|
802.3u
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s. The prior Ethernet speed was 10 Mbit/s. Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common. Fast Ethernet was introduced in 1995 as the IEEE 802.3u standard and remained the fastest version of Ethernet for three years before the introduction of Gigabit Ethernet. The acronym ''GE/FE'' is sometimes used for devices supporting both standards. Nomenclature The "100" in the media type designation refers to the transmission speed of 100 Mbit/s, while the "BASE" refers to baseband signaling. The letter following the dash ("T" or "F") refers to the physical medium that carries the signal (twisted pair or fiber, respectively), while the last character ("X", "4", etc.) refers to the line code method used. Fast Ethernet is sometimes referred to as 100BASE-X, where "X" is a placeholder for the FX and TX variants. General design Fast Ethernet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet Physical Layer
The physical-layer specifications of the Ethernet family of computer network standards are published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which defines the electrical or optical properties and the transfer speed of the physical connection between a device and the network or between network devices. It is complemented by the MAC layer and the logical link layer. The Ethernet physical layer has evolved over its existence starting in 1980 and encompasses multiple physical media interfaces and several orders of magnitude of speed from 1 Mbit/s to 400 Gbit/s. The physical medium ranges from bulky coaxial cable to twisted pair and optical fiber with a standardized reach of up to 80 km. In general, network protocol stack software will work similarly on all physical layers. Many Ethernet adapters and Network switch, switch ports support multiple speeds by using autonegotiation to set the speed and Duplex (telecommunications), duplex for the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonegotiation
Autonegotiation is a signaling mechanism and procedure used by Ethernet over twisted pair by which two connected devices choose common transmission parameters, such as speed, duplex mode, and flow control. In this process, the connected devices first share their capabilities regarding these parameters and then choose the highest performance transmission mode they both support. Autonegotiation is defined in clause 28 of IEEE 802.3. and was originally an optional component in the Fast Ethernet standard. It is backwards compatible with the normal link pulses (NLP) used by 10BASE-T. The protocol was significantly extended in the Gigabit Ethernet standard, and is mandatory for 1000BASE-T gigabit Ethernet over twisted pair. In the OSI model, autonegotiation resides in the physical layer. Standardization and interoperability In 1995, the Fast Ethernet standard was released. Because this introduced a new speed option for the same wires, it included a means for connected network adapter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet Over Twisted Pair
Ethernet over twisted-pair technologies use twisted-pair cables for the physical layer of an Ethernet computer network. They are a subset of all Ethernet physical layers. Early Ethernet used various grades of coaxial cable, but in 1984, StarLAN showed the potential of simple unshielded twisted pair. This led to the development of 10BASE-T and its successors 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-T and 10GBASE-T, supporting speeds of 10 and 100 megabit per second, then 1 and 10 gigabit per second respectively. Two new variants of 10 megabit per second Ethernet over a ''single'' twisted pair, known as 10BASE-T1S and 10BASE-T1L, were standardized in IEEE Std 802.3cg-2019. 10BASE-T1S has its origins in the automotive industry and may be useful in other short-distance applications where substantial electrical noise is present. 10BASE-T1L is a long-distance Ethernet, supporting connections up to 1 km in length. Both of these standards are finding applications implementing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
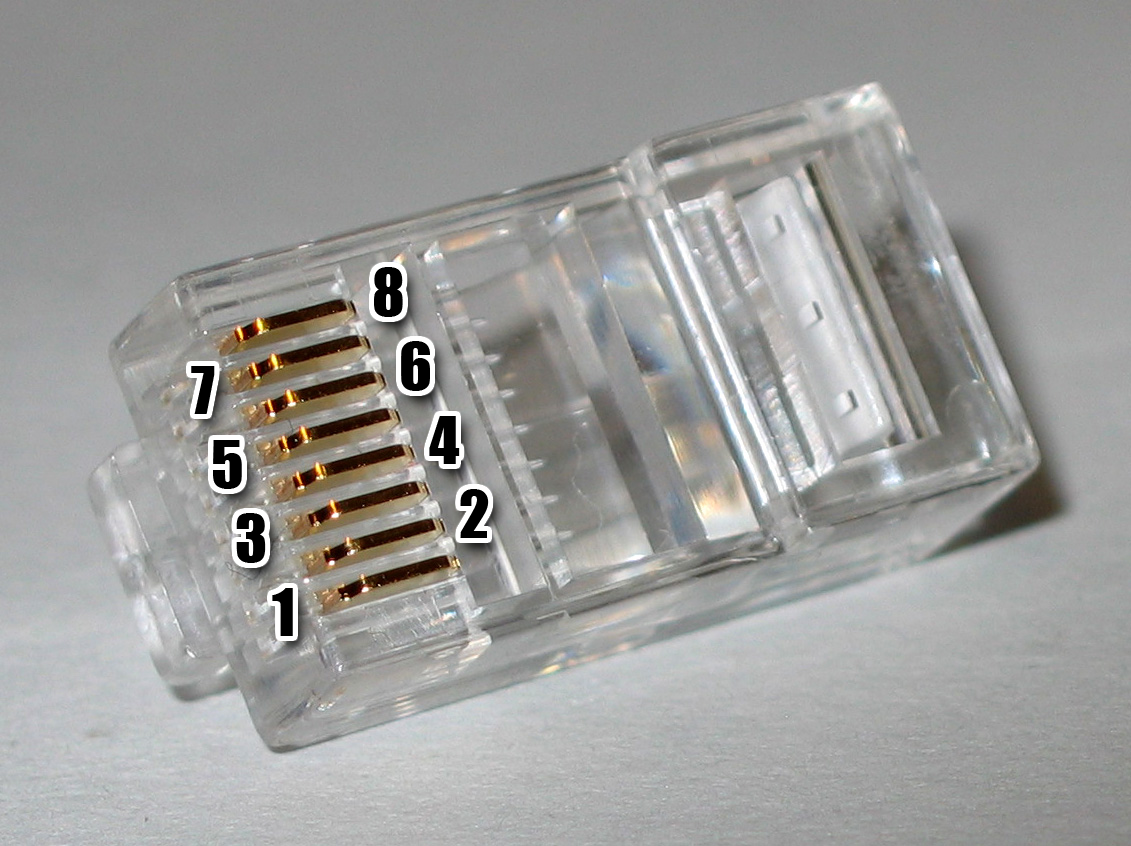
Reduced Media Independent Interface
The media-independent interface (MII) was originally defined as a standard interface to connect a Fast Ethernet (i.e., ) media access control (MAC) block to a PHY chip. The MII is standardized by IEEE 802.3u and connects different types of PHYs to MACs. Being ''media independent'' means that different types of PHY devices for connecting to different media (i.e. twisted pair, fiber optic, etc.) can be used without redesigning or replacing the MAC hardware. Thus any MAC may be used with any PHY, independent of the network signal transmission media. The MII can be used to connect a MAC to an external PHY using a pluggable connector, or directly to a PHY chip on the same PCB. On a PC the CNR connector Type B carries MII signals. Network data on the interface is framed using the IEEE Ethernet standard. As such it consists of a preamble, start frame delimiter, Ethernet headers, protocol-specific data and a cyclic redundancy check (CRC). The original MII transfers network data using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Media-independent Interface
The media-independent interface (MII) was originally defined as a standard interface to connect a Fast Ethernet (i.e., ) media access control (MAC) block to a PHY#Ethernet physical transceiver, PHY chip. The MII is standardized by IEEE 802.3u and connects different types of PHYs to MACs. Being ''media independent'' means that different types of PHY devices for connecting to different media (i.e. Ethernet over twisted pair, twisted pair, fiber optic, etc.) can be used without redesigning or replacing the MAC hardware. Thus any MAC may be used with any PHY, independent of the network signal transmission media. The MII can be used to connect a MAC to an external PHY using a pluggable connector, or directly to a PHY chip on the same Printed circuit board, PCB. On a PC the Communications and networking riser, CNR connector Type B carries MII signals. Network data on the interface is Ethernet frame, framed using the IEEE Ethernet standard. As such it consists of a preamble, start frame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
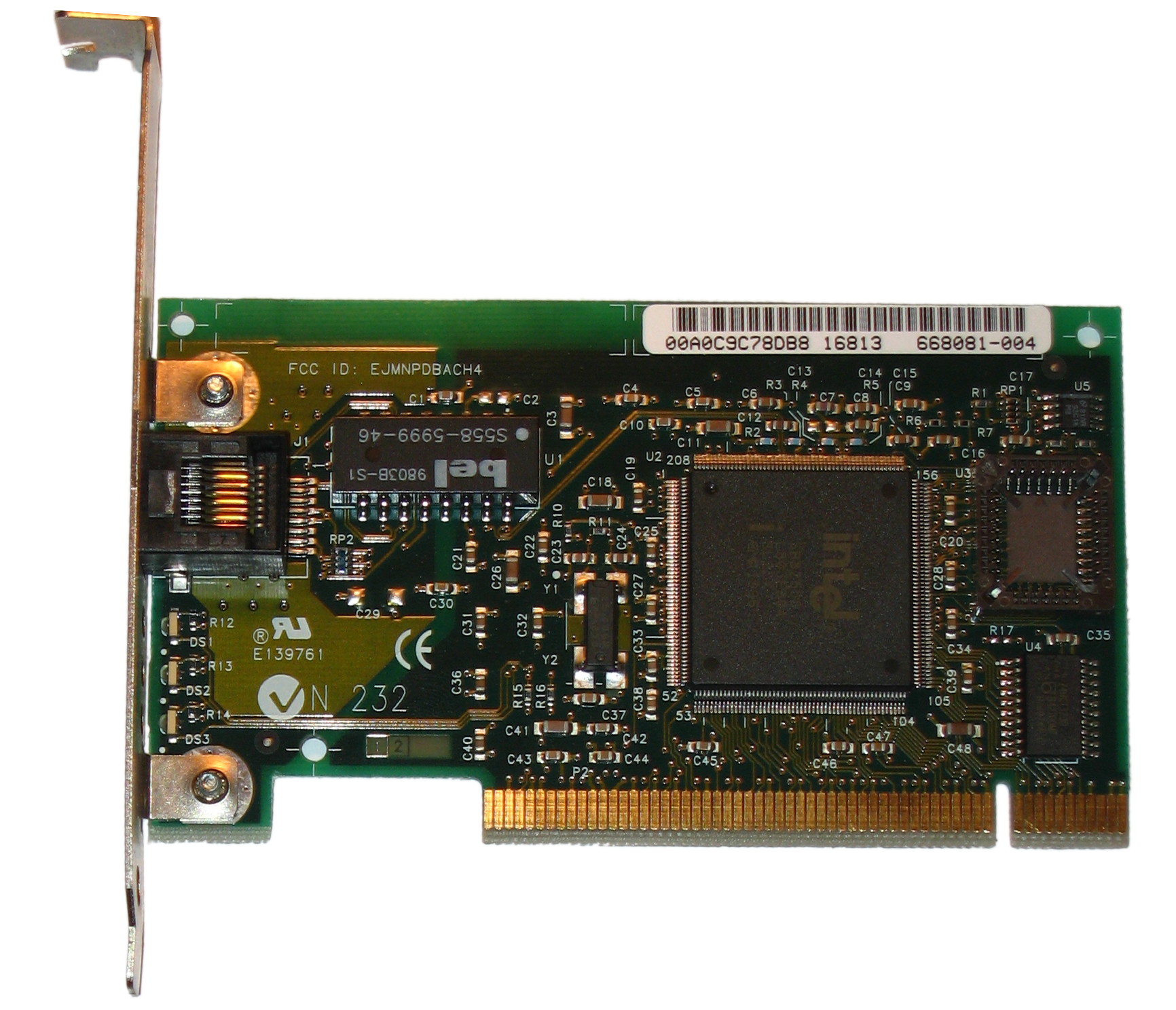
Intel Pro-100 82558 PCI NIC
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 series of instruction sets, the instruction sets found in most personal computers (PCs). Incorporated in Delaware, Intel ranked No. 45 in the 2020 ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 fiscal years. Intel supplies microprocessors for computer system manufacturers such as Acer, Lenovo, HP, and Dell. Intel also manufactures motherboard chipsets, network interface controllers and integrated circuits, flash memory, graphics chips, embedded processors and other devices related to communications and computing. Intel (''int''egrated and ''el''ectronics) was founded on July 18, 1968, by semiconductor pioneers Gordon Moore (of Moore's law) and Robert Noyce (1927–1990) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_connector_on_sun_ultra_1.jpg)
