|
9th Space Division
The 9th Space Division (9th SD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Force Space Command, being stationed at Patrick Air Force Base, Florida. It was inactivated on 1 October 1991. History Tactical Air Command The organization has had several periods of activation over its lifetime. Initially established in April 1949 as the 9th Air Division (Tactical) under Fourteenth Air Force, Continental Air Command at Pope Air Force Base, North Carolina, the command had no units assigned but was to act as a headquarters over tactical units. It was inactivated in August 1950. Air defense It was redesignated 9th Air Division (Defense) and reactivated in October 1954 by Air Defense Command (ADC) and assigned to Western Air Defense Force (WADF) at Geiger Field, Washington, taking over control of air defense units in eastern Washington, Oregon and Idaho from the 25th Air Division (AD), after the 25th AD was realigned over the Washington and Oregon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Force Space Command
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation). By mole fraction (i.e., by number of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air composition, temperature, and atmospheric pressure vary with altitude. Within the atmosphere, air suitable for use in photosynthesis by terrestrial plants and breathing of terrestrial animals is found only in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spokane Air Defense Sector
The Spokane Air Defense Sector (SPADS) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with the Air Defense Command 25th Air Division (25th AD) at Larson Air Force Base in Grant County, Washington History SAGE Air Defense Sector SPADS was established in September 1958, assuming responsibility for air defense in Eastern Washington, North Idaho, and Western Montana. The organization eventually also provided command and control over several interceptor aircraft and radar squadrons. On 8 September the new Semi Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) Direction Center (DC-15) became operational. DC-15 was equipped with dual AN/FSQ-7 Computers. The day-to-day operations of the command was to train and maintain tactical flying units flying jet interceptor aircraft (F-94 Starfire; F-102 Delta Dagger; F-106 Delta Dart) in a state of readiness with training missions and series of exercises with SAC and other units simulating interceptions of incoming enemy air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomasville Air Force Station
Thomasville Air Force Station (ADC ID: TM-197, NORAD ID: Z-197) is a closed United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station. It is located north-northwest of Thomasville, Alabama. It was closed in 1969. History Thomasville Air Force Station came into existence as part of Phase III of the Air Defense Command Mobile Radar program. On October 20, 1953 ADC requested a third phase of twenty-five radar sites be constructed. The 698th Aircraft Control and Warning Squadron moved to Thomasville on 1 September 1958 when a test model of the AN/FPS-35 radar was installed for evaluation. It was the first of the large radars to be deployed, and initially the station functioned as a Ground-Control Intercept (GCI) and warning station. As a GCI station, the squadron's role was to guide interceptor aircraft toward unidentified intruders picked up on the unit's radar scopes. Two AN/FPS-90 height-finder radars were added in the early 1960s. The Ground Air Transmitting Receivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AN/FPS-35
The AN/FPS-35 frequency diversity radar was a long range search radar used in the early 1960s. It was one of the largest air defense radars ever produced, with its antenna and supporting structure mounted on one of the largest rolling-element bearings in the world (with a ball pitch of 12 ft 7 inches in diameter.). Overview Sperry Corporation built 12 long range radars (picking up objects 200 miles away) in the 1960s to succeed existing Semi Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) to provide enhanced electronic countermeasures (ECM). The systems operated at 420 to 450 MHz. The antennas weighed and had numerous problems. The concrete tower bases were high and square in side dimensions. The prototype was developed at the Thomasville Aircraft Control and Warning Station in Thomasville, Alabama. The enclosed radar towers that supported all 12 of the FPS-35 antennas were prominent landmarks. All these radar towers were of the same basic design with 10 made primarily from concr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laredo Air Force Base
Laredo Air Force Base, is a since-deactivated Undergraduate Pilot Training (UPT) installation of the Air Training Command (ATC) in Laredo, Texas. The facility was originally established as Laredo Army Air Field, a World War II U.S. Army Air Force facility that began operations in November 1942, primarily as an aerial gunnery school with an associated gunnery range. The field became inactive in late 1945 and the property reverted to the city of Laredo, which used it as a municipal airport until 1950. That year, the base was reactivated and renamed Laredo Air Force Base in April 1952 to provide intermediate and advanced flight training for jet pilots, including pilot trainees from 24 countries. In the early 1960s, the Air Training Command transitioned to the Undergraduate Pilot Training (UPT) concept, where student pilots would take all flight training from basic through advanced at a single base. The initial host unit stationed at Laredo AFB was the 3640th Pilot Training Wing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moorestown, New Jersey
Moorestown is a Township (New Jersey), township in Burlington County, New Jersey, Burlington County in the U.S. state of New Jersey. It is an eastern suburb of Philadelphia and geographically part of the South Jersey region of the state. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, the township's population was 21,355, an increase of 629 (+3.0%) from the 2010 United States census, 2010 census count of 20,726, which reflected an increase of 1,709 (+9.0%) from the 19,017 counted in the 2000 United States census, 2000 census. Moorestown was authorized to be incorporated as a township by an act of the New Jersey Legislature on March 11, 1922, from portions of Chester Township (now Maple Shade Township, New Jersey, Maple Shade Township), subject to the approval of voters in the affected area in a referendum. Voters approved the creation on April 25, 1922.Snyder, John P''The Story of New Jersey's Civil Boundaries: 1606-1968'' Bureau of Geology and Topography; Trenton, New J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AN/FPS-49
The RCA 474L Ballistic Missile Early Warning System (BMEWS, "474L System", Project 474L) was a United States Air Force Cold War early warning radar, computer, and communications system, for ballistic missile detection. The network of twelve radars, which was constructed beginning in 1958 and became operational in 1961, was built to detect a "mass ballistic missile attack launched on northern approaches or15 to 25 minutes' warning time" also provided Project Space Track satellite data (e.g., about one-quarter of SPADATS observations). Background The Ballistic Missile Early Warning System (BMEWS) was a radar system built by the United States (with the cooperation of Canada and Denmark on whose territory some of the radars were sited) during the Cold War to give early warning of a Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) nuclear strike, to allow time for US bombers to get off the ground and land-based US ICBMs to be launched, to reduce the chances that a preemptive strik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis, also known as the October Crisis (of 1962) ( es, Crisis de Octubre) in Cuba, the Caribbean Crisis () in Russia, or the Missile Scare, was a 35-day (16 October – 20 November 1962) confrontation between the United States and the Soviet Union, which escalated into an international crisis when American deployments of missiles in Italy and Turkey were matched by Soviet deployments of similar ballistic missiles in Cuba. Despite the short time frame, the Cuban Missile Crisis remains a defining moment in national security and nuclear war preparation. The confrontation is often considered the closest the Cold War came to escalating into a full-scale nuclear war. In response to the presence of American Jupiter ballistic missiles in Italy and Turkey, the failed Bay of Pigs Invasion of 1961, and Soviet fears of a Cuban drift towards China, Soviet First Secretary Nikita Khrushchev agreed to Cuba's request to place nuclear missiles on the island to deter a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
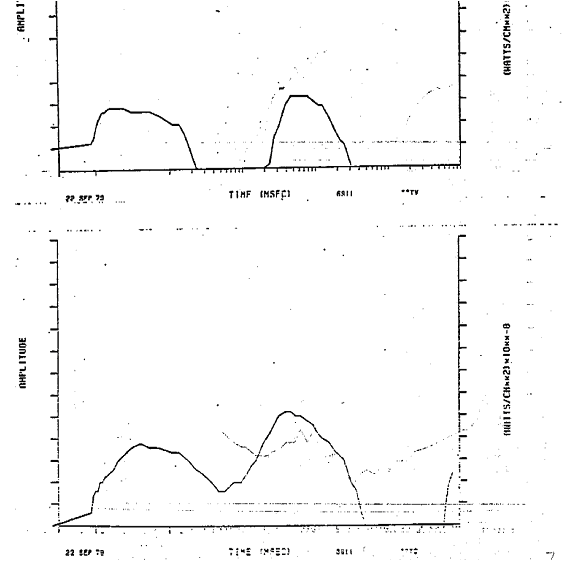
Bhangmeter
A bhangmeter is a non-imaging radiometer installed on reconnaissance and navigation satellites to detect atmospheric nuclear detonations and determine the yield of the nuclear weapon. They are also installed on some armored fighting vehicles, in particular NBC reconnaissance vehicles, in order to help detect, localise and analyse tactical nuclear detonations. They are often used alongside pressure and sound sensors in this role in addition to standard radiation sensors. Some nuclear bunkers and military facilities may also be equipped with such sensors alongside seismic event detectors. The bhangmeter was developed at Los Alamos National Laboratory by a team led by Herman Hoerlin. History The bhangmeter was invented, and the first proof-of-concept device was built, in 1948 to measure the nuclear test detonations of Operation Sandstone. Prototype and production instruments were later built by EG&G, and the name "bhangmeter" was coined in 1950 by Frederick Reines. Bhangmeters b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomb Alarm System
The Bomb Alarm System (also known as the Bomb Alarm Display System) was a US and UK network of optical bhangmeter sensors intended to confirm the detonation of an enemy nuclear weapon near cities or military installations within the US or at US operated early warning radar sites in the UK DEW Line, or Greenland. The BAS was designed by Western Union in 1959 and was in full operation by 1962. The BAS was the responsibility of the 9th Space Division. The BAS operated until 1967. The BAS sensors were designed to report the occurrence of a nuclear flash via telephone or telegraph lines before the sensor was destroyed by the explosion. They were designed to ignore spurious signals from lightning, sunlight, or electrical surges. See also * Strategic Air Command * Pinetree Line contemporary early warning RADAR. * National Emergency Alarm Repeater contemporary device. References Telecommunications equipment of the Cold War Western Union {{mil-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Detection And Tracking System
Space Detection and Tracking System, or SPADATS, was built in 1960 to integrate defense systems built by different branches of the United States Armed Forces and was placed under North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD). The Air Force had a program called Spacetrack, which was a network of space-probing cameras and radar. The Navy had a system called SPASUR, a space surveillance system that was "an electronic fence" the protected the southern United States. SPADATS was developed by the SpaceTrack Research and Development Facility, also called the 496L System Program Office, at Hanscom Field in Bedford, Massachusetts. ( Bendix, Sperry Rand and Hughes competed for SPADATS contract in the early 1962 on the basis of their prior experience in phased array technology.) It first operated at the Electronic Systems Command building at Hanscom and in 1963 was transferred to the Ent Air Force Base and then to the Cheyenne Mountain Complex in 1965 or 1966. From that point, the SpaceTrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |