|
ABB ALP-44
The ABB ALP-44 was an electric locomotive which was built by Asea Brown Boveri of Sweden between 1989 and 1997 for the NJ Transit Rail Operations, New Jersey Transit and SEPTA Regional Rail, SEPTA railway lines. Service New Jersey Transit New Jersey Transit acquired 32 ALP-44s for use on its electric railway lines. The first fifteen, numbered 4400–4414 and designated ALP-44O (Original), were delivered in 1990 (prototypes 4400 and 4401 in late 1989). Five additional units, numbered 4415–4419 and designated ALP-44E (Extended), were delivered in 1995. The final 12 locomotives, numbered 4420–4431 and designated ALP-44M (Microprocessor), were delivered in 1996 for the new Midtown Direct service. NJT's ALP-44s were to be overhauled for a cost of $2 million during a two-year period by Philadelphia-based Interfleet Technology. A car builder had not yet been selected to carry out the overhaul. However, by June 2009, NJT decided that it would be more efficient (economically and phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AAR Wheel Arrangement
The AAR wheel arrangement system is a method of classifying locomotive (or unit) wheel arrangements that was developed by the Association of American Railroads. Essentially a simplification of the European UIC classification, it is widely used in North America to describe Diesel locomotive, diesel and electric locomotives (including third-rail electric locomotives). It is not used for steam locomotives, which use the Whyte notation instead. The AAR system counts axles instead of wheels. Letters refer to powered axles, and numbers to unpowered (or idler) axles. "A" refers to one powered axle, "B" to two powered axles in a row, "C" to three powered axles in a row, and "D" to four powered axles in a row. "1" refers to one idler axle, and "2" to two idler axles in a row. A dash ("–") separates Bogie, trucks or wheel assemblies. A plus sign ("+") refers to articulation, either by connecting bogies with span bolsters or by connecting individual locomotives via solid drawbars instead of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interfleet Technology
SNC-Lavalin Rail & Transit (Interfleet Technology until 2015) is an international rail consultancy company headquartered in Derby, England. It was founded in 1994. In October 2011 the company was acquired by SNC-Lavalin. In January 2016 the company was renamed when it became integrated under the main SNC-Lavalin brand. History Formation and early years Interfleet Technology was formed in April 1994, as part of the privatisation of British Rail. Interfleet originated from the former InterCity Fleet Engineering division of the British Rail engineering and technical headquarters, which managed the rolling stock operated by the then InterCity sector of British Rail. From April 1994 to March 1996, the company traded as a subsidiary of the British Railways Board, then in March 1996, Interfleet was privatised by means of a Management and Employee Buy-Out, led by its directors. At the time of privatisation, the firm employed 99 staff and had one office in Derby. Turnover at that time w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11 KV AC Locomotives
Eleven or 11 may refer to: *11 (number), the natural number following 10 and preceding 12 * one of the years 11 BC, AD 11, 1911, 2011, or any year ending in 11 Literature * ''Eleven'' (novel), a 2006 novel by British author David Llewellyn *''Eleven'', a 1970 collection of short stories by Patricia Highsmith *''Eleven'', a 2004 children's novel in The Winnie Years by Lauren Myracle *''Eleven'', a 2008 children's novel by Patricia Reilly Giff *''Eleven'', a short story by Sandra Cisneros Music *Eleven (band), an American rock band * Eleven: A Music Company, an Australian record label *Up to eleven, an idiom from popular culture, coined in the movie ''This Is Spinal Tap'' Albums * ''11'' (The Smithereens album), 1989 * ''11'' (Ua album), 1996 * ''11'' (Bryan Adams album), 2008 * ''11'' (Sault album), 2022 * ''Eleven'' (Harry Connick, Jr. album), 1992 * ''Eleven'' (22-Pistepirkko album), 1998 * ''Eleven'' (Sugarcult album), 1999 * ''Eleven'' (B'z album), 2000 * ''Eleven'' (Reamonn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Lines
An overhead line or overhead wire is an electrical cable that is used to transmit electrical energy to electric locomotives, trolleybuses or trams. It is known variously as: * Overhead catenary * Overhead contact system (OCS) * Overhead equipment (OHE) * Overhead line equipment (OLE or OHLE) * Overhead lines (OHL) * Overhead wiring (OHW) * Traction wire * Trolley wire This article follows the International Union of Railways in using the generic term ''overhead line''. An overhead line consists of one or more wires (or rails, particularly in tunnels) situated over rail tracks, raised to a high electrical potential by connection to feeder stations at regular intervals. The feeder stations are usually fed from a high-voltage electrical grid. Overview Electric trains that collect their current from overhead lines use a device such as a pantograph, bow collector or trolley pole. It presses against the underside of the lowest overhead wire, the contact wire. Current collectors are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MARC Train
MARC (Maryland Area Rail Commuter) is a commuter rail system in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. MARC is administered by the Maryland Transit Administration (MTA) and operated under contract by Alstom and Amtrak on track owned by CSX Transportation (CSXT) and Amtrak. In , the system had a ridership of , or about per weekday as of , much less then the pre-pandemic daily ridership of 40,000 per weekday. With trains reaching speeds of , MARC has the highest top speed of any commuter railroad in the United States. Operations MARC has three lines that radiate from Washington Union Station, Union Station in Washington, D.C.: the Brunswick Line (18 weekday trains), the Camden Line (21 weekday trains), and the Penn Line (58 weekday trains). The Penn Line is the only line with weekend service, having 18 trains on Saturdays and 12 on Sundays. Service is reduced or suspended on certain Federal holidays. All MARC trains operate in Push-pull train, push-pull mode. The contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Train Control
Positive train control (PTC) is a family of automatic train protection systems deployed in the United States. Most of the United States' national rail network mileage has a form of PTC. These systems are generally designed to check that trains are moving safely and to stop them when they are not. A simplistic form of train traffic governance is ''negative'' train control, where trains must stop when issued a stop order and can move in the absence of such. An example of negative train control is Indusi. In contrast, ''positive'' train control restricts the train movement to an explicit allowance; movement is halted upon invalidation. A train operating under PTC receives a ''movement authority'' containing information about its location and where it is allowed to safely travel. As of 2019, the U.S. freight rail industry trade organization AAR claimed that the nation's largest freight railroads were operating PTC across 83.2 percent of the required route miles. The American Railwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens ACS-64
The Siemens ACS-64, or Amtrak Cities Sprinter, is an electric locomotive designed by Siemens Mobility for use on the Northeast Corridor (NEC) and the Keystone Corridor in the northeastern United States. The design was based on locomotives Siemens created for use in Europe and Asia, but with changes to comply with American standards. The ACS-64 is built at the Siemens factory in Florin, California, located outside of Sacramento. The first 70 locomotives were built for Amtrak to replace the railroad's fleet of aging AEM-7 and unreliable HHP-8 locomotives. The first ACS-64 entered service in February 2014 and deliveries continued until August 2016. SEPTA Regional Rail in Southeastern Pennsylvania operates a fleet of 15 ACS-64s since August 2018, on the agency's commuter rail routes. Design The design is based on the EuroSprinter and the Vectron platforms, which Siemens sells in Europe and Asia. Significant structural changes to the design were made to comply with American cras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norristown High Speed Line
The Norristown High Speed Line (NHSL), also called the Purple Line, the P&W, or Route 100,) is a interurban light rapid transit line operated by SEPTA, running between the 69th Street Transportation Center in Upper Darby and the Norristown Transportation Center in Norristown, Pennsylvania. Originally the Philadelphia and Western Railroad line, which is why the line is referred to by locals as "the P&W), the line runs entirely on its own right-of-way. By 2020, the Norristown Line had an average weekday ridership approaching 11,000 passengers. The Norristown High Speed Line is unique in its combination of transportation technologies. Originally chartered as a Class I (steam) railroad, the line is fully grade separated, collects power from a third rail, and has high-level platforms common to rapid transit systems or commuter rail systems such as New York City's Long Island Rail Road and Metro-North Railroad, but has onboard fare collection, mostly single-car operation, and frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
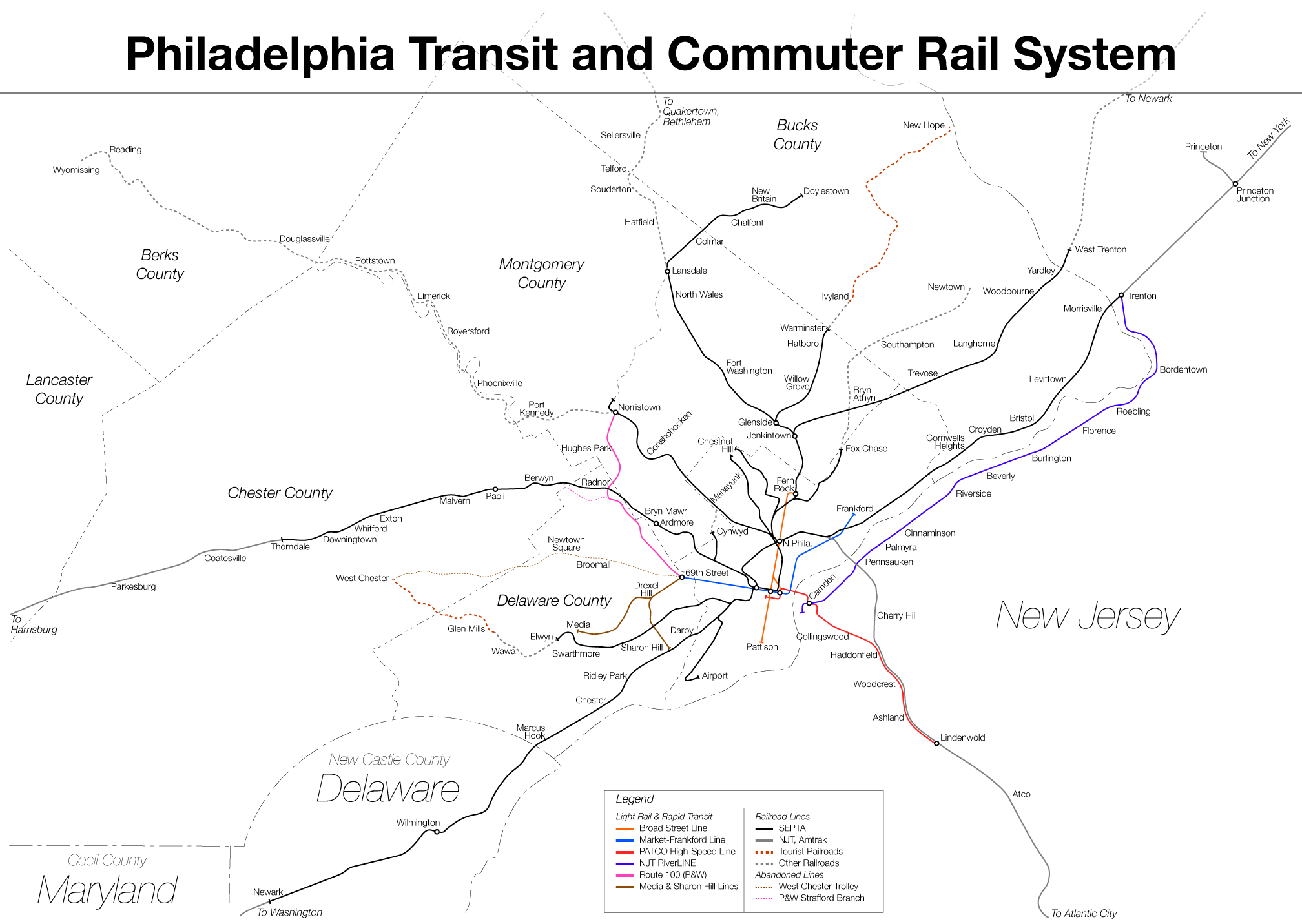
SEPTA
The Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) is a regional public transportation authority that operates bus, rapid transit, commuter rail, light rail, and electric trolleybus services for nearly 4 million people in five counties in and around Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It also manages projects that maintain, replace and expand its infrastructure, facilities and vehicles. SEPTA is the major transit provider for Philadelphia and the counties of Delaware, Montgomery, Bucks, and Chester. It is a state-created authority, with the majority of its board appointed by the five Pennsylvania counties it serves. While several SEPTA commuter rail lines terminate in the nearby states of Delaware and New Jersey, additional service to Philadelphia from those states is provided by other agencies: the PATCO Speedline from Camden County, New Jersey is run by the Delaware River Port Authority, a bi-state agency; NJ Transit operates many bus lines and a commuter rail line to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanhope, New Jersey
Stanhope is a borough in Sussex County, New Jersey, United States. As of the 2010 United States Census, the borough's population was 3,610,DP-1 - Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 for Stanhope borough, Sussex County, New Jersey , . Accessed September 16, 2012. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.png)