|
85th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 85th Infantry Division (German: ''85. Infantrie-division'') was a Wehrmacht division used in the Second World War. It participated in the German defence in the Battle of Normandy, and took part in the German counter-offensive in the Ardennes. Operational history The 85th Infantry Division was raised in February 1944 and placed under the command of Lieutenant General Kurt Chill, previously the commanding officer of the 122nd Infantry. Participating as an occupational division in German-occupied France, the 85th was part of the 15th Army's rear-guard in Northern France during the D-Day landings. It was moved to Normandy in early August as part of a relief force in the forming Falaise pocket, where it was to replace the ''12th SS-Panzer Division "Hitlerjugend"'' by August 11. On August 14, the division received help from second company of the 102nd SS Heavy Panzer Battalion as it travelled from Assy to Maizieres; its commander was killed when the escort convoy encountered a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (Wehrmacht)
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the German Air Force, ''Luftwaffe'' (German Air Force). , the German Army had a strength of 62,766 soldiers. History Overview A German army equipped, organized, and trained following a single doctrine and permanently unified under one command in 1871 during the unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia. From 1871 to 1919, the title ''German Army (German Empire), Deutsches Heer'' (German Army) was the official name of the German land forces. Following the German defeat in World War I and the end of the German Empire, the main army was dissolved. From 1921 to 1935 the name of the German land forces was the ''Reichswehr, Reichsheer'' (Army of the Empire) and from 1935 to 1945 the name ''German Army (We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Canadian Infantry Division
The 2nd Canadian Division, an infantry division of the Canadian Army, was mobilized for war service on 1September 1939 at the outset of World War II. Adopting the designation of the 2nd Canadian Infantry Division, it was initially composed of volunteers within brigades established along regional lines, though a halt in recruitment in the early months of the war caused a delay in the formation of brigade and divisional headquarters. With questions concerning overseas deployment resolved, the division's respective commands were formed in May and June 1940, and at British Prime Minister Winston Churchill's request, the division was deployed to the United Kingdom between 1August and 25December 1940, forming part of the Canadian Corps. Having performed well in training exercises during 1941 and early 1942, elements of the 2nd Division were selected as the main force for Operation Jubilee, a large-scale amphibious raid on the port of Dieppe in German-occupied France. On 19August 1942, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
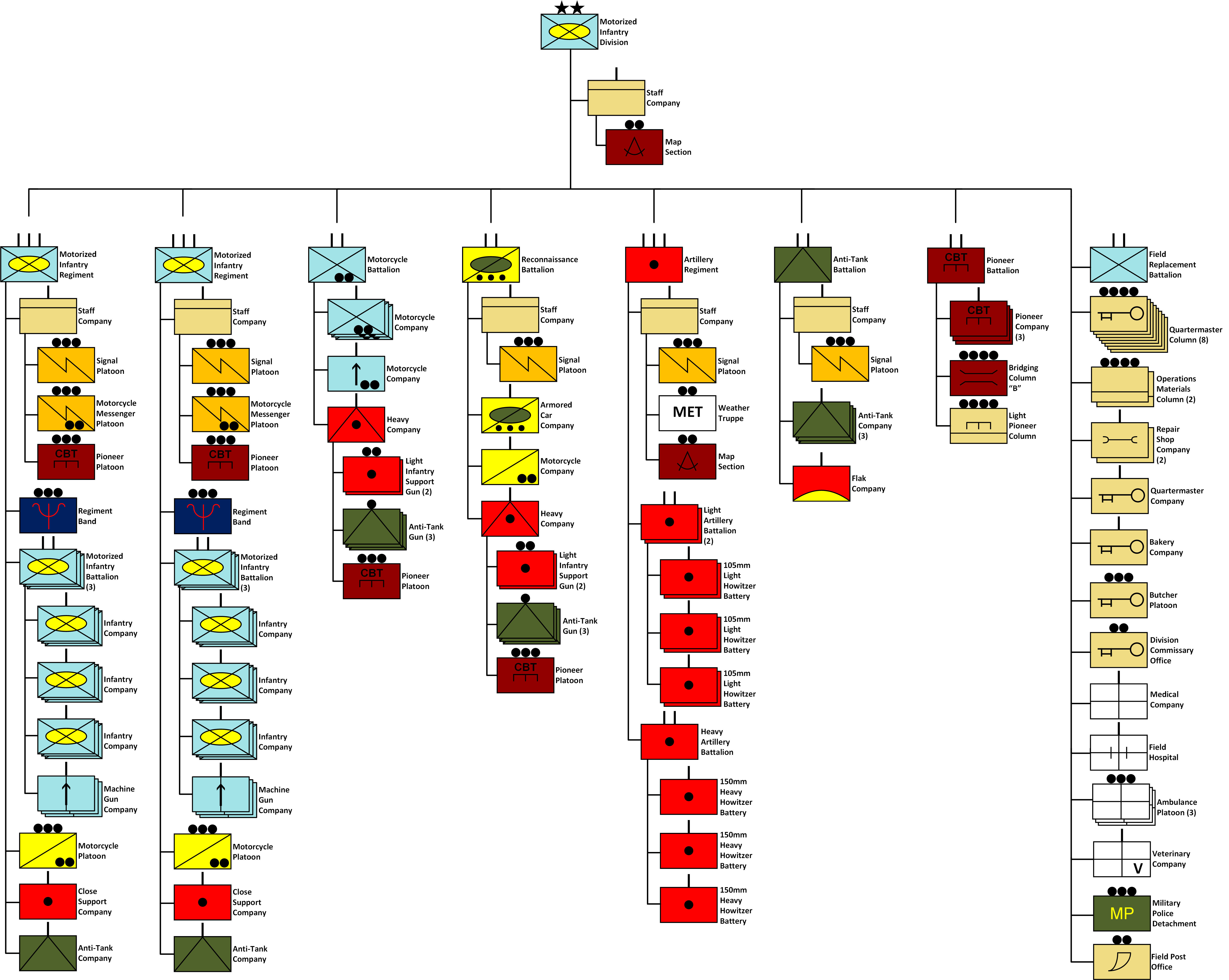
Infantry Divisions Of Germany During World War II
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets '' infant''. The individual-soldier term ''infantry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of German Divisions In World War II
This article lists divisions of the Wehrmacht (German Armed Forces) and Waffen-SS active during World War II, including divisions of the Heer (army), Luftwaffe (air force), and the Kriegsmarine (navy). Upgrades and reorganizations are shown only to identify the variant names for what is notionally a single unit; other upgrades and reorganizations are deferred to the individual articles. Due to the scope of this list, pre-war changes are not shown. Most of these divisions trained in Berlin, which is also where new military technology was kept and tested. German unit designations These designations are normally not translated and used in the German form in the unit name or description. ;''Bodenständige'': A static unit. Normally assigned to units who were deficient in transport and unable to move their own artillery. Many of these were divisions that had been mauled on the Eastern Front and were sent west to serve as coastal defence garrisons until sufficient resources were avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry Division Potsdam (Wehrmacht)
, image = , image_size = , caption = , dates = 29 March 1945 – 18 April 1945 , country = , branch = Heer (Wehrmacht) , type = Infantry , size = Division , command_structure = , garrison = , nickname = , motto = , colors = , march = , mascot = , battles = , notable_commanders = Infantry Division Potsdam () was a German infantry division of the ''Heer'' during World War II. It was active for only a few weeks near the very end of the war, starting in late March 1945. History Infantry Division Potsdam was part of the 35th and final '' Aufstellungswelle'', along with the infantry divisions Schl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Aachen
The Battle of Aachen was a combat action of World War II, fought by American and German forces in and around Aachen, Germany, between 2–21 October 1944. The city had been incorporated into the Siegfried Line, the main defensive network on Germany's western border; the Allies had hoped to capture it quickly and advance into the industrialized Ruhr Basin. Although most of Aachen's civilian population was evacuated before the battle began, much of the city was destroyed and both sides suffered heavy losses. It was one of the largest urban battles fought by U.S. forces in World War II, and the first city on German soil to be captured by the Allies. The battle ended with a German surrender, but their tenacious defense significantly disrupted Allied plans for the advance into Germany. Background By September 1944, the Western Allies had reached Germany's western border, which was protected by the extensive Siegfried Line. On 17 September, British, American, and Polish forces laun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hürtgen Forest
The Battle of Hürtgen Forest (german: Schlacht im Hürtgenwald) was a series of battles fought from 19 September to 16 December 1944, between American and German forces on the Western Front during World War II, in the Hürtgen Forest, a area about east of the Belgian–German border. It was the longest battle on German ground during World War II and is the longest single battle the U.S. Army has ever fought.Regan, ''More military blunders,'' p.178. The U.S. commanders' initial goal was to pin down German forces in the area to keep them from reinforcing the front lines farther north in the Battle of Aachen, where the US forces were fighting against the Siegfried Line network of fortified industrial towns and villages speckled with pillboxes, tank traps, and minefields. The Americans' initial tactical objectives were to take the village of Schmidt and clear Monschau. In a second phase the Allies wanted to advance to the Rur River as part of Operation Queen. ''Generalfeldmars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Parachute Army
The German 1st Parachute Army (1. ''Fallschirm-Armee'') was formed in September, 1944, comprising 30,000 men. History Its first commander was Colonel General Kurt Student, the ''Wehrmacht''s airborne pioneer. During the Allied Operation Market Garden, Student's men delayed the Allied advance across the south of the Netherlands. The 30,000 soldiers were likely the only combat-ready reserve forces in Germany at the time. However, few of the Army's units or personnel were paratroopers. Student was transferred to the Eastern Front, and on 18 November 1944, command of the First Parachute Army passed to General der Fallschirmtruppe Alfred Schlemm, who opposed the Canadian First Army during the Battle of the Reichswald. The Canadian First Army and Lieutenant-General William Hood Simpson’s U.S. Ninth Army compressed Schlemm’s forces into a small bridgehead on the west bank of the Rhine opposite Wesel. On 10 March 1945, the rearguard of the 1st Parachute Army evacuated their bridg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmut Bechler
__NOTOC__ Helmut Bechler (2 June 1898 – 9 January 1971) was a German general in the Wehrmacht during World War II who commanded the 85. Infanterie-Division. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross of Nazi Germany. Awards and decorations * German Cross in Gold on 19 December 1941 as '' Major'' in the I./Infanterie-Regiment 29 * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 26 March 1944 as ''Oberst ''Oberst'' () is a senior field officer rank in several German-speaking and Scandinavian countries, equivalent to colonel. It is currently used by both the ground and air forces of Austria, Germany, Switzerland, Denmark, and Norway. The Swedish ...'' and commander of Grenadier-Regiment 504Fellgiebel 2000, p. 107. References Citations Bibliography * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Bechler, Helmut 1898 births 1971 deaths People from Lengenfeld Military personnel from the Kingdom of Saxony Major generals of the German Army (Wehrmacht) German Army personnel of World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Calgary Highlanders
The Calgary Highlanders is a Canadian Army Primary Reserve infantry regiment, headquartered at Mewata Armouries in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. The regiment is a part-time reserve unit, under the command of 41 Canadian Brigade Group, itself part of 3rd Canadian Division, one of four region-based Canadian Army divisions. The regiment is one of only two regiments in the Canadian Forces (with The Canadian Scottish Regiment (Princess Mary's)) to wear an honorary distinction on their uniform, commemorating the counterattack at Kitcheners' Wood. On 9 January 2015, the regiment was recognized with the Canadian Forces' Unit Commendation for outstanding contributions to the war in Afghanistan. Badge The badge is based on that worn by the 10th Battalion, CEF, which the regiment perpetuates. Significantly, a St. Andrew's Cross has been added to the design (this is not a representation of the Roman Numeral ten as is often erroneously reported). The crown is of the reigning monarch; a Tudor Cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Parachute Division (Germany)
The 2nd Parachute Division (''2. Fallschirmjäger Division'') was an elite airborne division of German Wehrmacht (Luftwaffe) during World War II. Formation The 2nd Parachute Division was raised in 1943, with the 2nd Parachute Regiment, recently detached from the 1st Parachute Division serving as its nucleus. In May, the division was sent to Avignon in France, where it became part of the XI Flieger Corps along with the 1st Parachute Division. This Corps served as the reserve for the German 10th Army in Italy. When the Italian government started to crumble in September, the 2nd Parachute Division was dispatched to Italy. It carried out coastal defense duties near the Tiber estuary. The men moved to Rome in the evening of September 8 and participated in a subsequent operation to capture the Italian Army. The 1st Battalion of the 2nd Parachute Regiment participated in the capture of Leros Island in the Dodecanese. The island was then still occupied by Italian forces supplemented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich August Freiherr Von Der Heydte
Friedrich August Freiherr von der Heydte (30 March 1907 – 7 July 1994) was a German paratroop officer during World War II who later served in the armed forces of West Germany, achieving the rank of General. Following the war, Heydte pursued academic, political and military careers, as a Catholic-conservative professor of political science, a member of the Christian Social Union political party, and as a Bundeswehr reservist. In 1962, Heydte was involved in the Spiegel affair. Early life Friedrich August Freiherr von der Heydte joined the Reichswehr in April 1925. In 1927, he was released from military service to attend Innsbruck University, receiving a degree in economics. In 1927, Heydte was awarded his degree in law at Graz University. He joined the NSDAP on 1 May 1933, obtaining membership number 2.134.193. He entered the Sturm Abteilung the same year. In 1935 Heydte re-joined the Reichswehr where he attended staff training. World War II Heydte took part in the invasion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |