|
821st Main Space Intelligence Centre
The 821st Main Centre for Reconnaissance of Situation in Space ( rus, Главный центр разведки космической обстановки, GTsRKO) is the headquarters of the Russian military's space surveillance network, SKKP. The centre is part of the Russian Space Forces and receives intelligence from a network of reporting stations which includes the Russian missile attack early warning network as well as some stations only used for space surveillance such as Okno and Krona. The purpose of the SKKP is to detect satellites, identify them and to discern their orbits. It maintains the Russian catalogue of space objects and provides data which could be used to support space launches, feed an anti-satellite programme and provide intelligence on hostile military satellites. It is the Russian equivalent of the United States Space Surveillance Network. History The centre is based in the military village of Noginsk-9 ( rus, Ногинск-9) about a kilometer to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Space Forces
The Russian Space Forces ( rus, Космические войска России, Kosmicheskie voyska Rossii, KV) are a branch of the Russian Aerospace Forces, that provides aerospace warning, air and space sovereignty, and other related protection for Russia. Having been reestablished following August 1, 2015 merger between the Russian Air Force and the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces after the independent arm of service was dissolved in 2011. The Russian Space Forces were originally formed on August 10, 1992, alongside the creation of the Russian Armed Forces. The organization shared control of the Baikonur Cosmodrome with Roscosmos, the Federal Space Agency. It also operated the Plesetsk and the Svobodny Cosmodromes. However the Russian Space Forces were dissolved in July 1997 and incorporated into the Strategic Missile Forces. The Russian Space Forces were once again reformed as an independent troop on June 1, 2001, under a military reorganization. However, by December 2011 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protivo-Vozdushnaya Oborona
The Soviet Air Defence Forces (russian: войска ПВО, ''voyska protivovozdushnoy oborony'', ''voyska PVO'', ''V-PVO'', lit. ''Anti-Air Defence Troops''; and formerly ''protivovozdushnaya oborona strany'', ''PVO strany'', lit. ''Anti-Air Defence of the Country'') was the air defence branch of the Soviet Armed Forces. Formed in 1941, it continued being a service branch of the Russian Armed Forces after 1991 until it was merged into the Air Force in 1998. Unlike Western air defence forces, V-PVO was a branch of the military unto itself, separate from the Soviet Air Force (VVS) and Air Defence Troops of Ground Forces. During the Soviet period it was generally ranked third in importance of the Soviet services, behind the Strategic Rocket Forces and the Ground Forces. History Service during Second World War Preparations for creation of the air defence forces started in 1932, and by the beginning of Operation Barbarossa, June 1941, there were 13 PVO zones within the military dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint CIS Air Defence System
Joint CIS Air Defense System (russian: Объединённая система ПВО СНГ) is a unified system that comprises air defense units and elements of the former Soviet republics under control of the Coordination Committee on Air Defense of the Council of Ministers of Defense of the CIS. Currently there are 6 de facto members of JADS: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan. 70% of all expenditures of the military budget of the Commonwealth of Independent States are directed to the improvement and development of this system. History It was established on 10 February 1995 by the Almaty agreement. The was signed by Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Georgia, Turkmenistan, Ukraine and Uzbekistan. Georgia and Turkmenistan ceased their membership in 1997, while Uzbekistan is maintaining cooperation with Russia on a bilateral basis. By decision of the Council of CIS Heads of Governments of November 3, 1995, an effective fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titov Main Test And Space Systems Control Centre
The Titov Main Test and Space Systems Control Centre ( rus, Главный испытательный центр испытаний и управления космическими средствами (ГИЦИУ КС), Glavny Ispytatelny Tsentr Ispytany i Upravleniya Kosmicheskimi Sredstvami (GITSIU COP)) (also referenced as the Titov Space Control Centre and Titov Space Centre) is the main Russian military and commercial satellite control centre. It is run by the Russian Space Forces. Located roughly southwest of Moscow in closed town of Krasnoznamensk, the centre was built in 1957 as part of the Soviet space program, and was known by the name of Golitsyno-2. History A resolution of the Council of Ministers of 30 January 1956 provided for the establishment of a command and control complex for the first flight satellites. Work on the construction of the centre began on May 8, 1957. GITSIU COP and subordinate military units together with the Mission Control Centre support the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Space Troops
The Russian Space Forces ( rus, Космические войска России, Kosmicheskie voyska Rossii, KV) are a branch of the Russian Aerospace Forces, that provides aerospace warning, air and space sovereignty, and other related protection for Russia. Having been reestablished following August 1, 2015 merger between the Russian Air Force and the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces after the independent arm of service was dissolved in 2011. The Russian Space Forces were originally formed on August 10, 1992, alongside the creation of the Russian Armed Forces. The organization shared control of the Baikonur Cosmodrome with Roscosmos, the Federal Space Agency. It also operated the Plesetsk and the Svobodny Cosmodromes. However the Russian Space Forces were dissolved in July 1997 and incorporated into the Strategic Missile Forces. The Russian Space Forces were once again reformed as an independent troop on June 1, 2001, under a military reorganization. However, by December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Air Defence Forces
The Soviet Air Defence Forces (russian: войска ПВО, ''voyska protivovozdushnoy oborony'', ''voyska PVO'', ''V-PVO'', lit. ''Anti-Air Defence Troops''; and formerly ''protivovozdushnaya oborona strany'', ''PVO strany'', lit. ''Anti-Air Defence of the Country'') was the air defence branch of the Soviet Armed Forces. Formed in 1941, it continued being a service branch of the Russian Armed Forces after 1991 until it was merged into the Russian Air Force, Air Force in 1998. Unlike Western air defence forces, V-PVO was a branch of the military unto itself, separate from the Soviet Air Force (VVS) and Air Defence Troops of Ground Forces. During the Soviet period it was generally ranked third in importance of the Soviet services, behind the Strategic Rocket Forces and the Ground Forces. History Service during Second World War Preparations for creation of the air defence forces started in 1932, and by the beginning of Operation Barbarossa, June 1941, there were 13 PVO zones withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity, also known as radial speed or range rate, of a target with respect to an observer is the temporal rate of change, rate of change of the distance or Slant range, range between the two points. It is equivalent to the vector projection of the target-observer relative velocity onto the relative direction (geometry), relative direction connecting the two points. In astronomy, the point is usually taken to be the observer on Earth, so the radial velocity then denotes the speed with which the object moves away from the Earth (or approaches it, for a negative radial velocity). Formulation Given a differentiable vector \mathbf \in \mathbb^3 defining the instantaneous position of a target relative to an observer. Let with \mathbf \in \mathbb^3, the instantaneous velocity of the target with respect to the observer. The magnitude of the position vector \mathbf is defined as The quantity range rate is the time derivative of the magnitud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation Angle
In mathematics, a spherical coordinate system is a coordinate system for three-dimensional space where the position of a point is specified by three numbers: the ''radial distance'' of that point from a fixed origin, its ''polar angle'' measured from a fixed zenith direction, and the ''azimuthal angle'' of its orthogonal projection on a reference plane that passes through the origin and is orthogonal to the zenith, measured from a fixed reference direction on that plane. It can be seen as the three-dimensional version of the polar coordinate system. The radial distance is also called the ''radius'' or ''radial coordinate''. The polar angle may be called ''colatitude'', ''zenith angle'', '' normal angle'', or ''inclination angle''. When radius is fixed, the two angular coordinates make a coordinate system on the sphere sometimes called spherical polar coordinates. The use of symbols and the order of the coordinates differs among sources and disciplines. This article will use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azimuth
An azimuth (; from ar, اَلسُّمُوت, as-sumūt, the directions) is an angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system. More specifically, it is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north. Mathematically, the relative position vector from an observer (origin) to a point of interest is projected perpendicularly onto a reference plane (the horizontal plane); the angle between the projected vector and a reference vector on the reference plane is called the azimuth. When used as a celestial coordinate, the azimuth is the horizontal direction of a star or other astronomical object in the sky. The star is the point of interest, the reference plane is the local area (e.g. a circular area with a 5 km radius at sea level) around an observer on Earth's surface, and the reference vector points to true north. The azimuth is the angle between the north vector and the star's vector on the horizontal plane. Azimuth is usually measured in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector (mathematics And Physics)
In mathematics and physics, vector is a term that refers colloquially to some quantities that cannot be expressed by a single number (a scalar), or to elements of some vector spaces. Historically, vectors were introduced in geometry and physics (typically in mechanics) for quantities that have both a magnitude and a direction, such as displacements, forces and velocity. Such quantities are represented by geometric vectors in the same way as distances, masses and time are represented by real numbers. The term ''vector'' is also used, in some contexts, for tuples, which are finite sequences of numbers of a fixed length. Both geometric vectors and tuples can be added and scaled, and these vector operations led to the concept of a vector space, which is a set equipped with a vector addition and a scalar multiplication that satisfy some axioms generalizing the main properties of operations on the above sorts of vectors. A vector space formed by geometric vectors is called a Euclidean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
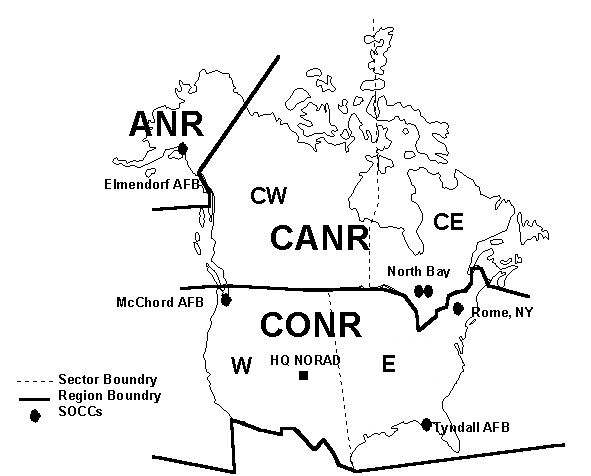
NORAD
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection for Canada and the continental United States. Headquarters for NORAD and the NORAD/United States Northern Command (USNORTHCOM) center are located at Peterson Space Force Base in El Paso County, near Colorado Springs, Colorado. The nearby Cheyenne Mountain Complex has the Alternate Command Center. The NORAD commander and deputy commander (CINCNORAD) are, respectively, a United States four-star general or equivalent and a Canadian lieutenant-general or equivalent. Organization CINCNORAD maintains the NORAD headquarters at Peterson Space Force Base near Colorado Springs, Colorado. The NORAD and USNORTHCOM Command Center at Peterson SFB serves as a central collection and coordination facility for a worldwide system of sensors designed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennant For Courage And Military Valour
Pennant may refer to: Flag or banner * Pennon (or pennant), a narrow, tapering flag ** Commissioning pennant, the traditional sign of a warship, flown from its masthead while the ship is in commission ** Broad pennant, flown from the masthead of a British Royal Navy ship to indicate the presence of a commodore on board ** Pennant (church), flown by navies during services on board ships * Pennant number, a number used to identify ships by the British Royal Navy and other navies of Europe and the Commonwealth * Pennant (sports), a commemorative flag displayed or flown by a league-winning team ** Pennant race, the race to clinch the division title in a regular baseball season * Pennant, a reference to Flag and pennant patterns in technical analysis of a stock market chart Places * Pennant, Ceredigion, Wales * Pennant, Powys, Wales * Pennant, Saskatchewan, Canada * Pennant Point, Nova Scotia, Canada * Pennant Hills, New South Wales, Australia People * Dafydd Pennant (16th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)