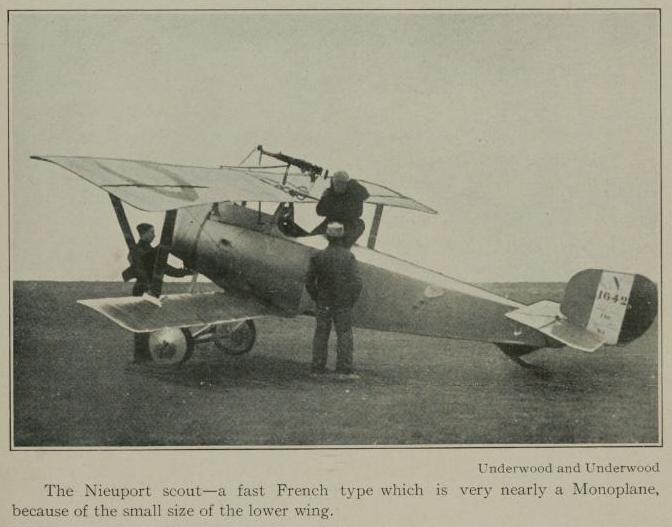
|
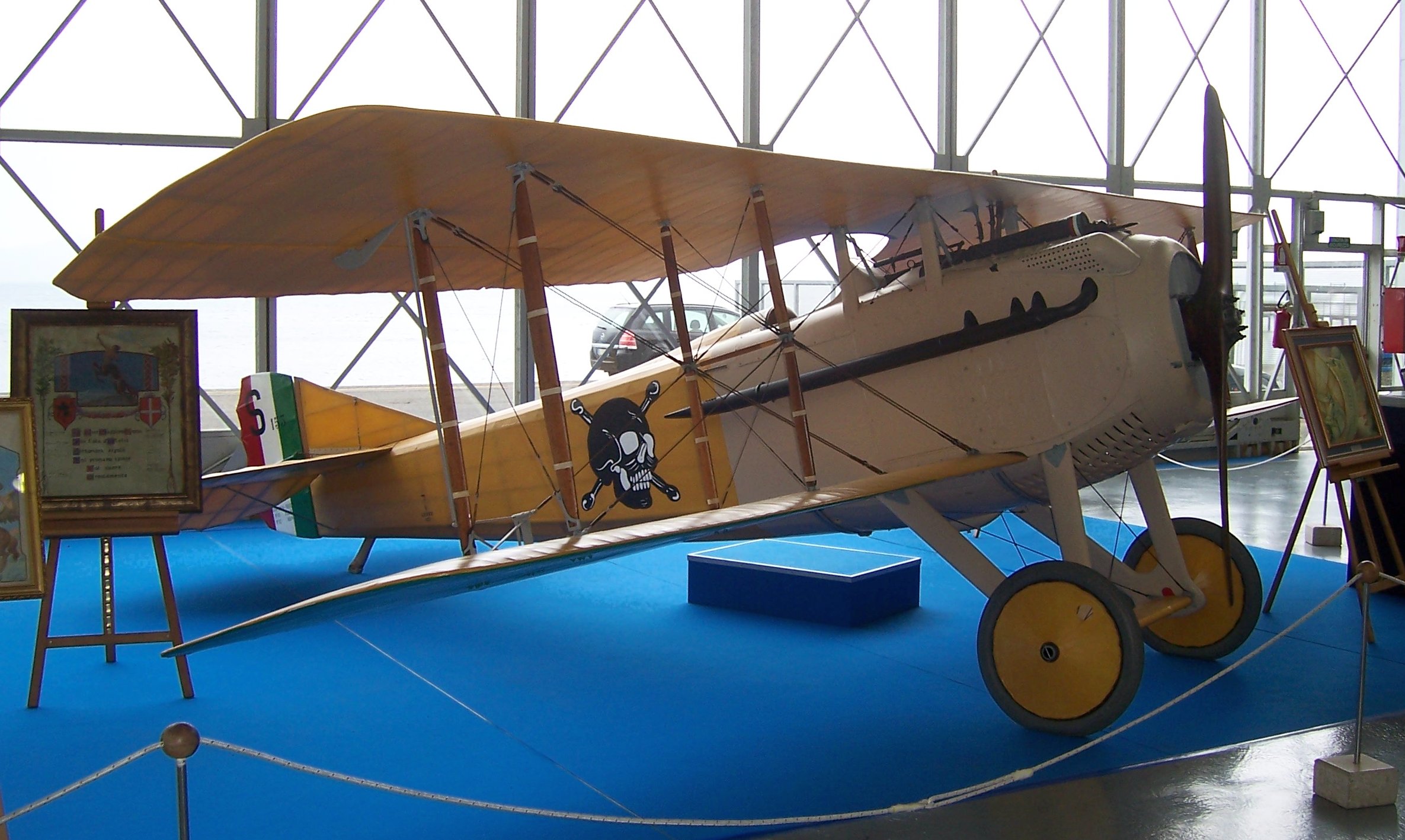
91a Squadriglia
''Squadriglia 91a'' was one of the later fighter squadrons that the Italian Army created, on 1 May 1917. Because it drew an experienced cadre of pilots from pre-existing ''70a Squadriglia'', the squadron scored 14 victories within its first month of flying combat. As a result, it became known as "the squadron of aces". The new unit was immediately drawn into the ongoing Battles of the Isonzo in northern Italy. In September 1917, the squadron would serve as test pilots of the universally condemned SIA 7 multipurpose aircraft. The squadron fought in the disastrous Battle of Caporetto in late 1917 and suffered through the subsequent retreat. On 11 April 1918, it returned to combat at Quinto di Treviso, with an added task of flying ground support missions. After Italy's top ace, Francesco Baracca was killed on such a mission, King Victor Emmanuel III renamed the squadron to honor the fallen ace. ''91a Squadriglia'' would end the war credited with 60 aerial victories for a cost of six k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regia Aeronautica
The Italian Royal Air Force (''Regia Aeronautica Italiana'') was the name of the air force of the Kingdom of Italy. It was established as a service independent of the Royal Italian Army from 1923 until 1946. In 1946, the monarchy was abolished and the Kingdom of Italy became the Italian Republic, whereupon the name of the air force changed to Aeronautica Militare. History Beginnings At the beginning of the twentieth century, Italy was at the forefront of aerial warfare: during the colonization of Libya in 1911, it made the first reconnaissance flight in history on 23 October, and the first ever bombing raid on 1 November. During World War I, the Italian ''Corpo Aeronautico Militare'', then still part of the ''Regio Esercito'' (Royal Army), operated a mix of French fighters and locally built bombers, notably the gigantic Caproni aircraft. The ''Regia Marina'' (Royal Navy) had its own air arm, operating locally built flying boats. Founding of the ''Regia Aeronautica'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulco Ruffo Di Calabria
Fulco VIII, Prince Ruffo di Calabria, 6th Duke of Guardia Lombarda (12 August 1884 – 23 August 1946) was an Italian World War I flying ace and senator of the Kingdom from 1934 until his death. He was the father of Paola, Queen of the Belgians (born Donna Paola Ruffo di Calabria). Family history Ademarus Rufus, who died in 1049, held the title of ''Comes'' in southern Italy. Siggerio Ruffo became Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II's grand marshal of the Kingdom of Sicily in 1235. After the 14th century, the family divided into two branches Ruffo di Scaletta and the Ruffo di Calabria, the latter to which Fulco belonged.Genealogisches Handbuch des Adels, Fürstliche Häuser XVI. "Ruffo". C.A. Starke Verlag, 2001, pp.522-529. . Fulco was the son of Fulco VII Beniamino Tristano Ruffo di Calabria, 5th Duke of Guardia Lombarda (1848–1901), and Laura Mosselman du Chenoy, a Belgian aristocrat, whose maternal grandfather was Count Jacques André Coghen, Belgium's second finance mini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Sabelli
Tenente Giovanni Sabelli was an Italian World War I flying ace credited with five aerial victories. At the start of World War I, he was already an experienced combat pilot. Early life On 23 September 1886 in Napoli,Franks 2000, p. 159. Sabelli was born into a wealthy family. He studied engineering in New York. Sabelli was a pilot even before World War I, having learned to fly at Brooklands, England in 1912. He was awarded his pilot's certificate by the Royal Aero Club on 30 January 1912. During the First Balkan War, he volunteered to fly combat for the Bulgarians against the Turks.Varriale 2009, pp. 92-93. Indeed, he was reputed to be one of the organizers of the air effort versus the Ottoman Empire. Flying career Sabelli volunteered for military service when Italy finally entered World War I. He was a reserve sotto-tenente in the Engineering Corps. Although already a licensed pilot and a combat veteran, he had to pass new flying examinations to fly for his country; he passed bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giorgio Pessi
Tenente Giorgio Pessi (alias Giuliano Parvis) was a World War I flying ace born in Austria-Hungary who chose to fly for Italy. He was credited with six aerial victories. Early life and service Giorgio Pessi was born on 17 November 1891 in Trieste, when it was part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. He attended the local technical high school before studying engineering in Vienna and architecture in Munich. After World War I began, he fled to Venice in January 1915. When Italy finally entered World War I, Pessi volunteered to serve as a Sottotenente in the 2nd Cavalry Regiment of the Italian army.Franks et al 1997, pp. 150-151. World War I aerial service Pessi transferred to aviation service. On 10 October 1916, he received his advanced pilot's license, having qualified on Nieuport 10s at Malpensa. He was retained there as an instructor until May 1917. On 3 May 1917, Pessi adopted the ''nom de guerre'' of Giuliano Parvis; he wanted to avoid repercussions from the vengeful Austro-Hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastone Novelli
Tenente Gastone Novelli was a World War I flying ace credited with eight aerial victories. Biography Gastone Novelli was born on 13 June 1895 in Ancona, Kingdom of Italy. He was the son of an Italian Army General. The young Novelli attended military schools–first the ''Collegio Militare'' in Rome, then the ''Scuola Militare'' in Modena. After graduation, he was commissioned as a '' Sottotenente'' in the 8th "Montebello" Lancers Regiment during February 1915. He then had a brief assignment as a reconnaissance scout for the 43rd Artillery Regiment. This led to his flying as an aerial observer for ''28a Squadriglia'' by August 1915.Franks et al 1997, p. 148. After application for pilot's training, Novelli was granted a pilot's license for the Caudron G.3 during April 1916. He qualified on Farmans three months later, at Busto Arsizio. He was posted to a reconnaissance squadron, ''30a Squadriglia'', and flew combat for them from 12 August 1916 until 20 January 1917. He earned a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pier Ruggero Piccio
Lieutenant General Count Pier Ruggero Piccio (27 September 1880 – 30 July 1965) was an Italian aviator and the founding Chief of Staff of the Italian Air Force. With 24 victories during his career, he is one of the principal Italian air aces of World War I, behind only Count Francesco Baracca and Tenente Silvio Scaroni. Piccio rose to the rank of Lieutenant General and in later years, became a Roman senator under the Fascists before and during World War II. Early life Pier Ruggero Piccio was born in Rome on 27 September 1880,Franks et al 1997, pp. 151-152. to Giacomo Piccio and Caterina Locatelli.Italian senate's website page on Picci(In Italian, translated by Microsoft) Retrieved 11 May 2013. He attended the Military Academy of Modena, enrolling on October 29, 1898. He graduated on September 8, 1900, as a sottotenente (second lieutenant)Variale 2009, pp. 75-78. assigned to the 43rd Infantry Regiment. In 1903, stultified by garrison duty, he had himself seconded to the Minis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padua
Padua ( ; it, Padova ; vec, Pàdova) is a city and ''comune'' in Veneto, northern Italy. Padua is on the river Bacchiglione, west of Venice. It is the capital of the province of Padua. It is also the economic and communications hub of the area. Padua's population is 214,000 (). The city is sometimes included, with Venice (Italian ''Venezia'') and Treviso, in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE) which has a population of around 2,600,000. Padua stands on the Bacchiglione, Bacchiglione River, west of Venice and southeast of Vicenza. The Brenta River, which once ran through the city, still touches the northern districts. Its agricultural setting is the Venetian Plain (''Pianura Veneta''). To the city's south west lies the Colli Euganei, Euganaean Hills, praised by Lucan and Martial, Petrarch, Ugo Foscolo, and Percy Bysshe Shelley, Shelley. Padua appears twice in the UNESCO World Heritage List: for its Botanical Garden of Padua, Botanical Garden, the most anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcade, Italy
Arcade is a comune in the province of Treviso, Veneto, northern Italy. Twin towns * Bernières-sur-Mer Bernières-sur-Mer (, literally ''Bernières on Sea''), in the arrondissement of Caen, is a commune in the Calvados department of Normandy, in northwestern France. It is part of the canton of Courseulles-sur-Mer. It lies on the English Channe ..., France, since 2011 References Cities and towns in Veneto {{Veneto-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartolomeo Costantini
Bartolomeo "Meo" Costantini (14 February 1889 in Vittorio Veneto – 19 July 1941 in Milan) was an Italian aviator and racing car driver, known for being the sporting manager of the Bugatti car manufacturer. Military service He joined the Italo-Turkish War (1911), and later became well known in World War I, where ''capitano'' Costantini became a flying ace with six victories flying a Spad in the ''Squadriglia degli Assi'', part of the Corpo Aeronautico Militare. Costantini used a Spad VII to score his first aerial victory in conjunction with Prince Fulco Ruffo di Calabria, on 25 October 1917. The next day, Costantini shot down another Aviatik reconnaissance plane over Castelmonte. A month later, on 23 November, he shared his third victory over a two-seater with Cesare Magistrini. A week later, he had another shared win. He did not score again for nine months. In August 1918, he acquired a newer Spad XIII that he used to round off his career. On the 12th, he singlehandedly defeat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators, major is one rank above captain, and one rank below lieutenant colonel. It is considered the most junior of the field officer ranks. Background Majors are typically assigned as specialised executive or operations officers for battalion-sized units of 300 to 1,200 soldiers while in some nations, like Germany, majors are often in command of a company. When used in hyphenated or combined fashion, the term can also imply seniority at other levels of rank, including ''general-major'' or ''major general'', denoting a low-level general officer, and ''sergeant major'', denoting the most senior non-commissioned officer (NCO) of a military unit. The term ''major'' can also be used with a hyphen to denote the leader of a military band such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sortie
A sortie (from the French word meaning ''exit'' or from Latin root ''surgere'' meaning to "rise up") is a deployment or dispatch of one military unit, be it an aircraft, ship, or troops, from a strongpoint. The term originated in siege warfare. In aviation In military aviation, a sortie is a combat mission of an individual aircraft, starting when the aircraft takes off. For example, one mission involving six aircraft would tally six sorties. The sortie rate is the number of sorties that a given unit can support in a given time. In siege warfare In siege warfare, the word ''sortie'' refers specifically to a sudden issuing of troops against the enemy from a defensive position—that is, an attack launched against the besiegers by the defenders. If the sortie is through a sally port, the verb ''to sally'' may be used interchangeably with ''to sortie''. Purposes of sorties include harassment of enemy troops, destruction of siege weaponry and engineering works, joining the relief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |