|
814 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 814 ( DCCCXIV) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events By place Byzantine Empire * April 13 – Byzantine–Bulgarian Wars: Over the winter Krum, ruler (''khan'') of the Bulgarian Empire, had assembled a huge army (including Slavs and Avars), for a campaign against the Byzantine Empire. But before he sets out for a major attack on Constantinople, he dies of a stroke. Krum is succeeded by his son Omurtag.John V.A. Fine, Jr. (1991). The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century, p. 99. . Europe * January 28 – Charlemagne dies of pleurisy in Aachen, after an almost 14-year reign (since 800) as the first Roman Emperor of Frankish origin (the precursor of the Holy Roman Emperor). He is embalmed and buried in Aachen Cathedral. Charlemagne is succeeded by his son Louis the Pious, as king of the Frankish Empire. * Louis I establishes himself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe 814
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
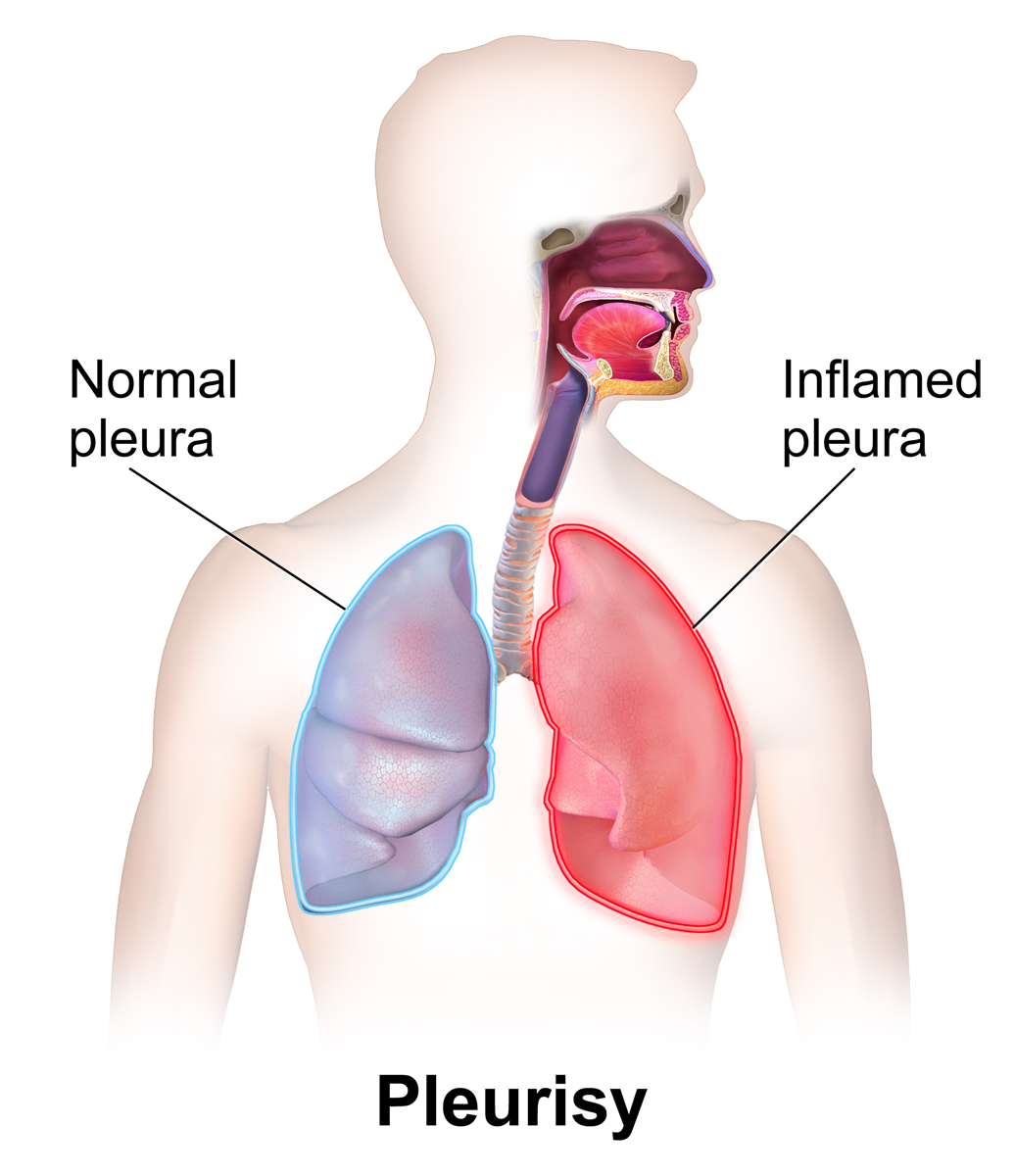
Pleurisy
Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant dull ache. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, fever, or weight loss, depending on the underlying cause. The most common cause is a viral infection. Other causes include bacterial infection, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, autoimmune disorders, lung cancer, following heart surgery, pancreatitis and asbestosis. Occasionally the cause remains unknown. The underlying mechanism involves the rubbing together of the pleurae instead of smooth gliding. Other conditions that can produce similar symptoms include pericarditis, heart attack, cholecystitis, pulmonary embolism, and pneumothorax. Diagnostic testing may include a chest X-ray, electrocardiogram (ECG), and blood tests. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Paracetamol (acetaminop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinsen Shōjiroku
is an imperially commissioned Japanese genealogical record. Thirty volumes in length, it was compiled under the order of Emperor Saga by his brother, the Imperial Prince Manta (万多親王, 788–830). Also by Fujiwara no Otsugu and Fujiwara no Sonohito et al. It was initially completed in 814, but underwent a revision to be recompleted in 815. Contents The record contains genealogical records for 1182 families. It categorizes these by their family roots: * imperial ancestry: 335 families * divine ancestry: 404 families; of which 246 were of direct heavenly descent, 128 were of heavenly cadet descent, and 30 of earthly divine descent. * foreign: 326 families; of which, 163 were from China, 104 from Baekje, 41 from Goguryeo, 9 from Silla Silla or Shilla (57 BCE – 935 CE) ( , Old Korean: Syera, Old Japanese: Siraki2) was a Korean kingdom located on the southern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula. Silla, along with Baekje and Goguryeo, formed the Three Kingdoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kornelimünster Abbey
Kornelimünster Abbey (german: Benediktinerabtei Kornelimünster), also known as Abbey of the Abbot Saint Benedict of Aniane and Pope Cornelius, is a Benedictine monastery that has been integrated since 1972. The abbey is located in Aachen (in the district of Kornelimünster/Walheim) in North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. History The monastery was founded in 814 on the river Inde by Benedict of Aniane, an adviser to Emperor Louis the Pious (successor to Charlemagne). The monastery was at first known as the "Monastery of the Redeemer on the Inde". In the mid-9th century, the monastery became an Imperial abbey ("Reichsunmittelbar") and received large endowments of land, as well as Biblical or Saviour's relics: a loincloth, a sudarium and two shroud-like cloths. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The female equivalent is abbess. Origins The title had its origin in the monasteries of Egypt and Syria, spread through the eastern Mediterranean, and soon became accepted generally in all languages as the designation of the head of a monastery. The word is derived from the Aramaic ' meaning "father" or ', meaning "my father" (it still has this meaning in contemporary Hebrew: אבא and Aramaic: ܐܒܐ) In the Septuagint, it was written as "abbas". At first it was employed as a respectful title for any monk, but it was soon restricted by canon law to certain priestly superiors. At times it was applied to various priests, e.g. at the court of the Frankish monarchy the ' ("of the palace"') and ' ("of the camp") were chaplains to the Merovingian and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, transcendental, and spiritual elements; however, there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacred things, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). a supernatural being or supernatural beings or "some sort of ultimacy and transcendence that will provide norms and power for the rest of life". Religious practices may include rituals, sermons, commemoration or veneration (of deities or saints), sacrifices, festivals, feasts, trances, initiations, funerary services, matrimonial services, meditation, prayer, music, art, dance, public service, or other aspects of human cultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adviser
An adviser or advisor is normally a person with more and deeper knowledge in a specific area and usually also includes persons with cross-functional and multidisciplinary expertise. An adviser's role is that of a mentor or guide and differs categorically from that of a task-specific consultant. An adviser is typically part of the leadership, whereas consultants fulfill functional roles. The spellings ''adviser'' and ''advisor'' have both been in use since the 16th century. ''Adviser'' has always been the more usual spelling, though ''advisor'' has gained frequency in recent years and is a common alternative, especially in North America. Etymology The use of ''adviser'' is of English origin, with "er" as a noun ending, and ''advisor'' of Latin origin. The words are etymological twin cognates and are considered interchangeable. Word usage Usage of the two words is normally a matter of choice, but they should not be used together in the same document. The Associated Press prefers (AP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedict Of Aniane
Benedict of Aniane ( la, Benedictus Anianensis; german: Benedikt von Aniane; 747 – 12 February 821 AD), born Witiza and called the Second Benedict, was a Benedictine monk and monastic reformer, who left a large imprint on the religious practice of the Carolingian Empire. His feast day is either February 11 or 12, depending on liturgical calendar. Life According to Ardo, Benedict's biographer, he was the son of a Visigoth, Aigulf, Count of Maguelonne (''Magalonensis comes''). Originally given the Gothic name Witiza, he was educated at the Frankish court of Pippin the Younger, and entered the royal service as a page. He served at the court of Charlemagne, and took part in the Italian campaign of Charlemagne in 773 where he almost drowned in the Ticino near Pavia while attempting to save his brother. The experience led him to act on a resolve which had been slowly forming in him, to renounce the world and live the monastic life. He later left the court and was received into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court (royal)
A royal court, often called simply a court when the royal context is clear, is an extended royal household in a monarchy, including all those who regularly attend on a monarch, or another central figure. Hence, the word "court" may also be applied to the coterie of a senior member of the nobility. Royal courts may have their seat in a designated place, several specific places, or be a mobile, itinerant court. In the largest courts, the royal households, many thousands of individuals comprised the court. These courtiers included the monarch or noble's camarilla and retinue, household, nobility, clergy, those with court appointments, bodyguards, and may also include emissaries from other kingdoms or visitors to the court. Prince étranger, Foreign princes and foreign nobility in exile may also seek refuge at a court. Near East, Near Eastern and Far East, Far Eastern courts often included the harem and Concubinage, concubines as well as eunuchs who fulfilled a variety of functions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, the Frankish king Charlemagne was crowned emperor in Rome by Pope Leo III in an effort to transfer the Roman Empire from Byzantine Empire to Europe. The Carolingian Empire is considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire. After a civil war (840–843) following the death of Emperor Louis the Pious, the empire was divided into autonomous kingdoms, with one king still recognised as emperor, but with little authority outside his own kingdom. The unity of the empire and the hereditary right of the Carolingians continued to be acknowledged. In 884, Charles the Fat reunited all the Carolingian kingdoms for the last time, but he died in 888 and the empire immediately split up. With the only r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis The Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquitaine from 781. As the only surviving son of Charlemagne and Hildegard, he became the sole ruler of the Franks after his father's death in 814, a position which he held until his death, save for the period 833–34, during which he was deposed. During his reign in Aquitaine, Louis was charged with the defence of the empire's southwestern frontier. He conquered Barcelona from the Emirate of Córdoba in 801 and asserted Frankish authority over Pamplona and the Basques south of the Pyrenees in 812. As emperor he included his adult sons, Lothair, Pepin and Louis, in the government and sought to establish a suitable division of the realm among them. The first decade of his reign was characterised by several tragedies and embarrassments, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aachen Cathedral
Aachen Cathedral (german: Aachener Dom) is a Roman Catholic church in Aachen, Germany and the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Aachen. One of the oldest cathedrals in Europe, it was constructed by order of Emperor Charlemagne, who was buried there in 814. From 936 to 1531, the Palatine Chapel saw the coronation of thirty-one German kings and twelve queens. The church has been the mother church of the Diocese of Aachen since 1930. In 1978, Aachen Cathedral was one of the first 12 items to be listed on the UNESCO list of World Heritage sites, because of its exceptional artistry, architecture, and central importance in the history of the Holy Roman Empire. History Charlemagne began the construction of the Palatine Chapel around 796, along with the rest of the palace structures. The construction is credited to Odo of Metz. The exact date of completion is unclear; however, a letter from Alcuin, in 798, states that it was nearing completion, and in 805, Pope Leo III consecrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |