|
ABCB5
ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 5 also known as P-glycoprotein ABCB5 is a plasma membrane-spanning protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ABCB5'' gene. ABCB5 is an ABC transporter and P-glycoprotein family member principally expressed in physiological skin and human malignant melanoma. Clinical significance ABCB5 has been suggested to regulate skin progenitor cell fusion and mediate chemotherapeutic drug resistance in stem-like tumor cell subpopulations in human malignant melanoma, colorectal cancer, and malignant pleural mesothelioma. It is commonly over-expressed on circulating melanoma tumour cells. Furthermore, the ABCB5+ melanoma- initiating cells were demonstrated to express FLT1 (''VEGFR1'') receptor tyrosine kinase which was functionally required for efficient xenograft tumor formation, as demonstrated by shRNA knockdown experiments. In colorectal cancer, ABCB5 was shown to act as a mediator of 5-FU patient chemoresistance, and had a further direct role ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IL-1β
Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) also known as leukocytic pyrogen, leukocytic endogenous mediator, mononuclear cell factor, lymphocyte activating factor and other names, is a cytokine protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL1B'' gene."Catabolin" is the name given by Jeremy Saklatvala for IL-1 alpha. There are two genes for interleukin-1 (IL-1): IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta (this gene). IL-1β precursor is cleaved by cytosolic caspase 1 (interleukin 1 beta convertase) to form mature IL-1β. Function The fever-producing property of human leukocytic pyrogen (interleukin 1) was purified by Dinarello in 1977 with a specific activity of 10–20 nanograms/kg. In 1979, Dinarello reported that purified human leukocytic pyrogen was the same molecule that was described by Igal Gery in 1972. He named it lymphocyte-activating factor (LAF) because it was a lymphocyte mitogen. It was not until 1984 that interleukin 1 was discovered to consist of two distinct proteins, now called interleukin-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 8
Interleukin 8 (IL-8 or chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 8, CXCL8) is a chemokine produced by macrophages and other cell types such as epithelial cells, airway smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Endothelial cells store IL-8 in their storage vesicles, the Weibel-Palade bodies. In humans, the interleukin-8 protein is encoded by the ''CXCL8'' gene. IL-8 is initially produced as a precursor peptide of 99 amino acids which then undergoes cleavage to create several active IL-8 isoforms. In culture, a 72 amino acid peptide is the major form secreted by macrophages. There are many receptors on the surface membrane capable of binding IL-8; the most frequently studied types are the G protein-coupled serpentine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2. Expression and affinity for IL-8 differs between the two receptors (CXCR1 > CXCR2). Through a chain of biochemical reactions, IL-8 is secreted and is an important mediator of the immune reaction in the innate immune system response. Function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABC Transporter
The ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC transporters) are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene families. It is represented in all extant phyla, from prokaryotes to humans. ABC transporters belong to translocases. ABC transporters often consist of multiple subunits, one or two of which are transmembrane proteins and one or two of which are membrane-associated AAA ATPases. The ATPase subunits utilize the energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding and hydrolysis to provide the energy needed for the translocation of substrates across membranes, either for uptake or for export of the substrate. Most of the uptake systems also have an extracytoplasmic receptor, a solute binding protein. Some homologous ATPases function in non-transport-related processes such as translation of RNA and DNA repair. ABC transporters are considered to be an ABC superfamily based on the similarities of the sequence and organization of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is approximately 43 dioptres. The cornea can be reshaped by surgical procedures such as LASIK. While the cornea contributes most of the eye's focusing power, its focus is fixed. Accommodation (the refocusing of light to better view near objects) is accomplished by changing the geometry of the lens. Medical terms related to the cornea often start with the prefix "'' kerat-''" from the Greek word κέρας, ''horn''. Structure The cornea has unmyelinated nerve endings sensitive to touch, temperature and chemicals; a touch of the cornea causes an involuntary reflex to close the eyelid. Because transparency is of prime importance, the healthy cornea does not have or need blood vess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral and cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracrine
Paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to cell signaling by endocrine factors, hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system; juxtacrine interactions; and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain. Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body - even between different s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CXCR1
Interleukin 8 receptor, alpha is a chemokine receptor. This name and the corresponding gene symbol IL8RA have been replaced by the HGNC approved name C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 1 and the approved symbol CXCR1. It has also been designated as CD181 ( cluster of differentiation 181). The IUPHAR Committee on Receptor Nomenclature and Drug Classification use the HGNC recommended name, CXCR1. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the G-protein-coupled receptor family. This protein is a receptor for interleukin 8 (IL8). It binds to IL8 with high affinity, and transduces the signal through a G-protein-activated second messenger system. Knockout studies in mice suggested that this protein inhibits embryonic oligodendrocyte precursor migration in developing spinal cord. IL8RA, IL8RB, which encodes another high affinity IL8 receptor, and IL8RBP, a pseudogene of IL8RB, form a gene cluster in a region mapped to chromosome 2q33-q36. Stimulation of CXCR1 in neut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-FU
Fluorouracil (5-FU), sold under the brand name Adrucil among others, is a cytotoxic chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. By intravenous injection it is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, and cervical cancer. As a cream it is used for actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and skin warts. Side effects of use by injection are common. They may include inflammation of the mouth, loss of appetite, low blood cell counts, hair loss, and inflammation of the skin. When used as a cream, irritation at the site of application usually occurs. Use of either form in pregnancy may harm the baby. Fluorouracil is in the antimetabolite and pyrimidine analog families of medications. How it works is not entirely clear, but it is believed to involve blocking the action of thymidylate synthase and thus stopping the production of DNA. Fluorouracil was patented in 1956 and came into medical use in 1962. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
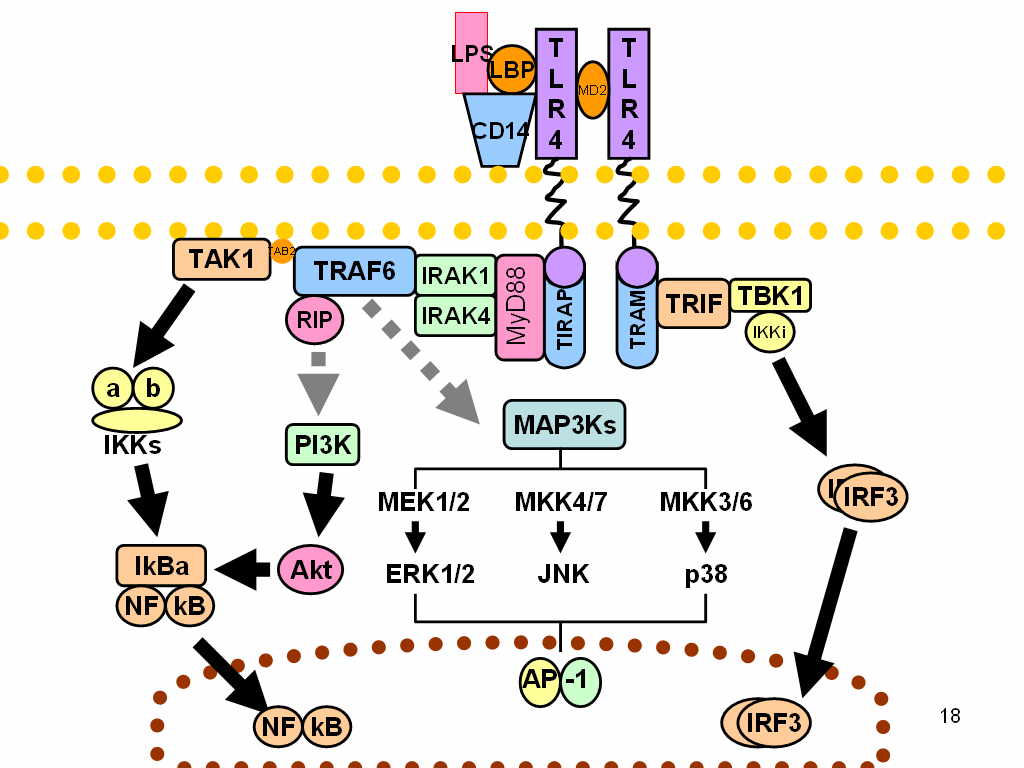
TLR4
Toll-like receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR4'' gene. TLR4 is a transmembrane protein, member of the toll-like receptor family, which belongs to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family. Its activation leads to an intracellular signaling pathway NF-κB and inflammatory cytokine production which is responsible for activating the innate immune system. TLR4 expressing cells are myeloid (erythrocytes, granulocytes, macrophages) rather than lymphoid (T-cells, B-cells, NK cells). Most myeloid cells also express high levels of CD14, which facilitates activation of TLR4 by LPS. It is most well known for recognizing lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a component present in many Gram-negative bacteria (e.g. ''Neisseria'' spp.) and selected Gram-positive bacteria. Its ligands also include several viral proteins, polysaccharide, and a variety of endogenous proteins such as low-density lipoprotein, beta-defensins, and heat shock protein. Palmitic acid and lauric aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ShRNA
A short hairpin RNA or small hairpin RNA (shRNA/Hairpin Vector) is an artificial RNA molecule with a tight hairpin turn that can be used to silence target gene expression via RNA interference (RNAi). Expression of shRNA in cells is typically accomplished by delivery of plasmids or through viral or bacterial vectors. shRNA is an advantageous mediator of RNAi in that it has a relatively low rate of degradation and turnover. However, it requires use of an expression vector, which has the potential to cause side effects in medicinal applications. The promoter choice is essential to achieve robust shRNA expression. At first, polymerase III promoters such as U6 and H1 were used; however, these promoters lack spatial and temporal control. As such, there has been a shift to using polymerase II promoters, which are inducible, to regulate shRNA expression. Delivery Expression of shRNA in cells can be obtained by delivery of plasmids or through viral or bacterial vectors. Delivery of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |