeged, from Arad, Romania, Arad, from Gyula, Hungary, Gyula, from Timișoara (Temesvár), and from Budapest. The climate is warmer than anywhere else in Hungary, with hot, dry summers. The town is noted for its onion which is a hungarikum, the spa and the thermal bath. The Makó International Onion Festival, the largest of its kind, is held annually. Makó is a popular tourist destination in Hungary. The Makó gas field, located near the town, is the largest natural gas field in Central Europe. The gas volume is more than 600 billion cubic metres (21 trillion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |