|
ABM Treaty
The Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty (ABM Treaty or ABMT) (1972–2002) was an arms control treaty between the United States and the Soviet Union on the limitation of the anti-ballistic missile (ABM) systems used in defending areas against ballistic missile-delivered nuclear weapons. It was intended to reduce pressures to build more nuclear weapons to maintain deterrence. Under the terms of the treaty, each party was limited to two ABM complexes, each of which was to be limited to 100 anti-ballistic missiles. Signed in 1972, it was in force for the next 30 years. In 1997, five years after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, four former Soviet republics agreed with the United States to succeed the USSR's role in the treaty. In June 2002 the United States withdrew from the treaty, leading to its termination, citing risks of nuclear blackmail. Background Throughout the late 1950s and into the 1960s, the United States and the Soviet Union had been developing missile systems with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United States Constitution (1789). See alsTitle 10, Subtitle B, Chapter 301, Section 3001 The oldest and most senior branch of the U.S. military in order of precedence, the modern U.S. Army has its roots in the Continental Army, which was formed 14 June 1775 to fight the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783)—before the United States was established as a country. After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army.Library of CongressJournals of the Continental Congress, Volume 27/ref> The United States Army considers itself to be a continuation of the Continental Army, and thus considers its institutional inception to be the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Science+Business Media
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
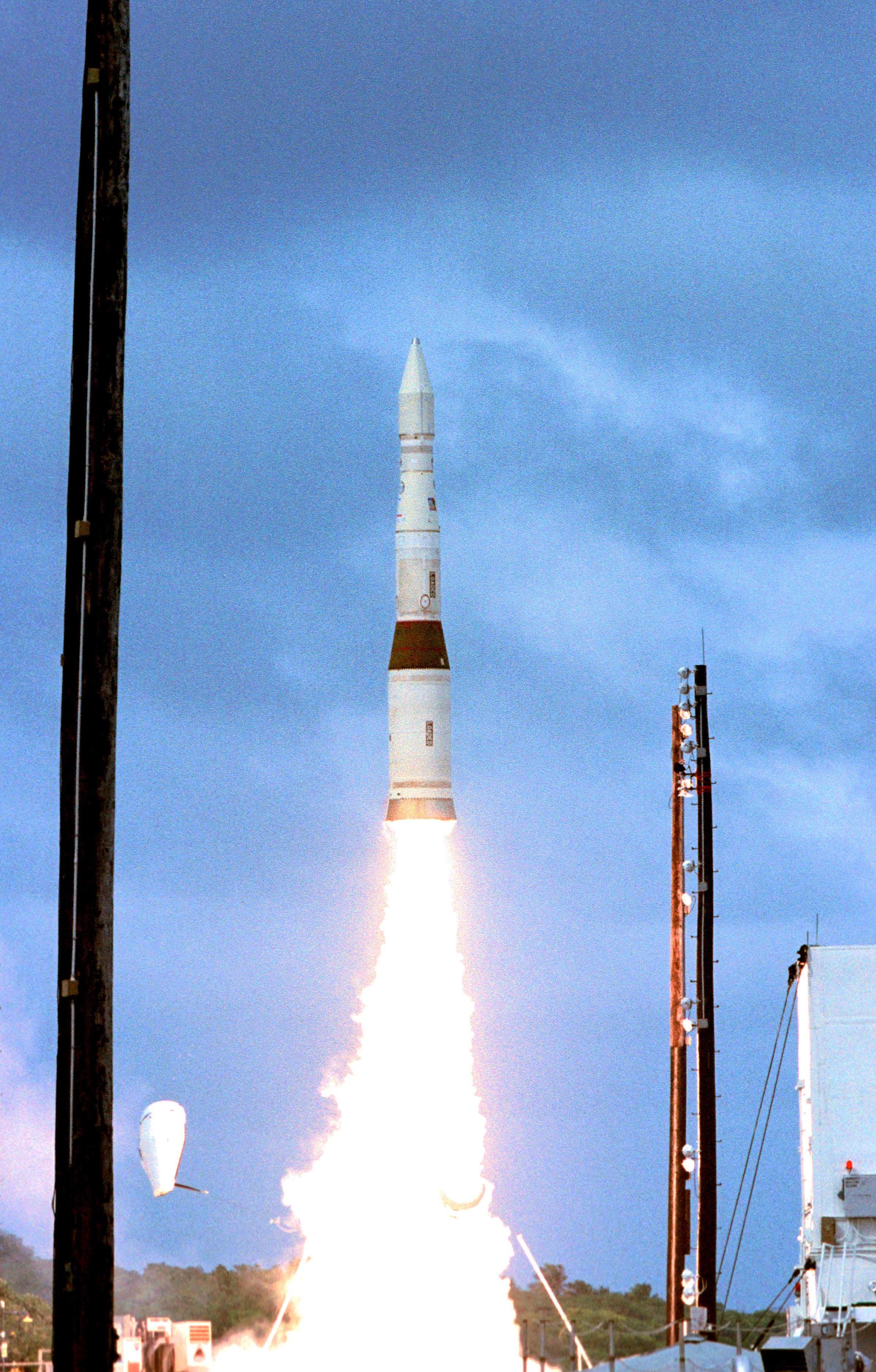
Safeguard Program
The Safeguard Program was a U.S. Army anti-ballistic missile (ABM) system designed to protect the U.S. Air Force's Minuteman ICBM silos from attack, thus preserving the US's nuclear deterrent fleet. It was intended primarily to protect against the very small Chinese ICBM fleet, limited Soviet attacks and various other limited-launch scenarios. A full-scale attack by the Soviets would easily overwhelm it. It was designed to allow gradual upgrades to provide similar lightweight coverage over the entire United States over time. Safeguard was the ultimate development of an ever-changing series of designs produced by Bell Labs that started in the 1950s with the LIM-49 Nike Zeus. By 1960 it was clear that Zeus offered almost no protection against a sophisticated attack using decoys. A new design emerged, Nike-X, with the ability to defend against attacks with hundreds of warheads and thousands of decoys, but the cost of the system was enormous. Looking for alternatives, the Sentinel pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Missile Defense
National missile defense (NMD) is a generic term for a type of missile defense intended to shield an entire country against incoming missiles, such as intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBMs) or other ballistic missiles. This is also used to refer to the American nationwide antimissile program the United States has had in development since the 1990s. After the renaming in 2002, the term now refers to the entire program, not just the ground-based interceptors and associated facilities. This article focuses mainly on this system and a brief history of earlier systems which led to it. Other elements that could potentially be integrated into NMD include anti-ballistic missiles, or sea-based, space-based, laser, and high altitude missile systems. The NMD program is limited in scope and designed to counter a relatively small ICBM attack from a less sophisticated adversary. Unlike the earlier Strategic Defense Initiative program, it is not designed to be a robust shield against a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sprint (missile)
The Sprint was a two-stage, solid-fuel anti-ballistic missile (ABM), armed with a W66 enhanced-radiation thermonuclear warhead used by the United States Army from 1975-1976. It was designed to intercept incoming reentry vehicles (RV) after they had descended below an altitude of about , where the thickening air stripped away any decoys or radar reflectors and exposed the RV to observation by radar. As the RV would be traveling at about , Sprint had to have phenomenal performance to achieve an interception in the few seconds before the RV reached its target. Sprint accelerated at 100 ''g'', reaching a speed of in 5 seconds. Such a high velocity at relatively low altitudes created skin temperatures up to , requiring an ablative shield to dissipate the heat. The high temperature caused a plasma to form around the missile, requiring extremely powerful radio signals to reach it for guidance. The missile glowed bright white as it flew. Sprint was the centerpiece of the Nike-X sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Nike
Project Nike (Greek: Νίκη, "Victory") was a U.S. Army project, proposed in May 1945 by Bell Laboratories, to develop a line-of-sight anti-aircraft missile system. The project delivered the United States' first operational anti-aircraft missile system, the Nike Ajax, in 1953. A great number of the technologies and rocket systems used for developing the Nike Ajax were re-used for a number of functions, many of which were given the "Nike" name (after Nike, the goddess of victory from Greek mythology). The missile's first-stage solid rocket booster became the basis for many types of rocket including the Nike Hercules missile and NASA's Nike Smoke rocket, used for upper-atmosphere research. History Project Nike began during 1944 when the War Department demanded a new air defense system to combat new jet aircraft, as existing gun-based systems proved largely incapable of dealing with the speeds and altitudes at which jet aircraft operated. Two proposals were accepted. Bell La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
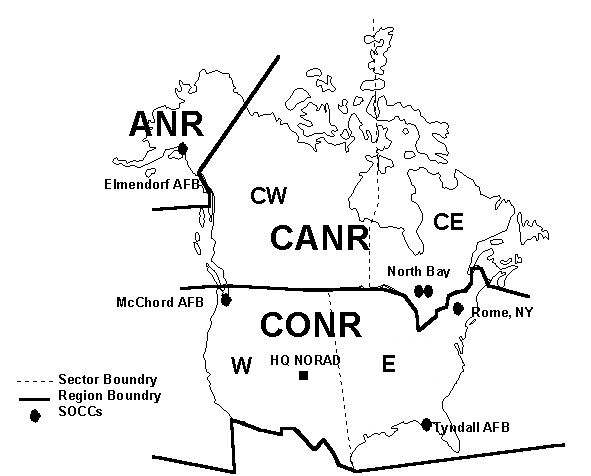
NORAD
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection for Canada and the continental United States. Headquarters for NORAD and the NORAD/United States Northern Command (USNORTHCOM) center are located at Peterson Space Force Base in El Paso County, near Colorado Springs, Colorado. The nearby Cheyenne Mountain Complex has the Alternate Command Center. The NORAD commander and deputy commander (CINCNORAD) are, respectively, a United States four-star general or equivalent and a Canadian lieutenant-general or equivalent. Organization CINCNORAD maintains the NORAD headquarters at Peterson Space Force Base near Colorado Springs, Colorado. The NORAD and USNORTHCOM Command Center at Peterson SFB serves as a central collection and coordination facility for a worldwide system of sensors designed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. Russia, the United States, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Early ICBMs had limited precision, which made them suitable for use only against the largest targets, such as cities. They were seen as a "safe" basing option, one that would keep the deterrent force close to home where it would be difficult to attack. Attacks against military targets (especially hardened ones) still demanded th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Blackmail
Nuclear blackmail is a form of nuclear strategy in which an aggressor uses the threat of use of nuclear weapons to force an adversary to perform some action or make some concessions. It is a type of extortion that is related to brinkmanship. Effectiveness Nuclear blackmail is usually ineffective against a rational opponent that has or is an ally of a power with assured destruction capability. If the opponent has nuclear weapons, nuclear blackmail becomes a threat of conflict escalation. In that situation if the opponent refuses to respond, one's choices are withdrawal of the threat of nuclear attack, incurring a major loss of prestige (both in domestic and international politics), or carrying out the threat resulting in mutual nuclear destruction. During the Cold War, the explicit threat of nuclear warfare to force an opponent to perform or not to perform an action was rare since most nations of any importance were allies of the Soviet Union or the United States. History In 1950, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Soviet Republics
The post-Soviet states, also known as the former Soviet Union (FSU), the former Soviet Republics and in Russia as the near abroad (russian: links=no, ближнее зарубежье, blizhneye zarubezhye), are the 15 sovereign states that were union republics of the Soviet Union, which emerged and re-emerged from the Soviet Union following its dissolution in 1991. Russia is the primary ''de facto'' internationally recognized successor state to the Soviet Union after the Cold War; while Ukraine has, by law, proclaimed that it is a state-successor of both the Ukrainian SSR and the Soviet Union which remained under dispute over formerly Soviet-owned properties. The three Baltic states – Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania – were the first to declare their independence from the USSR, between March and May 1990, claiming continuity from the original states that existed prior to their annexation by the Soviet Union in 1940. The remaining 12 republics all subsequently seceded, all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |